0523
IRIS-DL: A Deep Learning Software Tool for Identifying Genetic Mutations in Gliomas and Meningiomas1Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey, 2Brain Tumor Research Group, Acibadem University, Istanbul, Turkey, 3Department of Medical Pathology, Acibadem University, Istanbul, Turkey, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, Acibadem University, Istanbul, Turkey, 5Department of Neurosurgery, Acibadem University, Istanbul, Turkey, 6Department of Radiology, Acıbadem University, Istanbul, Turkey
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Deep Learning
Intelligent Radiological Imaging Systems (IRIS)-DL is a deep learning software tool that includes libraries for segmenting tumor regions and identifying several genetic mutations in gliomas and meningiomas. The tool has three modules, which are “Model Library”, “Trainer”, and “Plotter”. In the “Model Library”, the users could run pre-trained models on their local data. The “Trainer” module is for creating custom AI (conventional machine learning, artificial neural networks, and deep learning) models on the user data. Lastly, “Plotter” module is for data visualization and explorative data analysis.Summary of Main Findings
This study implemented IRIS-DL, a deep learning software tool, that has nine pre-trained AI models using different MRI modalities designed to identify IDH and TERTp mutations in gliomas and NF2 mutation and S100 immunopositivity in meningiomas.Introduction
Identifying genetic mutations in brain tumors has become important to elucidate tumor biology and to predict treatment response. Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) and telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter (TERTp) mutations in gliomas result in different clinical behavior and survival rates [1-3]. On the other hand, S100 protein expression in meningiomas is a relevant indicator of prognosis, and it is more common in benign meningiomas than atypical ones [4-6]. Additionally, neurofibromatosis type 2 loss (NF2-L) in meningiomas has been linked to worse overall survival [7]. Deep learning (DL) has gained popularity in MRI data analysis due to adequate hardware capabilities and large amounts of available data. However, most of the available tools have not been used by the clinicians and there is still a need for open-source DL frameworks that are robust, optimized, and user-friendly. In this study, we have developed a user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI) supported software tool, named IRIS-DL, that has built-in models to perform tumor segmentation and to identify several genetic mutations in gliomas and meningiomas based on multimodal MRI data. In IRIS-DL, we propose two models for detecting NF2-L using 1D-convolutional neural networks (CNN) and logistic regression. 1D-CNN was trained on 1H-MRS data and the logistic regression model was trained on radiomics features generated from T1w MRI. Additionally, the tool has three different 2D-CNN models trained on T2w MRI, susceptibility-weighted MRI (SWI), and relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) maps for detecting S100 immunopositivity in meningiomas. For the detection of IDH and TERTp mutational subgroups, 1D-CNN models were trained on 1H-MRS data using the attention mechanism. Moreover, IRIS-DL offers one tumor segmentation model trained on T2w MRI. Finally, IRIS-DL has two other modules for creating custom models using field-independent data and visualizing the data distribution.Methods
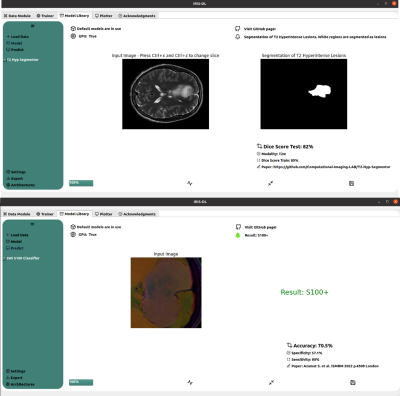
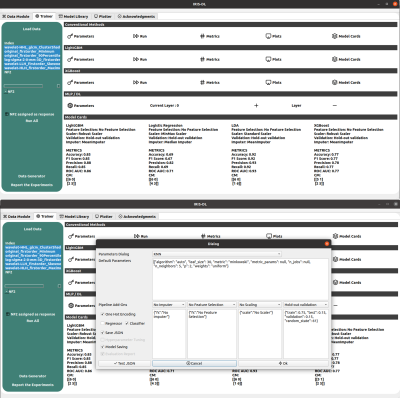
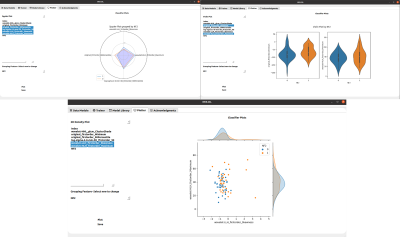
IRIS-DL was coded in Python and its GUI was created using QtDesigner5. IRIS-DL has three main components, which are “Model Library”, “Trainer” and “Plotter”. Model Library: This module offers published AI models to non-AI expert users to try on their local data. The user could select models from dropdown menus, get predictions by clicking on one button and see the results on the same page without any need for other third-party tools. Currently, IRIS-DL has nine different AI models [8-13], performing tumor segmentation or classification, trained on several different MRI data of meningiomas or gliomas (Figure 1). Trainer: The trainer module provides all the necessary components for customizing the whole AI pipeline and enhancing the model performance (Figure 2). IRIS-DL has 10 conventional machine learning algorithms -SVMs, KNNs, AdaBoost, LogisticRegression, LDA, GradientBoosting, Random Forests, Decision Trees, LDA, Naive Bayes, XGBoost, LightGBM-, MLP models, and DL models, four imputers -KNNImputer, MeanImputer, Most Frequent, MedianImputer-, 12 feature selection methods, seven scaler methods, and two validation methods. The results of the trained models are shown in the model cards and typical metrics, such as the accuracy, precision, and recall for the classification problems, root mean square error (RMSE), MSE and MAE for regression problems, and Dice Score and Intersection of Union (IoU) for segmentation problems, are computed. Plotter: This component provides 14 different data visualization options to provide insight into the data and conduct explorative data analysis (EDA) (Figure 3).Results
Currently, nine AI models have been implemented in IRIS-DL Model Library. The trainer module not only offers an easy-to-use experience but also full control of the pipeline parameters. Besides the visualization module, the results could be exported for further tasks like benchmarking using the reporter tool. IRIS-DL is publicly available at our laboratory’s GitHub page.Synopsis
Intelligent Radiological Imaging Systems (IRIS)-DL is a deep learning software tool that includes libraries for segmenting tumor regions and identifying several genetic mutations in gliomas and meningiomas. The tool has three modules, which are “Model Library”, “Trainer”, and “Plotter”. In the “Model Library”, the users could run pre-trained models on their local data. The “Trainer” module is for creating custom AI (conventional machine learning, artificial neural networks, and deep learning) models on the user data. Lastly, “Plotter” module is for data visualization and explorative data analysis.Acknowledgements
This study has been supported by TUBITAK 1001 grant 119S520 and TUBITAK 1003 grant 216S432.References
1. Eckel-Passow, J.E., et al., Glioma Groups Based on 1p/19q, IDH, and TERT Promoter Mutations in Tumors. N Engl J Med, 2015. 372(26): p. 2499-508.
2. Ogura, R., et al., Immunohistochemical profiles of IDH1, MGMT and P53: practical significance for prognostication of patients with diffuse gliomas. Neuropathology, 2015. 35(4): p. 324-35.
3. Takano, S., et al., Immunohistochemistry on IDH 1/2, ATRX, p53 and Ki-67 substitute molecular genetic testing and predict patient prognosis in grade III adult diffuse gliomas. Brain Tumor Pathol, 2016. 33(2): p. 107-16.
4. Hancq, S., et al., Detection of S100B, S100A6 and galectin-3 ligands in meningiomas as markers of aggressiveness. Int J Oncol, 2004. 25(5): p. 1233-1240.
5. Hancq, S., et al., S100A5: a marker of recurrence in WHO grade I meningiomas. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology, 2004. 30(2): p. 178-187.
6. Abeloos, L. and F. Lefranc, Could serum measurements of S100 proteins be reliable markers to predict recurrence in meningiomas? Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, 2011. 49(6): p. 971-975.
7. Baser, M.E., et al., Evaluation of clinical diagnostic criteria for neurofibromatosis 2. Neurology, 2002. 59(11): p. 1759.
8. Buz Yaluğ B, Ersen Danyeli A, Ekşi MŞ, Tan K, Can Ö, Yakicier C, Pamir MN, Dincer A, Ozduman K, Ozturk-Isik E. Differentiation of NF2 loss and S100 presence in Meningioma using Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast MRI with Machine Learning Approach. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. London, UK, May 7-12, 2022
9. Azamat S, Buz-Yaluğ B, Baş A, Ozcan A, Ersen Danyeli A, Pamir MN, Dinçer A, Ozduman K, Ozturk-Isik E. Susceptibility Weighted MRI for Predicting Critical Developmental Regulatory S100 Proteins in Meningiomas at 3T. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. London, England, UK. May 07-12, 2022
10. Identification of NF2 loss in meningiomas using 1H-MRS at 3T. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine and Biology. London, UK, May 7-12, 2022
11. Sumer Esra, Tan K, Ersen Danyeli A, Can Ö, Yakicier C, Pamir MN, Dincer A, Ozduman K, Ozturk-Isik E. Meningiomas with NF2-Loss Exhibit Strong Radiomics Correlations on Contrast Enhanced T1-Weighted MRI at 3T. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine and Biology. London, UK, May 7-12, 2022
12. Bas A, Tan K, Ersen Danyeli A, Can Ö, Yakicier C, Pamir MN, Dincer A, Ozduman K, Ozturk-Isik E. Identification of S100 Immunopositivity on T2-weighted MRI Using Deep Learning. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine and Biology. London, UK, May 7-12, 2022
13. Bas A, Sacli-Bilmez B, Danyeli AE, Yakicier C, Pamir MN, Ozduman K, Dincer A, Ozturk-Isik E. 1D-CNN for the Detection of IDH and TERTp Mutations in Diffuse Gliomas using Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. Vancouver, Canada May 15-20, 2021 14.