0517
Relationship between muscle fat,vertebral density and ectopic fat deposition in patients with T2DM using IDEAL-IQ1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips health care, Dalian, China, 3GE health care, Dalian, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Endocrine, Diabetes
This study was carried out to evaluate the correlations between abdominal fat, vertebral density and ectopic fat deposition patients with T2DM using IDEAL-IQ.We found that SAT area,VAT area,Pancreatic FF and Abdominal wall muscle FF was positively correlated with BMD in patients with T2DM.Introduction
Studies have indicated that the body fat content and distribution of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM ) are different from those of normal people. Most T2DM patients are central obese【1】. At present, there have been studies on the correlation between body composition and bone mineral density (BMD) of T2DM patients, but the number of reports is small. In addition, Most of them are limited to the elderly and postmenopausal women【2-4】, and there is a lack of comprehensive analysis and research on the overall population of T2DM patients. The aim of this study was to analyze fat distribution, the lumbar volumetric BMD and changes of skeletal muscle using the iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL-IQ) in patients with T2DM, and to assess the correlations between abdominal fat, vertebral density and ectopic fat deposition .Methods
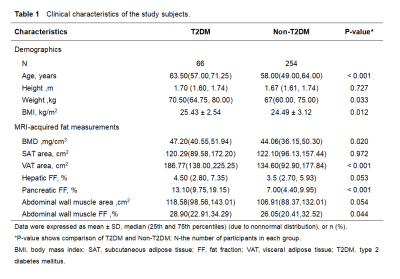
A total of 320 subjects with median age of 59 years were enrolled in the study,which included 66 patients with T2DM and 254 patients without diabetes. Visceral adipose tissue (VAT) area , subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) area , abdominal wall muscule area and fat fraction (FF) at the L1–L2 levels, hepatic FF, pancreatic FF were assessed by MRI FF maps. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS (Version 25.0 ,SPSS Inc., IL)and GraphPad Prism (Version 8.4.0, GraphPad software, LLC). The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to test the normality of the variables in overall subjects. Normally distributed data were expressed as means ± standard deviations, and nonnormally distributed data were expressed as medians and ranges. The statistical significance between means was calculated by t-test, analysis of variance or Mann-Whitney U test when appropriate. The correlations between abdominal fat, vertebral density and ectopic fat deposition variables were analyzed with the Pearson correlation test for normally distributed variables and Spearman correlation test for non-normally distributed data.Results
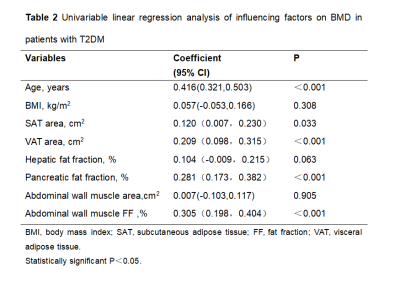
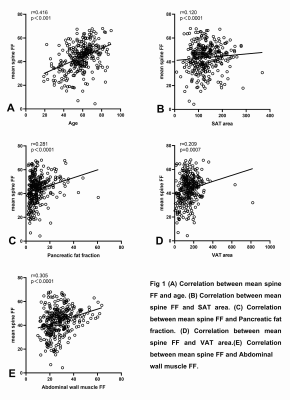
The body mass index (BMI), BMD and Abdominal wall muscle FF of T2DM group were higher than those of non-T2DM group (P<0.05). VAT area and Pancreatic FF was found to be significantly higher in participants with T2DM than in non-T2DM group (p < 0.05)(table 1). Age(r = 0.416, p< 0.001), SAT area(r = 0.120, p = 0.033), VAT area(r =0.209, p< 0.001), Pancreatic FF(r =0.281, p< 0.001)and Abdominal wall muscle FF(r =0.305, p< 0.001)were positively associated with BMD(Table 2) (Fig 1).Discussion
This study showed that patients with T2DM had higher BMI, BMD,VAT area, Pancreatic FF and Abdominal wall muscle FF than non-T2DM, which might be related to the metabolic abnormalities caused by T2DM. Our findings showed that SAT area,VAT area,Pancreatic FF and Abdominal wall muscle FF was positively correlated with BMD in diabetes patients. Our study had several limitations. the sample size of our study was relatively small , and another limitation is the lack of age matched controls, we still need to increase the sample size and match the age to provide reliable data support for the research of BMD in T2DM.Conclusions
The changes in body composition in patients with T2DM were mainly increased in VAT area, Pancreatic FF, Abdominal wall muscle FF, and they were positively correlated with BMD. These findings further the understanding of the association between abdominal fat, vertebral density and ectopic fat deposition, and help to determine the reasonable muscle fat ratio to prevent the occurrence of fracture in T2DM patients.Keywords
abdominal fat, Bone mineral density, ectopic fat deposition, IDEAL-IQ ,Type 2 diabetes mellitusAcknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
【1】Jia R, Huang M, Qian L, et al. The Depletion of Carbohydrate Metabolic Genes in the Gut Microbiome Contributes to the Transition From Central Obesity to Type 2 Diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:747646.
【2】Raška I Jr, Rašková M, Zikán V, Škrha J. Body composition is associated with bone and glucose metabolism in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Physiol Res. 2017;66(1):99-111.
【3】Bell KE, Paris MT, Avrutin E, Mourtzakis M. Altered features of body composition in older adults with type 2 diabetes and prediabetes compared with matched controls. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(2):1087-1099.
【4】Gao L, Zhang P, Wang Y, et al. Relationship between body composition and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):893.