0511
High-resolution single-breath-hold 3D MRCP using accelerated 3D Gradient and Spin-Echo (GraSE) with Compressed SENSE
Takumi Ogawa1, Michinobu Nagao2, Yasuhiro Goto1, Masami Yoneyama3, Johannes M Peeters4, Isao Shiina1, Yutaka Hamatani1, Kazuo Kodaira1, Mana Kato1, and Shuji Sakai2
1Department of Radiological Services, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Diagnostic image & Nuclear Medicine, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands
1Department of Radiological Services, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Diagnostic image & Nuclear Medicine, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands
Synopsis
Keywords: Digestive, Biliary
Breath-hold MRCP has gained more attention in routine clinical MRI, but its limited scan time during the breath-hold period often results in poor signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and spatial-resolution. Despite being a single breath-hold method, 3D gradient and spin-echo (GraSE) sequence has been reported to provide high image quality. In this study, accelerated GraSE sequence combined with Compressed SENSE has been developed to obtain high-resolution MRCP images with a single breath-hold.Introduction
3D MRCP is typically obtained by either respiratory-triggering or breath-holding. Although respiratory-triggered 3D heavily T2-weighted turbo spin echo (TSE) based sequence has commonly been used for 3D MRCP, this technique tends to have a long acquisition time depending on patients’ respiration frequency. In addition, it sometimes provides poor image quality in patients with irregular breathing [1]. On the other hand, breath-hold MRCP has gained more attention in routine clinical MRI, but its limited scan time during the breath-hold period often results in poor signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and lower spatial-resolution. We may be able to obtain higher SNR images with longer scan times, but in practice such a protocol is unrealistic with reduced success rate of the examination due toincomplete breath-holding. Therefore, several techniques have been reported to shorten the acquisition time in MRCP [2,3], such as Gradient and Spin-Echo (GraSE) and 3D TSE with compressed sensing sensitivity encoding (Compressed SENSE). 3D GraSE is a hybrid technique of alternately acquired gradient echoes and spin echoes in the echo trains [4-6]. Despite being a single breath-hold method, this sequence has been reported to provide better image quality than respiratory-triggered 3D MRCP [5,6]. Furthermore, it has been found to have lower sensitivity to motion artifacts compared with conventional TSE method [7]. Accelerated 3D GraSE combined with Compressed SENSE has recently been developed to obtain high-resolution 3D MRCP images within a single breath-hold. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of accelerated CS-GraSE for MRCP by comparing with conventional SENSE-GraSE and conventional respiratory-triggered 3D TSE MRCP.Methods
METHODS 3D MRCP images of six healthy volunteers (five males and one female, age range: 27-47 years) were obtained by 3.0T MR system (Ingenia, Philips healthcare). The study was approved by the local IRB, and written informed consent was obtained from all subjects. We compared four types of 3D MRCP images: conventional 3D TSE respiratory-triggering technique (RT-TSE), conventional 3D single breath-hold GraSE using SENSE (conventional-GraSE), high-resolution breath-hold GraSE with a SENSE factor of 12 (HR SENSE12-GraSE), and high-resolution 3D breath-hold GraSE with Compressed SENSE factor of 12 (HR CS12-GraSE). For assessment of overall image quality, sharpness and noise and artifacts, we evaluated them at a 4-point scale with “4” being excellent, “1” was severely impacted image quality) by two blinded readers. Visual evaluation was assessed by Steel-Dwass test. As a quantitative evaluation, the contrast ratio (CR) of the common bile duct (CBD) to the liver and the SNR of the CBD were measured. SNR CBD and CR CBD-liver were calculated as follows: SNR CBD = SI CBD/ SD noise, CR CBD-liver = [SI CBD – SI liver] / [SI CBD + SI liver] where SI CBD and SI liver are the mean average signal intensity of the CBD and liver respectively, and the corresponding SD noise is the standard deviation at the same location on the noise images obtained in a separate noise scan. Imaging parameters for respective sequences are as follows. RT-TSE: FOV=330*330mm, voxel size=1.0*0.8*2.2mm3, TR/TE/FA=2000/643/90, SPIR, NSA=1, CS-SENSE=4 and (displayed) acquisition time=1min54s. Conventional GraSE: FOV=330*330mm, voxel size=1.4*1.8*2.4mm3, TR/TE/FA=300/101/90, TSE factor=10/EPI factor=7, SPIR, NSA=1, SENSE (phase*slice)=4.0*1.0 and actual acquisition time=20s. HR SENSE GraSE: FOV=330*330mm, voxel size=1.4*1.4*2.0mm3, TR/TE/FA=300/93/90, TSE factor=8/EPI factor=7, SPIR, NSA=1, SENSE=6.0*2.0 and acquisition time=14s. HR CS GraSE: FOV=330*330mm, voxel size=1.4*1.4*2.0mm3, TR/TE/FA=300/93/90, TSE factor=8/EPI factor=7, SPIR, NSA=1, CS-SENSE=12.0 and actual acquisition time=14s.Results and Discussion
Figure1 shows the representative 3D MRCP images with actual acquisition time using conventional RT-TSE, conventional-GraSE, HR SENSE12-GraSE and HR CS12-GraSE. Figure 2 shows the source images of 3D MRCP of breath-holding three sequences (conventional-GraSE, HR SENSE12-GraSE and HR CS12-GraSE). HR SENSE12-GraSE showed severe image noise compared to conventional-GraSE. In contrast, HR CS12-GraSE showed similar SNR to conventional GraSE. Figure 3 shows the results of SNR and CR measurements among four sequences. RT-TSE showed the highest value for both SNR and CR, but there was no significant difference in comparison with HR CS12-GraSE. Figure 4 shows the results of the visual evaluation. HR CS12-GraSE showed the highest value in all overall image quality, sharpness and noise and artifacts. For overall image quality, HR CS12-GraSE was significantly higher than HR SENSE12-GraSE (p<0.001), but not significantly different from RT-TSE to conventional-GraSE. For sharpness, HR CS12-GraSE was significantly higher than the other three sequences (p<0.01), and for noise and artifacts, HR CS12-GraSE was significantly better than RT-TSE and HR SENSE12-GraSE (p<0.001). The average scan time for conventional RT-TSE method, conventional-GraSE and HR CS12-GraSE was 2 minutes 40 seconds, 20 seconds and 14 seconds, respectively. Therefore, HR CS12-GraSE can shorten about 90% of the scan time compared to conventional RT-TSE, and about 25% compared to conventional-GraSE. From the results of SNR and CR, HR SENSE12-GraSE had a low SNR due to increased g-factor noise by high SENSE factor. On the other hand, HR CS12-GraSE had high SNR and improved image quality due to effect of Compressed SENSE recontraction including denoising (Figure5). HR CS12-GraSE achieved higher SNR and contrast despite the increased spatial-resolution.Conclusion
Accelerated GraSE combined with Compressed SENSE provides high-resolution MRCP with high SNR and contrast in a single14 seconds breath-hold.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgements found.References
[1] Glockner JF, Saranathan M, Bayram E, Lee CU (2013) Breath-held MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) using a 3D Dixon fat-water separated balanced steady state free precession sequence. Magn Reson Imaging 31:1263–1270 [2] Zhang J, Israel GM, Hecht EM, Krinsky GA, Babb JS, Lee VS (2006) Isotropic 3D T2-weighted MR cholangiopancreatography with parallel imaging: feasibility study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:1564–1570 [3] Nandalur KR, Hussain HK, Weadock WJ et al (2008) Possible biliary disease: diagnostic performance of high-spatial-resolution isotropic 3D T2-weighted MRCP. Radiology 249:883–890 [4] Feinberg DA, Oshio K (1991) GRASE (gradient- and spin-echo) MR imaging: a new fast clinical imaging technique. Radiology 181:597–602 [5] Ju Gang Nam, Jeong Min Lee, Hyo-Jin Kang, Sang Min Lee (2018) GRASE Revisited: breath-hold three-dimensional (3D) magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography using a Gradient and Spin Echo (GRASE) technique at 3T. [6] Morikatsu Yoshida, Takeshi Nakaura, Taihei Inoue, Shota Tanoue, Sentaro Takada, Daisuke Utsunomiya, Shota Tsumagari, Kazunori Harada & Yasuyuki Yamashita (2018) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography with GRASE sequence at 3.0T: does it improve image quality and acquisition time as compared with 3D TSE? [7] Baessler B, Schaarschmidt F, Stehning C, Schnackenburg B, Maintz D, Bunck AC (2015) Cardiac T2-mapping using a fast gradient echo spin echo sequence - first in vitro and in vivo experience. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 17:67Figures
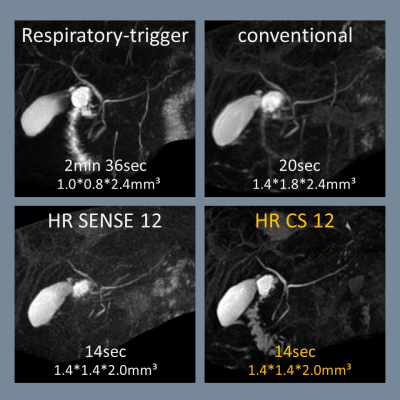
Figure1. Representative 3D MRCP images with actual acquisition
time using conventional RT-TSE, conventional-GraSE, HR SENSE12-GraSE and HR CS12-GraSE.
The HR CS12-GraSE can shorten about 90% of the scan time compared to
conventional RT-TSE, and about 25% compared to conventional-GraSE.
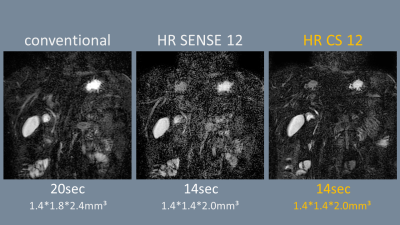
Figure2. The source images of 3D MRCP of
breath-holding three sequences (conventional-GraSE, HR SENSE12-GraSE and HR
CS12-GraSE). HR SENSE12-GraSE showed severe image noise compared to
conventional-GraSE. In contrast, HR CS12-GraSE showed similar SNR to conventional-GraSE.
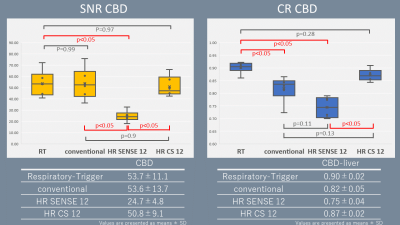
Figure3. Results of SNR and CR among four
sequences. RT-TSE showed the highest value for both SNR and CR, but there was
no significant difference in comparison with HR CS12-GraSE.
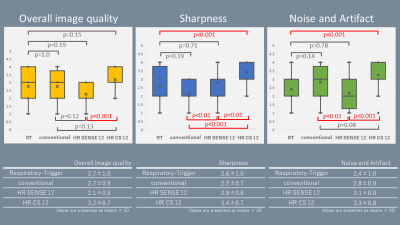
Figure4. Results of the visual evaluation. The HR CS12-GraSE
showed the highest value in all overall image quality, sharpness and noise and
artifacts. For overall image quality, HR CS12-GraSE was significantly higher
than HR SENSE12-GraSE (p<0.001), but not significantly different from RT-TSE
to conventional-GraSE. For sharpness, HR CS12-GraSE was significantly higher
than the other three sequences (p<0.01), and for noise and artifacts, HR
CS12-GraSE was significantly better than RT-TSE and HR SENSE12-GraSE
(p<0.001).
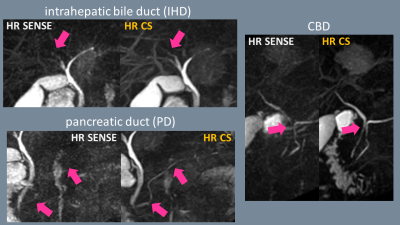
Figure5. Comparison of HR SENSE12-GraSE and HR
CS12-GraSE. The HR CS12-GraSE achieved higher SNR and contrast despite the
increased spatial-resolution.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/0511