0412
Investigating the impact of ketogenic diet in Alzheimer’s disease using 1H MRS1UCSF, San Francisco, CA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Alzheimer's Disease, Spectroscopy, metabolism
Ketogenic diet (KD) may be used to treat cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In hAPPJ20 AD mice fed KD, improved spatial learning has been noted, but mechanisms driving this cognitive change remains unclear. Here we used 1H MRS to probe the effect of KD on brain metabolism in hAPPJ20 mice fed either a control diet or KD. Increases in prefrontal creatine and Glx in KD-fed mice and increased Tau in male KD-fed mice were observed. Male KD-fed mice also demonstrated better spatial learning on the Morris water maze. Thus, KD may improve brain energetics and neurotransmission supporting cognitive function.
Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease with no cure, projected to affect 152.8 million people by 2050. It is essential, and urgent, to better understand the disease to enable the identification and differentiation of disease sub-types, develop treatments and improve monitoring of treatment efficacy. Longitudinal assessment of AD pathogenesis using non-invasive and specific imaging approaches is crucial.Recently, a ketogenic diet (KD, often involving a beta-hydroxybutyrate, BHB, supplement) has been proposed as a therapy for AD1-5, and studies in memory-impaired adults and mild to moderate AD patients showed cognitive improvements following KD administration6,7. It is thus vital that we have the tools to understand ketone metabolism in the brain, both in untreated AD and following treatment with KD. However, current methods of monitoring KD in humans are indirect, consisting of measuring BHB blood levels. A clinically applicable non-invasive and direct imaging method capable of measuring in vivo metabolic changes is still needed.
It has recently been demonstrated that KD can improve context-dependent and visual-spatial learning in the hAPPJ20 AD mouse model8. However, the effect of KD on brain metabolism in this model has not been investigated in vivo. We thus applied a clinically relevant method, proton MR spectroscopy (1H MRS), to the study of AD mice fed with KD, and tested if we could monitor changes in metabolite levels in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) owing to its involvement in spatial learning.
Material & Methods
Animals: 35 hAPPJ20 mice (22 females, 13 males, 2 months-old) were given either a control diet (CD) (n=17) or ketogenic diet (KD, comprising of b-hydroxybutyrate-d4 or BHB) (n=18) for 4 months. During the 3rd month of diet, behavioral testing consisting of elevated plus maze, open field test, and Morris water maze was performed. After 4 months of diet, mice were weighed, and blood ketone levels measured using a portable ketone meter.MRS acquisition: Following behavioral testing, 1H MRS spectra were acquired on a 14.1Tesla Varian (Vnmrj 4) system equipped with a millipede 1H coil (diameter 40mm), from a 2x 2x2 mm3 voxel in the PFC using a PRESS sequence (TR = 2000ms, TE1 = 10ms, TE2 = 10ms, 512 averages, VAPOR water suppression).
Processing: MRS data were apodized using jMRUI (v6). Spectral fitting and quantification were done using LCModel for the following metabolites: N-acetyl aspartate (NAA); sum of glycerophosphocholine, phosphocholine and choline (GPC+PC+Cho); sum of phosphocreatine and creatine (PCr+Cr); glutamate (Glu), glutamine (Gln), sum of glutamate and glutamine (Glx); myoinositol (mI); taurine (Tau); and g-aminobutyric acid (GABA).. For final statistical analyses, only mice with metabolites CRLB (%SD) values of < 20% were selected, leading to 30 mice for analysis (groups: 8 females CD, 7 males CD, 9 females KD, 6 males KD). 2-way ANOVA was performed using Prism 9 to assess the effects of diet (control vs. keto), sex (female vs. male), and interaction (diet x sex).
Results
As shown in Figure 1, body weight and blood ketone levels were significantly higher in the KD group compared to CD, indicating a successful effect of KD. A typical PRESS spectrum from the PFC voxel is shown in Figure 2. A significant effect of diet was observed for two metabolites: PCrCr [F (1,26) = 4.34, p = 0.047] and Glx [F (1,26) = 13.58, p = 0.001], where KD resulted in higher levels of these metabolites in the PFC (Figure 3). A significant diet x sex interaction effect was observed for Tau [F (1,26) = 4.38, p = 0.046], where male mice on KD demonstrated higher levels of Tau in the PFC compared to male mice on CD (Figures 3 and 4). As for behavior, specifically pertaining to spatial learning, male mice on KD demonstrated a significantly higher number of platform crossings compared to those on CD (Figure 5). This was not observed in female mice on either diet.Discussion
In summary, KD resulted in increased levels of prefrontal PCrCr and Glx, and the increase in prefrontal Tau post-KD was observed only in male mice. KD also improved spatial learning in hAPP-J20 mice (an effect also observed only in males). It is plausible that this improvement is associated with higher levels of Tau observed in these animals post-KD. Taurine functions as a neuroprotectant against b-amyloid-related neuropathology, as well as benefits neuronal proliferation, synaptogenesis, and synaptic plasticity9. This suggests its effects on improving learning and memory. In addition, higher levels of Glx and increased glutamatergic neurotransmission ascribed to BHB10 can also contribute to improved spatial learning given glutamate’s role in these processes11.Conclusions and Future Directions
Our results indicate that KD may result in improved brain energetics and neurotransmission that can be detected using in vivo 1H MRS (as implicated by increased PCrCr and Glx post-KD). Improvement in spatial learning, assessed by the Morris water maze, may also be a result of KD, and this needs to be further explored. Along with the PFC, the hippocampus is also required for spatial and associative learning12. Importantly it is one of the main structures implicated in AD. Our future directions thus include 1H MRS investigation of the effect of KD on hippocampal metabolites.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH/NIA R01AG064170, a fellowship from the Alzheimer's association ( AARF-20-678090) and a fellowship from the Brightfocus foundation (A2020928F).References
1. A ketone ester diet exhibits anxiolytic and cognition-sparing properties, and lessens amyloid and tau pathologies in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Kashiwaya, Y. et al. Neurobiol. Aging 34, 1530–1539 (2013).
2. Ketogenic Medium Chain Triglycerides Increase Brain Energy Metabolism in Alzheimer's Disease. Croteau, E. et al. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 64, 551–561 (2018).
3. Effects of ketone bodies in Alzheimer's disease in relation to neural hypometabolism, β-amyloid toxicity, and astrocyte function. Hertz, L., Chen, Y. & Waagepetersen, H.S. J. Neurochem. 134, 7–20 (2015).
4. Hypometabolism as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease. Costantini, L.C., Barr, L.J., Vogel, J.L. & Henderson, S.T. BMC Neurosci. 9 Suppl 2, S16 (2008).
5. Ketone bodies as a therapeutic for Alzheimer's disease. Henderson, S.T. Neurotherapeutics 5, 470–480 (2008).
6. Effects of beta-hydroxybutyrate on cognition in memory-impaired adults. Reger, M.A. et al. Neurobiol. Aging 25, 311–314 (2004).
7. Study of the ketogenic agent AC-1202 in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Henderson, S.T. et al. Nutr. Metab. (Lond). 6, 31 (2009).
8. Betahydroxybutyrate suppresses epileptiform spikes and improves cognition in Alzheimer’s mouse model. J.C. Newman, F. Kroll, S. Ulrich, J.J. Palop, E.M. Verdin. Innovation in Aging, Volume 1, Issue suppl 1, July 2017, Pages 1151–1152.
9. Evaluation of the neuroprotective effect of taurine in Alzheimer’s disease using functional molecular imaging. Se Jong Oh, et al. Scientific Reports volume 10, Article number: 15551 (2020).
10. β-Hydroxybutyrate: A Signaling Metabolite. John C. Newman and Eric Verdin. Annu Rev Nutr. 2017 Aug 21; 37: 51–76.
11. Group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptor function and its regulation of learning and memory in the aging brain. Caroline Ménard and Rémi Quirion. Front. Pharmacol., 12 October 2012.
12. Frequency-specific hippocampal-prefrontal interactions during associative learning. Scott L. Brincat and Earl K. Miller. Nat Neurosci. 2015 Apr; 18(4): 576–581.
Figures
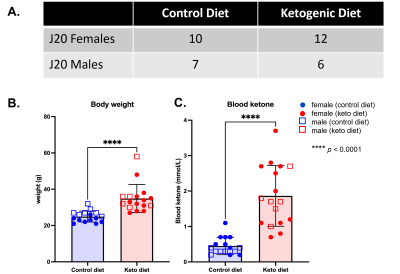
Figure 1 – Animals and ketogenic diet – (A) Number of hAPPJ20 mice per group of diet and sex. (B) Body weight is significantly increased in mice fed KD for 4 months compared to mice fed a control diet (****p<0.001). (C) Blood ketone levels are significantly increased in KD-fed mice at 4 months compared to mice fed control diet (****p<0.001), indicating a successful effect of diet.
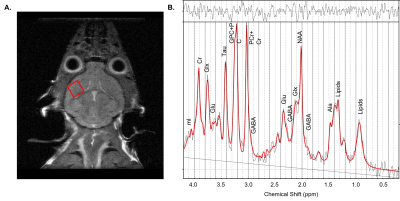
Figure 2 - 1H MRS of the mouse prefrontal cortex– (A) Representative T2-weighted anatomical image with a 2 x 2 x 2 mm3 PRESS voxel placed in the mouse prefrontal cortex (PFC) and (B) corresponding 1H MRS spectrum acquired from the voxel and fitted with LCmodel (red).
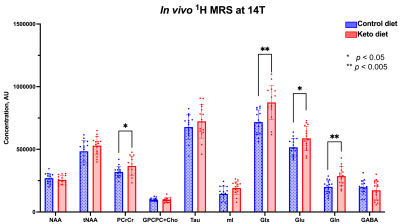
Figure 3 – Metabolite levels in the PFC of hAPPJ20 mice fed ketogenic diet: Effect of diet. Significantly higher levels of PCrCr, Glx, Glu, and Gln can be seen in the PFC of KD-fed mice compared to CD-fed ones (*p<0.05; **p<0.005).
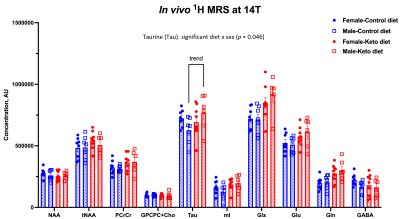
Figure 4 – Metabolite levels in the PFC of hAPPJ20 mice fed ketogenic diet: Effect of diet and sex. A significant diet x sex interaction effect was observed for Tau [F (1,26) = 4.38, p = 0.046], where male mice on KD demonstrated higher levels of Tau in the PFC compared to male mice on CD.
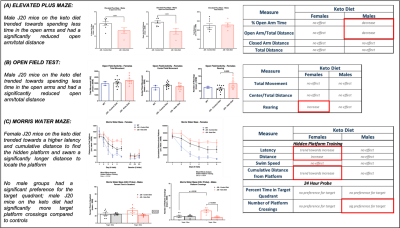
Figure 5 – Behavioral testing. Results showing trends and significant differences between KD vs CD and male vs female groups for the following behavioral tests: (A) Elevated Plus Maze (measures anxiety), (B) Open Field Test (measures activity, anxiety, and willingness to explore), and (C) Morris Water Maze (measures spatial learning).