0384
Conditional Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models for Inverse MR Image Recovery1Department of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 3Department of Biomedical Data Science, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence
High-resolution, multi-contrast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocols are required for accurate clinical diagnoses, but are limited by long scan times. Recovering high-quality, multi-contrast images from low-quality accelerated acquisitions is a promising approach to mitigate this limitation. Prior studies have demonstrated deep-learning for tasks such as contrast synthesis, image super-resolution, and image reconstruction. However, each of these tasks requires different architectures and training paradigms. Motivated by these challenges, we introduce a unified conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM) for inverse MR image recovery. Experiments performed on three image recovery tasks demonstrate that DDPMs achieve superior performance compared to prior state-of-the-art approaches.Introduction
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offers unmatched versatility to capture images. Yet, prolonged scan-sessions required for multi-contrast, high-resolution protocols often involve accelerated scans with missing contrasts or low-quality images. Such protocols can be achieved using inverse recovery of high-quality images from undersampled k-space data11 or synthesis of excluded contrasts3. Recent studies developed deep models to solve inverse recovery problems in accelerated MRI. Several utilized convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or generative adversarial networks (GANs) to outperform traditional non-learning-based methods11 for contrast synthesis5,8, super-resolution2, and reconstruction6,12,14,18,19. However, each of these models require different training paradigms and specialized architectures, and GAN-based approaches suffer from unstable training, resulting in hallucinatory features13.Denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) are a new class of generative image models7 that outperform CNN- and GAN-based approaches with improved training stability and inference performance. Particularly, DDPMs achieved remarkable synthesis quality for unconditional image generation7, conditional tasks such as super-resolution17,18, and to capture data-driven priors for MRI reconstruction4,9,20,. However, it has not yet been explored whether conditional DDPMs can be used in a supervised setup for diverse MRI recovery tasks or whether DDPMs can be used as a unifying framework. Motivated by these challenges, we propose a conditional DDPM for inverse image recovery in accelerated MRI. We comparatively demonstrate our DDPM against multiple state-of-the-art baselines, and show that it can be effectively used for contrast synthesis, image reconstruction, and image superresolution without changing the training paradigm.
Methods
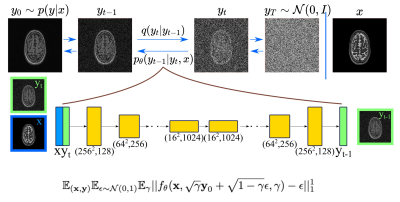
Conditional DDPM: Given a dataset $$$\mathcal{D} = \{x_i,y_i\}_{i=1}^N$$$ of input-output pairs that arise from an unknown conditional distribution $$$p(\textbf{y}|\textbf{x})$$$, we aim to recover $$$y_0$$$ from $$$\textbf{x}$$$ which may be noisy undersampled images, low-resolution images or source contrast images. To learn a constrained mapping between source image $$$\textbf{x}$$$ and target image $$$\textbf{y}_0 \sim p(\textbf{y}|\textbf{x})$$$, we use a conditional DDPM. The conditional DDPM applies a fixed forward Gaussian diffusion process to target image $$$\textbf{y}_0$$$, which is a Markovian process that gradually adds Gaussian noise over $$$T$$$ iterations denoted as $$$q(y_t|y_{t-1})$$$. At inference, the learned reverse process $$$p_\theta(y_{t-1}|y_t,x)$$$ is used to generate target image $$$y$$$ in $$$T$$$ iterative refinement steps. The reverse process starts from a noise image $$$\textbf{y}_T \sim \mathbb{N}(\textbf{0},\textbf{I})$$$, and iteratively refines the image using learned conditional distributions to generate the target image $$$\textbf{y}_0$$$. Conditioning on the source image $$$x$$$ is performed by concatenating $$$\textbf{x}$$$ as an additional channel to the network input. Our method, and the loss function are shown in Fig.1.Ensemble Learning: Since DDPMs are probabilistic models, sampling from DDPMs at inference typically results in different predictions. To reduce the variance of the predictions from different inferences, one approach is to sample multiple predictions, and combine the results. Here, we average the results of multiple (n=5) outputs to get final result.
Data: T1- and T2-weighted images from 80 subjects in the IXI dataset were used with 64 training, 6 validation, and 7 test subjects. From each subject, 75 axial cross-sections with brain regions were selected.
Implementation Details: DDPM models were trained via Adam optimizer10 on A6000-GPU for 1M iterations with batch size of 16 with UNet architecture17. Learning rate was 1e-4, and exponential moving average was 0.9999. Number of input channels was 2 (condition-image and noise), number of output channels was 1 (target-image). Total number of diffusion steps was 2000 during training, and 1000 for inference, yielding a 40sec inference. Linear noise schedule ranged in [1e-6,1e-4] during training and in [1e-4,1e-1] during testing.
Competing Methods: We compared our method against three state-of-the-art methods involving CNNs, GANs, and transformers. The first one was a classical CNN baseline based on UNet8. As a GAN model, the second competing method was pix2pix8, which is the most common model for image recovery tasks. In pix2pix, UNet generator was trained together with PatchGAN discriminator. Third, we compared our DDPM against to the latest MRI synthesis network ResViT21, that demonstrated transformer-based aggregated residual blocks for high-quality image generation. All competing methods were implemented as described in original manuscripts.
Results
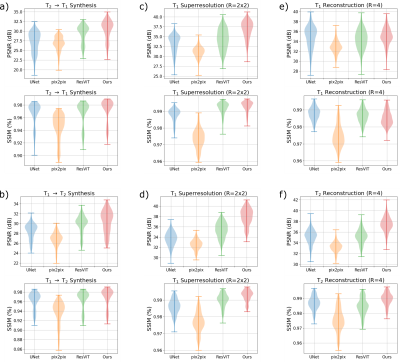
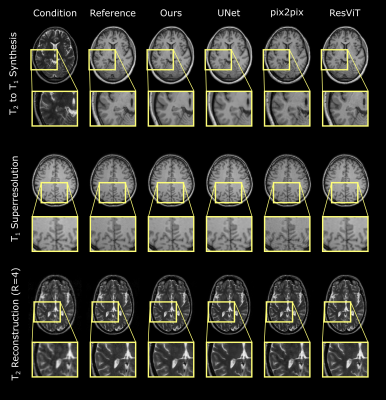
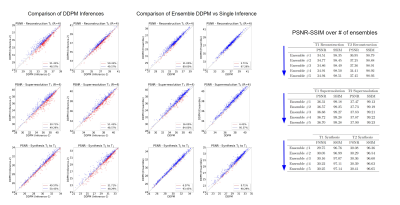
Experiments were conducted on three image recovery tasks: contrast synthesis (T1-to-T2 synthesis, T2-to-T1 synthesis), superresolution (T1 at R=2x2, T2 at R=2x2), and reconstruction (T1 at R=4, T2 at R=4). PSNR and SSIM metrics were used to compare image quality between recovered and ground-truth target images (Fig. 2). Representative images from the three tasks are displayed in Fig. 3. Reported measurements and images denote that our DDPM model outperforms all competing methods with increased PSNR and SSIM values as well as improved quality and accuracy. We further demonstrated the benefit of the ensemble strategy we employed in our implementation. Fig. 4 shows that, two different inferences of the same DDPM yields very different results, with each being better for 50% of the slices with large PSNR differences, whereas the ensemble DDPM pervasively yields enhanced performance compared to a single inference, around 90%.Discussion
Here we presented conditional DDPMs for inverse MR image recovery, and showed that our model achieves improved performance against several state-of-the-art baselines. Further, we showed that DDPMs can be used as a unifying framework for multiple MR image recovery tasks without requiring any tuning to translate across tasks. Ongoing work involves more efficient training and inference strategies.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Stanford Radiological Sciences Laboratory Neuroimaging Seed Funding, NIH Grants R01 EB009690, R01 EB026136 and NSF Grant DGE-1656518, and NIH research grants: R01-EB020613, R01-EB019437, R01-MH116173, P41EB030006, and U01-EB025162, and GE Healthcare.References
1. https://brain-development.org/ixi-dataset/
2. Chaudhari, A.S., Fang, Z., Kogan, F., Wood, J., Stevens, K.J., Gibbons, E.K., Lee,J.H., Gold, G.E., Hargreaves, B.A.: Super-resolution musculoskeletal mri using deeplearning. Magnetic resonance in medicine 80(5), 2139–2154 (2018)
3. Chaudhari, A.S., Sandino, C.M., Cole, E.K., Larson, D.B., Gold, G.E., Vasanawala,S.S., Lungren, M.P., Hargreaves, B.A., Langlotz, C.P.: Prospective deployment ofdeep learning in mri: a framework for important considerations, challenges, andrecommendations for best practices. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 54(2),357–371 (2021)
4. Chung, H., Ye, J.C.: Score-based diffusion models for accelerated mri (2022)
5. Dar, S.U., Yurt, M., Karacan, L., Erdem, A., Erdem, E., Çukur, T.: Image synthe-sis in multi-contrast mri with conditional generative adversarial networks. IEEETransactions on Medical Imaging 38(10), 2375–2388 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2901750
6. Hammernik, K., Klatzer, T., Kobler, E., Recht, M.P., Sodickson, D.K., Pock, T.,Knoll, F.: Learning a variational network for reconstruction of accelerated mri data.Magnetic resonance in medicine 79(6), 3055–3071 (2018)
7. Ho, J., Jain, A., Abbeel, P.: Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: Larochelle,H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M.F., Lin, H. (eds.) Advances in NeuralInformation Processing Systems. vol. 33, pp. 6840–6851. Curran Associates, Inc.(2020), https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2020/file/4c5bcfec8584af0d967f1ab10179ca4b-Paper.pdf
8. Isola, P., Zhu, J.Y., Zhou, T., Efros, A.A.: Image-to-image translation with condi-tional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computervision and pattern recognition. pp. 1125–1134 (2017)
9. Jalal, A., Arvinte, M., Daras, G., Price, E., Dimakis, A.G., Tamir, J.: Robustcompressed sensing mri with deep generative priors. Advances in Neural InformationProcessing Systems 34 (2021)
10. Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In: ICLR(Poster) (2015), http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
11. Lustig, M., Donoho, D.L., Santos, J.M., Pauly, J.M.: Compressed sensing mri. IEEEsignal processing magazine 25(2), 72–82 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2007.914728
12. Mardani, M., Gong, E., Cheng, J.Y., Vasanawala, S.S., Zaharchuk, G., Xing, L.,Pauly, J.M.: Deep generative adversarial neural networks for compressive sensingmri. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 38(1), 167–179 (2018)
13. Muckley, M.J., Riemenschneider, B., Radmanesh, A., Kim, S., Jeong, G., Ko, J.,Jun, Y., Shin, H., Hwang, D., Mostapha, M., et al.: Results of the 2020 fastmrichallenge for machine learning mr image reconstruction. IEEE transactions onmedical imaging 40(9), 2306–2317 (2021)
14. Ozturkler, B., Sahiner, A., Ergen, T., Desai, A.D., Sandino, C.M., Vasanawala,S., Pauly, J.M., Mardani, M., Pilanci, M.: Gleam: Greedy learning for large-scaleaccelerated mri reconstruction (2022). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2207.08393, https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.08393
15. Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J., Chanan, G., Killeen, T.,Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N., Antiga, L., Desmaison, A., Köpf, A., Yang, E., DeVito, Z.,Raison, M., Tejani, A., Chilamkurthy, S., Steiner, B., Fang, L., Bai, J., Chintala, S.:Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: NeurIPS(2019)
16. Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedicalimage segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical image computing andcomputer-assisted intervention. pp. 234–241. Springer (2015)
17. Saharia, C., Chan, W., Chang, H., Lee, C.A., Ho, J., Salimans, T., Fleet, D.J.,Norouzi, M.: Palette: Image-to-image diffusion models (2021)
18. Saharia, C., Ho, J., Chan, W., Salimans, T., Fleet, D.J., Norouzi, M.: Imagesuper-resolution via iterative refinement. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.07636 (2021)
19. Sandino, C.M., Cheng, J.Y., Chen, F., Mardani, M., Pauly, J.M., Vasanawala, S.S.:Compressed sensing: From research to clinical practice with deep neural networks:Shortening scan times for magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE signal processingmagazine 37(1), 117–127 (2020)
20. Song, Y., Shen, L., Xing, L., Ermon, S.: Solving inverse problems in medical imagingwith score-based generative models. In: International Conference on LearningRepresentations (2022), https://openreview.net/forum?id=vaRCHVj0uGI
21. Dalmaz O, Yurt M, Cukur T. ResViT: Residual Vision Transformers for Multimodal Medical Image Synthesis. IEEE TMI 2022; 3167808
22. Xie, Y., & Li, Q. (2022). Measurement-conditioned Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model for Under-sampled Medical Image Reconstruction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.03623.
23. Chung, H., Lee, E. S., & Ye, J. C. (2022). MR Image Denoising and Super-Resolution Using Regularized Reverse Diffusion. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.12621.
24. Dorjsembe, Z., Odonchimed, S., & Xiao, F. (2022, April). Three-Dimensional Medical Image Synthesis with Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. In Medical Imaging with Deep Learning.
Figures