0359
IVIM-DWI for the preoperative prediction of perineural invasion status in rectal cancer: A feasibility study with multivariate model analysis1Lixia District, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital, Jinan, China, 2MR Research, GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Data Analysis, Cancer
This study aimed to determine the clinical potential of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) DWI in predicting perineural invasion (PNI) of rectal cancer (RC). IVIM parameters derived from different mathematical models, including apparent diffusion coefficient from mono-exponential model, true diffusion coefficientand and perfusion fraction from bi-exponential model, and the distributed diffusion coefficient from stretched-exponential model showed significant differences between 72 with PNI and 76 without PNI. With these findings, IVIM may thus be considered effective in preoperatively predicting PNI status in RC and further help clinicians make individual treatment plans.Introduction
Colorectal cancer was ranked second in cancer-related deaths in 2018 1. Perineural invasion (PNI) is a significant predictor of rectal cancer (RC) prognosis 2. Neoadjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy before surgery can benefit PNI+ patients with RC. Nevertheless, PNI+ can only be judged by postoperative pathology. Studies 3-5 have suggested that perineural microenvironment can change dispersion and micro-perfusion of lesion by biochemical reactions and activation of cytokines. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) DWI using multi-b values have been reported to relate with the enlargement of cell nucleus, tight arrangement of cells and proliferation of new blood vessels in cancer tissues, affecting dispersion and pre-fusion of water molecules 6. Multiple mathematic models can be applied with IVIM-DWI, such as mono-exponential model (ME) with parameter of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), bi-exponential model (BE) with true diffusion coefficient (D), pseudo-diffusion coefficient (D*) and perfusion fraction (f), and stretched exponential model (SE) with distributed diffusion coefficient (DDC) and water molecular diffusion heterogeneity index (α). With multi-b-value IVIM, micro-EMVI has been effectively diagnosed in RC 7. With these, IVIM-DWI was assumed to hold clinical potential in predicting PNI+. However, so far no studies have explored this. Therefore, the aim of study was to explore the feasibility of IVIM-DWI with ME, BE and SEM analytic models for preoperative prediction of RC with PNI.Materials and Methods
Subjects76 RC without PNI patients (45 male and 31 female, mean age 64.50 ± 11.00 years) and 72 RC with PNI patients (44 male and 28 female, mean age 62.40 ± 10.70 years) were included in study. All lesions were confirmed by pathology. Each participant underwent IVIM-DWI scanning before surgery.
MRI experiments
All patients underwent MRI measurements on a 3.0 T system (Discovery 750w; GE Healthcare) using an eight-channel phased-array body coil in the supine position. Fast-spin-echo (FSE) T2WIs were separately performed in the sagittal, coronal and oblique views. Axial spin-echo echo-planar-image based IVIM-DWI scanning was performed with 11 b-values applied, namely 0, 20, 50, 100, 150, 200, 400, 600, 800, 1000, and 1500 s/mm2. The number of excitation (NEX) was 2 for b values of 20, 50, 100, and 150 s/mm2, 4 for b values of 0, 200, 400, 600, 1000 and 1500 s/mm2; and 6 for b value of 800 s/mm2 . The total scan time was 21 mins.
Image Analysis
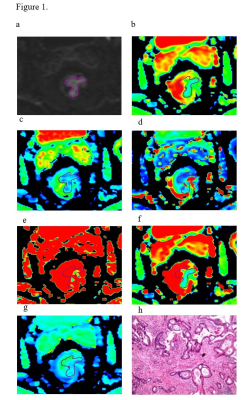
All MR data were transferred to Advantage Workstation (version AW 4.6, GE Medical Systems). IVIM-DWI data were separately post-processed in ME, BE and SEM models with a vendor-provided software (Function tool MADC; GE Healthcare). Parametric mappings of ADC, D, D*, f, DDC, and α were obtained accordingly. Two radiologists were independently employed for image analyses. Referring to the T2WI, the regions of interest (ROIs) with size between 50 and 500 mm2 (Figure 1) were manually sketched on the largest cross-sectional area of the tumor, excluding necrosis and cystic lesions, on diffusion images at b-value of 1000s/mm2 and then copied to each parametric mapping.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 26.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) and MedCalc 11.4 (MedCalc, Mariakerke, Belgium). The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to determine the consistency between the two observers. The independent-sample t-test or Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare IVIM parameters between PNI+ group and PNI- group. The independent risk factors were separately determined using multivariate binary logistic regression analysis. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance of each parameter by obtaining the area under the ROC curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity and accuracy. Significant threshold was set as p < 0.05. The nomogram and calibration curve were used to evaluate the combined model.
Results
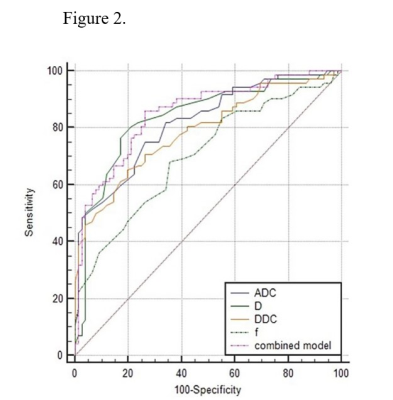
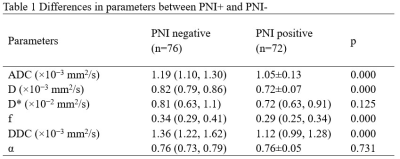
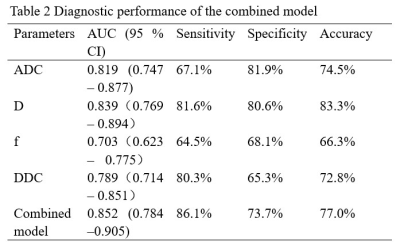
Inter-observer agreement was validated for measuring ADC, D, f, and DDC between two radiologists with high ICCs of 0.805, 0.787, 0.837, and 0.815. ADC, D, f, and DDC showed lower values in PNI+ group compared to PNI- group (all p<0.05;Tab.1). Moreover, ADC and D were demonstrated to be independent risk factors for PNI+ (P = 0.048 and 0.023, respectively). Through ROC analysis, ADC, D and the model combining ADC and D showed robust diagnostic efficacies, with respective AUCs of 0.819, 0.839 and 0.852. (Tab.2, Fig.2). The comprehensive diagnostic efficiency with sensitivity (81.6%), specificity (80.6%) and accuracy (83.3%) of D value in predicting PNI+ is better.Discussion and conclusions
In this study, significantly different IVIM parameters of ADC, D, f, and DDC were revealed between PNI+ group and PNI- group. We speculated that the interaction between nerves and tumor cells can trigger biochemical reactions and activate various cytokines, promoting the enlargement of tumor nuclei, the cells rearrangement and the growth of new blood vessels 6, thus affecting dispersion and micro-perfusion. Furthermore, ADC and D can easily and effectively predict preoperative PNI status, and D was revealed with the best combined effect in terms of sensitivity, specificity and accuracy. A multivariate model of combined IVIM-DWI can improve the diagnostic efficiency but without significance. In conclusion, ADC, D and the combined models all showed robust diagnostic efficiency. In terms of a comprehensive evaluation, D was validated with the best combination of sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy.Acknowledgements
My special thanks go to thank Dr. Weiqiang Dou of GE Healthcare for careful review of my dissertation and his valuable comments.References
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394-424. 2. Kim YI, Kim CW, Kim JH, et al. Clinical Implication of Perineural and Lymphovascular Invasion In Rectal CancerPatients Who Underwent Surgery After Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2021.
3. Bakst RL, Wong RJ. Mechanisms of Perineural Invasion. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2016;77(2):96-106.
4. Melgarejo da Rosa M, Clara Sampaio M, Virginia Cavalcanti Santos R, et al. Unveiling the pathogenesis of perineural invasion from the perspective of neuroactive molecules. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;188:114547.
5. Liang D, Shi S, Xu J, et al. New insights into perineural invasion of pancreatic cancer: More than pain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1865(2):111-22.
6. Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, et al. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology. 1986;161(2):401-7.
7. Zhao L, Liang M, Yang Y, Zhang H, Zhao X. Prediction of false-negative extramural venous invasion in patients with rectal cancer using multiple mathematical models of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2021;139:109731.
Figures