0166
Adversarial Diffusion Probabilistic Models for Unpaired MRI Contrast Translation1Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey, 2National Magnetic Resonance Research Center (UMRAM), Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey, 3Neuroscience Program, Aysel Sabuncu Brain Research Center, Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey
Synopsis
Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence
Synthesis of missing contrasts in an MRI protocol via translation from acquired contrasts can reduce costs associated with prolonged exams. Current learning-based translation methods are predominantly based on generative adversarial networks (GAN) that implicitly characterize the distribution of the target contrast, with limits fidelity of synthesized images. Here we present SynDiff, a novel conditional adversarial diffusion model for computationally efficient, high-fidelity contrast translation. SynDiff enables training on unpaired datasets, thanks to its cycle-consistent architecture with coupled diffusion processes. Demonstrations on multi-contrast MRI datasets indicate the superiority of SynDiff against competing GAN and diffusion models.Introduction
Multi-contrast MRI captures complementary information regarding an anatomy by collecting separate tissue contrasts1, so it can improve diagnostic accuracy and downstream imaging tasks2. Unfortunately, economic and labor costs associated with prolonged exams prohibit broadspread utilization of extensive multi-contrast protocols3,4. MRI contrast translation is a promising solution that synthesizes a missing target contrast given a subset of acquired source contrasts5-9. In recent years, learning-based translation with generative adversarial networks (GAN) have empowered performance leaps in image realism10-15. However, GAN models provide an indirect characterization of the target image distribution without evaluating likelihood. Such implicit modeling is susceptible to learning biases including early discriminator convergence and mode collapse, which limits fidelity of synthesized images16,17.Here, we introduce a novel adversarial diffusion model, SynDiff, to perform computationally efficient and high-quality MRI contrast translation. Unlike vanilla diffusion models16,17, SynDiff leverages a fast conditional diffusion process with large step sizes to generate the target image. A novel adversarial projector attains accurate sampling over large reverse diffusion steps. To enable practical training on unpaired datasets, a cycle-consistent architecture is devised with coupled diffusion processes between source-target contrasts.
Methods
SynDiff: SynDiff is a novel adversarial diffusion model for efficient, high-fidelity translation between source and target contrasts of a given anatomy. SynDiff employs a fast conditional diffusion process with an adversarial projector for accurate sampling over large step sizes (Fig. 1).Adversarial Diffusion:
a) Forward Process: Here, we propose fast diffusion with the following forward process:
$$x_t=\sqrt{1-\gamma_t}x_{t-k}+\sqrt{\gamma_t}\epsilon\implies q(x_t|x_{t-k})=\mathcal{N}\left(x_t;\sqrt{1-\gamma_t}x_{t-k},\gamma_t\mathrm{I}\right)$$
where $$$x_t$$$ is the image at time step $$$t$$$ of the diffusion process, $$$\epsilon$$$ is a standart normal noise variable, $$$k \gg 1$$$ is step size, and $$$\gamma_t$$$ is the noise variance.
b) Reverse Process: For efficient sampling in the reverse process, we introduce a novel adversarial projector that captures the complex transition probability $$$q(x_{t-k}| x_t, y)$$$ for large $$$k$$$, where $$$y$$$ is the guiding source image.
Conditional generator $$$G_{\theta}(x_t,y,t)$$$ performs gradual denoising in each reverse step to estimate $$$\hat{x}_{t-k} \sim p_{\theta}(x_{t-k}|x_t, y)$$$.
Discriminator $$$D_{\theta}(\{\hat{x}_{t-k} \mbox{ or } x_{t-k}\},x_t,t)$$$ distinguishes samples drawn from estimated versus true denoising distributions ($$$p_{\theta}(x_{t-k}|x_t, y)$$$ vs. $$$q(x_{t-k}| x_t, y)$$$).
c) Sampling: The denoising distribution is then estimated via recursive projections through the generator $$$G_{\theta}^{[\cdot]}$$$:
$$ p_{\theta}(x_{t-k}|x_t, y) := q(x_{t-k}|x_t, \tilde{x}_0=G_{\theta}^{[t/k]}(x_t, y, t))$$
The final denoised image is computed via sampling after repeated projections across $$$T/k$$$ reverse diffusion steps, where $$$T$$$ is the length of the entire diffusion process:
$$\hat{x}_0 \sim p_{\theta}(x_{0}|x_k, y)$$
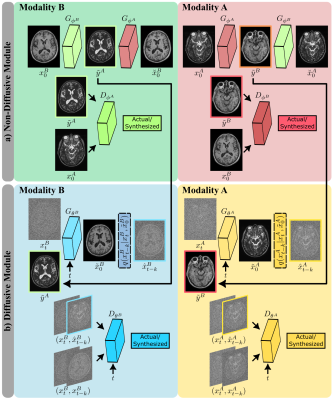
Cycle-consistent architecture: To learn from unpaired source-target images, SynDiff leverages a pair of diffusive and non-diffusive subnetworks (Fig. 2). Non-diffusive generators serve to produce estimates of anatomically-paired source images for given target images. These source estimates are required to condition the diffusive generators. Both subnetworks are trained via a non-saturating adversarial loss, along with an $$$\ell_1$$$-norm based cycle-consistency loss9.
Implementation Details: Code for SynDiff is available at https://github.com/icon-lab/SynDiff. Modeling was performed via PyTorch and Adam optimizer ($$$\beta_1=0.5,\beta_2=0.9$$$) with $$$10^{-4}$$$ learning rate for $$$50$$$ epochs. $$$T$$$=1000 was used with a step size of $$$k$$$=250.
Datasets
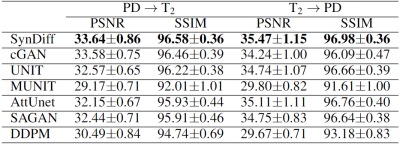
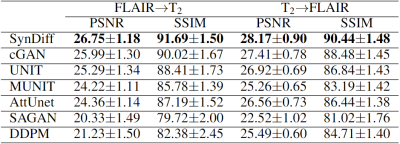
SynDiff was demonstrated on two multi-contrast brain MRI datasets, IXI (https://brain-development.org/ixi-dataset/) and BRATS18. In IXI, $$$T_2$$$-, and $$$PD$$$-weighted brain images from 40 healthy subjects were analyzed (train: 25, val: 5, test: 10). In BRATS, $$$T_2$$$-, and $$$FLAIR$$$-weighted brain images from 55 glioma patients were analyzed (train: 25, val: 10, test: 20). 100 2D axial cross-sections were selected from each subject.Results
We comparatively demonstrated SynDiff against several state-of-the-art competing methods, including GAN-based (cGAN9, AttUnet19, SAGAN20, UNIT21, MUNIT22) and diffusion (DDPM17) models. All models were trained on unpaired source-target contrasts for the following translation tasks: $$$PD\rightarrow T_2$$$ and $$$T_2\rightarrow PD$$$ in IXI, $$$FLAIR\rightarrow T_2$$$ and $$$T_2\rightarrow FLAIR$$$ in BRATS ($$$source\rightarrow target$$$). PSNR and SSIM between reference and synthesized images for all methods are listed in Fig. 3 for IXI, in Fig. 4 for BRATS. In all tasks, SynDiff achieves the highest performance among competing methods ($$$p<0.05$$$, signed-rank test). On average across tasks, SynDiff outperforms GAN-based methods by 2.12dB PSNR and 3.40% SSIM, and DDPM by 4.29dB PSNR and 5.17% SSIM. Representative target images are displayed in Fig. 5 for a) IXI and b) BRATS. SynDiff enhances translation performance, especially near pathological regions, where competing methods show suboptimal acuity. Overall, SynDiff generates images with fewer artifacts, lower noise levels, and more accurate tissue visualization compared to baselines.Discussion
In this study, we introduced an MRI translation method based on adversarial diffusion modeling to alleviate the limitations of current GAN models, which suffer from poor image fidelity. For improved performance and flexibility in model training, SynDiff leverages a fast diffusion process with large step size to conditionally synthesize target images and an adversarial projector for accurate sampling in reverse diffusion steps. To our knowledge, this is the first adversarial diffusion model for MRI synthesis and the first cycle-consistent diffusion model for unpaired MR contrast translation. Our results indicate the superior performance of SynDiff against state-of-the-art GAN and diffusion models. Thus, SynDiff holds great promise for rapid, reliable imputation of missing sequences in multi-contrast MR imaging.Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a TUBITAK BIDEB, a TUBA GEBIP 2015 fellowship, and a BAGEP 2017 fellowship.References
1. B. Moraal et al., “Multi-contrast, isotropic, single-slab 3d MR imaging in multiple sclerosis,” Eur. Radiol., vol. 18, pp. 2311–2320, 2008.
2. J. E. Iglesias, E. Konukoglu, D. Zikic, B. Glocker, K. Van Leemput, and B. Fischl, “Is synthesizing MRI contrast useful for inter-modality analysis?,” in Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist.Interv., pp. 631–638, 2013.
3. A. Jog, A. Carass, S. Roy, D. L. Pham, and J. L. Prince, “Random forest regression for magnetic resonance image synthesis,” vol. 35, pp. 475–488, 2017.
4. T. Joyce, A. Chartsias, and S. A. Tsaftaris, “Robust multi-modal MR image synthesis,” in Med.Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv., pp. 347–355, 2017.
5. J. Denck, J. Guehring, A. Maier, and E. Rothgang, “Enhanced magnetic resonance image synthesis with contrast-aware generative adversarial networks,” Journal of Imaging, vol. 7, p. 133, 08 2021.
6. Wang G, Gong E, Banerjee S, Martin D, Tong E, Choi J, Chen H, Wintermark M, Pauly JM, Zaharchuk G. Synthesize High-Quality Multi-Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging From Multi-Echo Acquisition Using Multi-Task Deep Generative Model. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020 Oct;39(10):3089-3099.
7. Lee, D., Moon, WJ. & Ye, J.C. Assessing the importance of magnetic resonance contrasts using collaborative generative adversarial networks. Nat Mach Intell 2, 34–42 (2020).
8. Kim S, Jang H, Hong S, Hong YS, Bae WC, Kim S, Hwang D. Fat-saturated image generation from multi-contrast MRIs using generative adversarial networks with Bloch equation-based autoencoder regularization. Med Image Anal. 2021 Oct;73:102198.
9. S. U. Dar, M. Yurt, L. Karacan, A. Erdem, E. Erdem, and T. Çukur, “Image synthesis in multi-contrast MRI with conditional generative adversarial networks,” IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 38, no. 10, pp. 2375–2388, 2019.
10. B. Yu, L. Zhou, L. Wang, J. Fripp, and P. Bourgeat, “3D cGAN based cross-modality MR image synthesis for brain tumor segmentation,” Int. Symp. Biomed. Imaging, pp. 626–630, 2018.
11. H. Li, J. C. Paetzold, A. Sekuboyina, F. Kofler, J. Zhang, J. S. Kirschke, B. Wiestler, and B. Menze, “DiamondGAN: Unified multi-modal generative adversarial networks for MRI sequences synthesis,” in Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv., pp. 795–803, 2019.
12. O. Dalmaz, M. Yurt, and T. Çukur, "ResViT: Residual Vision Transformers for Multimodal Medical Image Synthesis," in IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 41, no. 10, pp. 2598-2614, Oct. 2022.
13.Pan, Y., Liu, M., Lian, C., Zhou, T., Xia, Y., and Shen, D. (2018). Synthesizing Missing PET from MRI with Cycle-consistent Generative Adversarial Networks for Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis. MICCAI International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 11072, 455-463
14.Chartsias, A., Joyce, T., Dharmakumar, R., Tsaftaris, S.A., 2017. Adversarial image synthesis for unpaired multi-modal cardiac data, in: Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging. pp. 3–13.
15.Hiasa, Y. et al. 2018. Cross-Modality Image Synthesis from Unpaired Data Using CycleGAN, Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging. pp. 31–41
16. P. Dhariwal and A. Nichol, “Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis,” in Advances in neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 34, pp. 8780–8794, Curran Associates, Inc., 2021.
17. J. Ho, A. Jain, and P. Abbeel, “Denoising diffusion probabilistic models,” in Advances in neural information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 6840–6851, 2020.
18. B. H. Menze et al., "The Multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Benchmark (BRATS)," in IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, vol. 34, no. 10, pp. 1993- 2024, Oct. 2015.
19. O. Oktay, J. Schlemper, L. L. Folgoc, M. J. Lee, M. Heinrich, K. Misawa, K. Mori, S. G.McDonagh, N. Hammerla, B. Kainz, B. Glocker, and D. Rueckert, “Attention U-Net: Learning where to look for the pancreas,” arXiv:1804.03999, 2018.
20. H. Zhang, I. Goodfellow, D. Metaxas, and A. Odena, “Self-attention generative adversarial networks,” in Int. Conf. Mach. Learn., vol. 97, pp. 7354–7363, 2019.
21. M.-Y. Liu, T. Breuel, and J. Kautz, “Unsupervised image-to-image translation networks,” advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 30, Curran Associates, Inc., 2017.
22. X. Huang, M.-Y. Liu, S. Belongie, and J. Kautz, “Multimodal unsupervised image-to-image translation,” in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp. 172–189, 2018.6
Figures
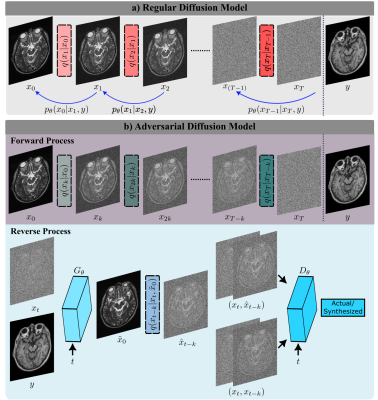
a) Regular diffusion models gradually transform between actual image samples and isotropic Gaussian noise in $$$T$$$ steps where $$$T$$$ is on the order of thousands. b) The proposed adversarial diffusion model instead performs fast transformation in $$$T/k$$$ steps, with step size $$$k\gg 1$$$. To capture complex reverse transition probabilities, a novel adversarial projector is introduced that leverages a diffusive generator and discriminator to synthesize a denoised image ($$$\hat{x}_{t-k}$$$), given $$$x_t$$$ and conditioned on the source contrast $$$y$$$.
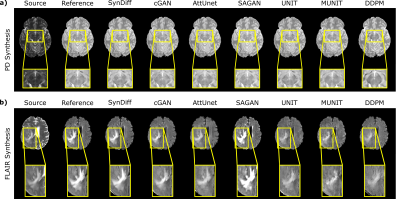
Representative translation results from SynDiff and competing methods. Source, reference target, and synthesized target images are displayed for a) $$$T_2\rightarrow PD$$$ in IXI, b) $$$T_2\rightarrow FLAIR$$$ in BRATS. SynDiff provides enhanced translation performance, especially near pathological regions, in contrast to competing methods with relatively poor tissue depictions. Overall, images generated by SynDiff have better-delineated tissue boundaries with fewer artifacts and lower noise levels.