0149
Feasibility study of diusion weighted imaging of nasopharynx using split-echo TSE-DWI combined with MultiVane acquisition
Kun Wang1, Yujie Yu1, Maoxue Wang1, Ming Li1, Xiance Zhao2, Peng Wu2, and Kan Deng3
1The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China
1The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Brain
Diusion weighted imaging (DWI) has high sensitivity in the dierential diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. However,the DWI based on SE-EPI has poor imaging quality in the nasopharynx. A combination of Multi-Vane (MV) and SPLICE(MV-SPLICE) were developed to reduce ELT, as well as improve SNR and the imaging quality of DWI. This study compares theDWI images of three acquisition sequences in nasopharynx,including DWI TSE without SPLICE(TSE), TSE with SPLICE(TSE-XD), and TSE with MV-SPICE(TSE-XD-MV) and proves that TSE with MV-SPLICE DWI based TSE with MV-SPLICE provides anexcellence imaging scheme of DWI for the clinical diagnosis of nasopharyngeal diseases.Synopsis
Diusion weighted imaging (DWI) has high sensitivity in the dierential diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. However,the DWI based on SE-EPI has poor imaging quality in the nasopharynx. A combination of Multi-Vane and split-echo acquisition of TSE signals(MV-SPLICE) were developed to reduce ELT, as well as improve SNR and the imaging quality of DWI. This study compares the DWI images of three acquisition sequences in nasopharynx,including DWI TSE without SPLICE(TSE), TSE with SPLICE(TSE-XD), and TSE with MV-SPICE(TSE-XD-MV) and proves that TSE with MV-SPLICE DWI based TSE with MV-SPLICE provides anexcellence imaging scheme of DWI for the clinical diagnosis of nasopharyngeal diseases.Introduction
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is one of the most common tumors in China, and its early diagnosis and treatment has agreat impact on the prognosis1. Diusion weighted imaging (DWI) has high sensitivity in the dierential diagnosis ofnasopharyngeal carcinoma. However, the conventional DWI based on spin-echo-echo planar imaging (SE-EPI) has poorimaging quality in the nasopharynx, which is mainly due to the serious image distortion caused by the eld inhomogeneityof skull, gas and soft tissues, and cannot meet diagnostic requirements. The DWI based on turbo spin echo (TSE) sequencecan eectively reduce image distortion, but the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) decreases obviously, which aects the diagnosisof microcancer lesions2. The SPLICE (split-echo acquisition of TSE signals) has a higher SNR due to acquire both the SE andstimulated echoes (STE), but images are blurring due to the long echo-train-length (ETL)3. Therefore, a combination ofMulti-Vane (MV) and SPLICE(MV-SPLICE) were developed to reduce ELT, as well as improve SNR and the imaging quality ofDWI. The aim of this study is to evaluate the image quality of DWI based on TSE with MV-SPLICE in nasopharynx imagingcompared to DWI with SPLICE and without SPLICE.Methods
55 patients (25 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma and 30 patients with normal nasopharyngeal mucosa) underwentnasopharyngeal MR examination with an Ingenia CX 3.0T scanner. There were 34 males and 21 females, aged 54.65 ± 14.73years. DWI images were acquired with three dierent schemes: TSE without SPLICE(TSE), TSE with SPLICE(TSE-XD), and TSEwith MV-SPICE(TSE-XD-MV), and the parameters were described in Table 1. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) of the mucosa tissue comparing with temporal bone were calculated, as Figure 1 demonstrates. SNR andCNR of nasopharyngeal DWI images with three schemes were assessed using the paired sample t test. Qualitativeassessment of DWI images were evaluated using the Wilcoxon paired sign rank test.Results
SNR of DWI with MV-SLIPCE (6.29±3.30) was better than those acquired in the other two schemes, but there was nostatistical dierence between the TSE with SPLICE (5.90 ± 2.46) and TSE with MV-SPLICE (P = 0.237). CNR of DWI with MV-SLIPCE (35.74 ± 16.35) was signicantly higher than that in the other two acquisition schemes (TSE without SPLICE: 19.08 ±10.67; TSE with SPLICE: 25.70 ± 10.64), and the dierence was statistically signicant between each two schemes (P <0.001). Qualitative results showed that the image quality of DWI with MV-SLIPCE (4.75 ± 0.52) was also signicantly betterthan that of other two acquisition schemes (TSE without SPLICE: 1.85 ± 0.49; TSE with SPLICE: 3.23 ± 0.67), the dierencewas statistically signicant between each two schemes (P < 0.001), as Table 1 and Figure 2 demonstrate.Conclusion
This study compares the DWI images of three acquisition sequences in nasopharynx, and proves that TSE with MV-SPLICE can 1) improve SNR and CNR, 2) eliminate the image distortion artifacts of nasopharynx without signicantly increasing theacquisition time, 3) and improve the image quality to display the structural details of nasopharynx. Therefore, DWI basedTSE with MV-SPLICE provides an excellence imaging scheme of DWI for the clinical diagnosis of nasopharyngeal diseases.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Cao, Su-Mei, Malcolm J. Simons, and Chao-Nan Qian. "The prevalence and prevention of nasopharyngeal carcinoma inChina." Chinese journal of cancer 30.2 (2011): 114.
2. Mikayama, Ryoji, et al. "Comparison of intravoxel incoherent motion diusion-weighted imaging between turbo spin-echo and echo-planar imaging of the head and neck." European radiology28.1 (2018): 316-324.
3.. Sakamoto, Junichiro, et al. "Tissue characterization of head and neck lesions using diusion-weighted MR imaging withSPLICE." European journal of radiology 69.2 (2009): 260-268.
Figures
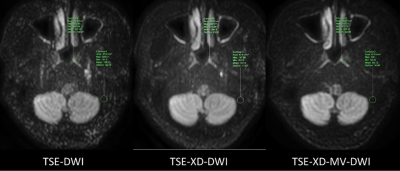
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of selecting the regions of interest (ROIs) to calculate CNR and SNR. The ROIs of the three DWIschemes were located in the same area of nasopharyngeal mucosa and temporal bone.
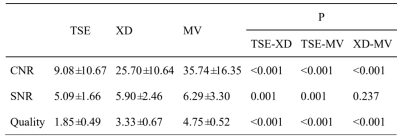
Table 1. Results of qualitative and quantitative analysis of three schemes of DWI images.
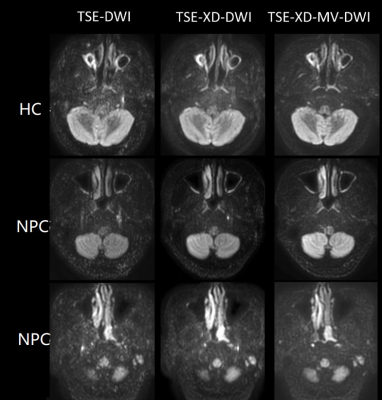
Figure 2. One health control and two patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The signal-to-noise ratio of TSE with MV-SPLICE DWI image is improved, and the background suppression is stranger than others. NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma;HC, health control.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/0149