0124
Effects of Levodopa Therapy on Neurovascular Coupling in Parkinson’s Disease Patients1Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China, 2Department of Neurology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Parkinson's Disease, Neurodegeneration
Introduction
Normal brain functions rely on the coupling between cerebral blood flow (CBF) and neural activity. This neurovascular coupling was impaired in Parkinson’s Disease (PD) patients, yet how this coupling changes after levodopa therapy remains unexplored.Objective
To investigate the effect of levodopa therapy on neurovascular coupling in PD patients.Methods
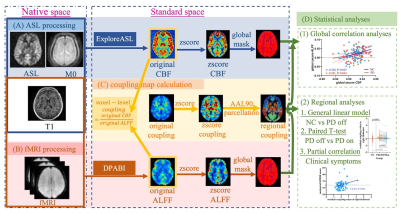
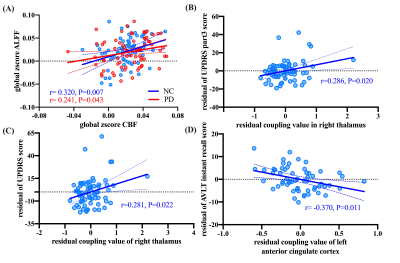
A total of 69 normal control (NC) and 71 PD patients were retrospectively enrolled. Neuropsychological assessments and MRI scanning were conducted in NC and patients before and after the levodopa therapy. CBF and neural activity were measured by arterial spin labeling (ASL) and the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF) from resting-state functional MRI, respectively. Global neurovascular coupling was calculated using Pearson’s correlation coefficient between CBF and ALFF. The CBF/ALFF ratio was calculated in each voxel and neurovascular coupling values were extracted in each brain region defined by Automatic Anatomical Labelling (AAL) atlas. General linear model was used for comparing regional neurovascular coupling differences between PD and NC. Paired T-test was conducted to explore regional neurovascular coupling alterations after levodopa therapy in patients. Partial correlations were calculated to investigate the relationship between regional neurovascular coupling, medication treatment, and clinical symptoms. Bonferroni correction was used for multiple comparison corrections.Results
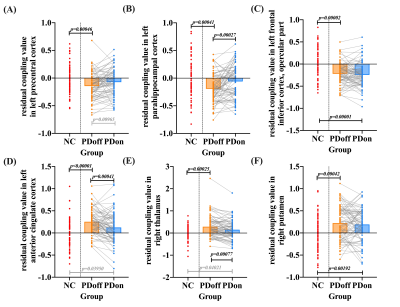
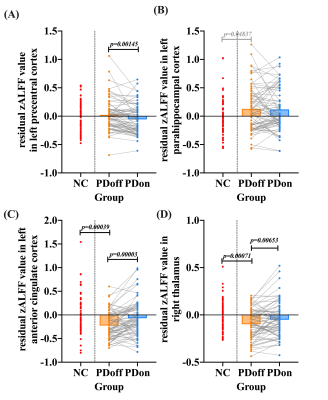
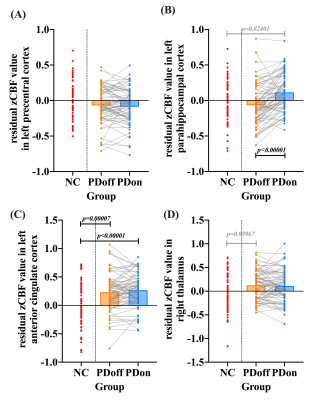
Significant positive correlations were observed between global CBF and ALFF in both NC (r= 0.320, P=0.007) and patients (r= 0.241, P=0.043). PD patients showed significantly lower regional neurovascular coupling in left precentral cortex, left frontal inferior cortex, and left parahippocampal cortex than NC (P<0.001). Meanwhile, significantly increased regional neurovascular coupling was found in left anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), right putamen, and right thalamus in patients (P<0.001). After levodopa therapy, regional neurovascular coupling in left parahippocampus, left ACC, and right thalamus was normalized in PD patients, and ALFF alterations made a major contribution to such normalization effect. The neurovascular coupling in left ACC was negatively correlated with instant memory ability (r= -0.370, P=0.011) in patients. The neurovascular coupling in right thalamus was significantly associated with the severity of motor symptoms (r=0.286, P=0.020).Conclusion
Abnormal neurovascular coupling was found in PD patients. These impairments were partially normalized after levodopa therapy, and ALFF alterations played a primary role in this normalization effect.Keywords
Parkinson’s disease; Levodopa therapy; fMRI (Resting State); Neurovascular couplingAcknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 82271935, 81971577, 82171888, and 82001767), the 13th Five-year Plan for National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFC1306600), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. LQ21H180008 and LQ20H180012), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 2021T140599 and 2019M662082), the National Natural Science Foundation of China's Major Regional International Cooperation Project (Grant No. 81520108010), and the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. 2020C03020).
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists. We certify that we have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for the appropriateness of the experimental design and method, and the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the data. We also assured that all of the authors listed had sufficient contributions to the conception and design, execution, or analysis and interpretation of data. The content of this manuscript has not been published in a scientific journal, book, or other venue.
References
Figures