0025
Free water diffusion volume fraction from NODDI suggests inflammation may drive decreased memory performance in Subjective Cognitive Decline1Radiology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Alzheimer's Disease, Neuroinflammation
Evidence suggests subjective cognitive decline (SCD) is an early risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. We analyzed the associations between memory and diffusion microstructure in the lower cingulum white matter bundle in SCD with DTI and NODDI. Better memory performance was associated with decreased free water volume fraction (FWVF) in the SCD group but not the control group. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to find differences in the associations between NODDI FWVF and memory in SCD in the lower cingulum. This finding supports prior findings of increased neuroinflammation in the earliest stages of Alzheimer’s Disease.Introduction
Biological changes occur in the brain up to 20 years before disease onset in Alzheimer’s disease (1). Thus, there is particular interest in early diagnosis for Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. The term “subjective cognitive decline” (SCD) was created in 2014 to describe patients who complain of memory difficulties but score normally on cognitive testing (2, 3). Incidence rates of dementia are increased in SCD in both multicenter studies (4) and meta-analyses (5). Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has successfully found differences between SCD and controls (6, 7), as well as between SCD participants who progress to mild cognitive impairment and SCD participants who do not (8, 9). In particular, diffusion changes in the lower cingulum bundle were shown to impact memory performance in both mild cognitive impairment (10-12) and SCD (7, 13-16). However, past applications of microstructure diffusion MRI models such as NODDI (17) failed to elucidate the microstructural changes underlying these differences in diffusion (18-20). Here we employed both DTI and NODDI to examine microstructural associations with memory function, as described by the delayed story recall from Wechsler Memory Scale Third UK edition (WMS-III UK) (21), in SCD versus control participants. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to apply the NODDI model to a cohort of over 100 SCD participants.Methods
This study utilized the Cambridge Centre for Ageing and Neuroscience (Cam-CAN) dataset. The full details of data collection are described elsewhere (22, 23). Three hundred twenty-five participants over the age of 55 who had both cognitive health and diffusion MRI data were included in the analysis. Of these participants, 127 answered affirmatively to the question “Do you feel you have any problems with your memory?”. These 127 participants were labeled as subjective cognitive decline (SCD) patients. The remaining 198 were used as control participants. Differences between groups in age, memory performance, and gender distribution were assessed with t-tests and chi-squared tests in R.MRI was collected on a 3 T Siemens TIM Trio scanner with a 32-channel head coil. Diffusion weighted images included 3 images with b = 0, and b values of 1000 and 2000 s/mm2 with 30 gradient directions each (22, 23). Image noise and Gibbs ringing were attenuated using MRtrix3 dwidenoise (24-26) and mrdegibbs (27, 28). Motion correction was achieved using FSL mcflirt (29). Fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), radial diffusivity (RD) and axial diffusivity (AD) maps were generated for each participant using FSL’s dtifit (30). NODDI models and maps for orientation dispersion (OD), intracellular volume fraction (ICVF), and free water volume fraction (FWVF) (17) were generated for each participant using AMICO (31). All images then underwent nonlinear transforms to standard space using FSL’s TBSS (32). Rather than a skeleton mask, the lower right and left cingulum bundles were extracted from the ICBM-DTI-81 white-matter labels atlas (33) and employed as region of interests (ROIs). ROI averages of each measure were then generated in MATLAB. Linear regression models were completed in R using the diffusion metrics as the dependent variable, delayed story recall performance as the independent variable, and a term describing the interaction between delayed story recall and group. Voxel-wise analyses employed TFCE (34) and were generated using FSL’s randomise (35).Results
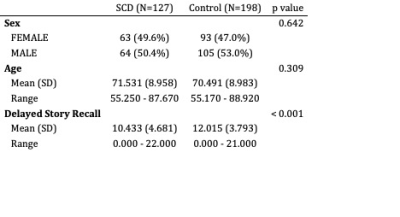
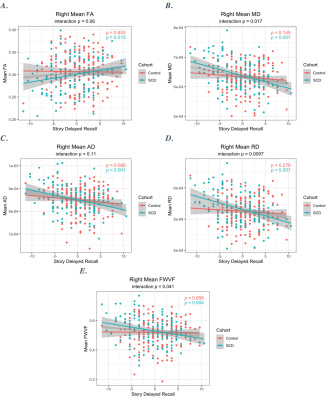
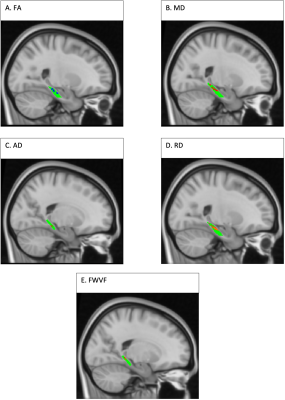
SCD and controls groups had similar age and sex distributions (Table 1). There was a significant difference in WMS-R delayed story recall between these groups (Table 1).For the right lower cingulum, there was a significant interaction effect between group and memory performance for MD, RD, and FWVF (Figure 1). Decreased MD, RD, and FWVF were associated with improved memory in SCD, versus controls (Figure 1). Voxel-wise analysis with multiple comparisons correction confirmed this finding (Figure 2). Voxel-wise analyses also detected a memory by group interaction for FA and AD for the right lower cingulum (Figure 2), which was not seen in the regional metrics. Post-hoc analyses revealed that correlations with delayed story recall were significant for regional averages of FA, MD, AD, RD, and FWVF in SCD, but not in controls (Figure 1). For all the evaluated microstructural metrics, group differences were not significant after correcting for age.Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to successfully find differences in the associations between NODDI FWVF and memory in SCD in the lower cingulum. FWVF has previously been shown to be sensitive to neuroinflammation, possibly due to the presence of edema (36). There is significant evidence that neuroinflammation plays an important role in Alzheimer’s Disease, particularly in the earliest stages of the disorder (37). Using this uniquely large cohort, current data suggest that increased neuroinflammation in SCD may contribute to impaired memory function, thus supporting the early neuroinflammatory hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease.Conclusion
Microstructural modeling of diffusion MRI is a valuable tool in the study of SCD as it relates to the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Our results indicate that the presence of increased neuroinflammation in SCD drives differences in diffusion metrics’ associations with memory between groups. Future work will include available T1w, T2w, and magnetization transfer images to further elucidate microstructural contributions to impaired memory in SCD.Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a Developmental Project Grant awarded by the NYU Langone Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center supported by the National Institute on Aging (NIA) grants P30AG066512. Data used for this project was provided by the Cambridge Centre for Ageing and Neuroscience (Cam-CAN). Cam-CAN funding was provided by the UK Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (grant number BB/H008217/1), together with support from the UK Medical Research Council and University of Cambridge, UK.References
1. Jack Jr CR, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ, Petersen RC, Weiner MW, Aisen PS, Shaw LM, Vemuri P, Wiste HJ, Weigand SD. Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer's disease: an updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. The Lancet Neurology. 2013;12(2):207-16.
2. Jessen F, Amariglio RE, Buckley RF, van der Flier WM, Han Y, Molinuevo JL, Rabin L, Rentz DM, Rodriguez-Gomez O, Saykin AJ. The characterisation of subjective cognitive decline. The Lancet Neurology. 2020;19(3):271-8.
3. Jessen F, Amariglio RE, Van Boxtel M, Breteler M, Ceccaldi M, Chételat G, Dubois B, Dufouil C, Ellis KA, Van Der Flier WM. A conceptual framework for research on subjective cognitive decline in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & dementia. 2014;10(6):844-52.
4. Slot RE, Sikkes SA, Berkhof J, Brodaty H, Buckley R, Cavedo E, Dardiotis E, Guillo‐Benarous F, Hampel H, Kochan NA. Subjective cognitive decline and rates of incident Alzheimer's disease and non–Alzheimer's disease dementia. Alzheimer's & Dementia. 2019;15(3):465-76.
5. Mitchell AJ, Beaumont H, Ferguson D, Yadegarfar M, Stubbs B. Risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in older people with subjective memory complaints: meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2014;130(6):439-51. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/acps.12336.
6. Selnes P, Fjell AM, Gjerstad L, Bjørnerud A, Wallin A, Due-Tønnessen P, Grambaite R, Stenset V, Fladby T. White matter imaging changes in subjective and mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer's & dementia. 2012;8:S112-S21.
7. Brueggen K, Dyrba M, Cardenas-Blanco A, Schneider A, Fliessbach K, Buerger K, Janowitz D, Peters O, Menne F, Priller J. Structural integrity in subjective cognitive decline, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease based on multicenter diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurol. 2019;266(10):2465-74.
8. Sun Y, Yang FC, Lin CP, Han Y. Biochemical and neuroimaging studies in subjective cognitive decline: progress and perspectives. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015;21(10):768-75. Epub 20150413. doi: 10.1111/cns.12395. PubMed PMID: 25864576; PMCID: PMC6493085.
9. Selnes P, Aarsland D, Bjornerud A, Gjerstad L, Wallin A, Hessen E, Reinvang I, Grambaite R, Auning E, Kjaervik VK, Due-Tonnessen P, Stenset V, Fladby T. Diffusion tensor imaging surpasses cerebrospinal fluid as predictor of cognitive decline and medial temporal lobe atrophy in subjective cognitive impairment and mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33(3):723-36. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-121603. PubMed PMID: 23186987.
10. Fan LY, Lai YM, Chen TF, Hsu YC, Chen PY, Huang KZ, Cheng TW, Tseng WYI, Hua MS, Chen YF. Diminution of context association memory structure in subjects with subjective cognitive decline. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018;39(6):2549-62.
11. Alves GS, O’Dwyer L, Jurcoane A, Oertel-Knöchel V, Knöchel C, Prvulovic D, Sudo F, Alves CE, Valente L, Moreira D. Different patterns of white matter degeneration using multiple diffusion indices and volumetric data in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer patients. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52859.
12. Wen Q, Mustafi SM, Li J, Risacher SL, Tallman E, Brown SA, West JD, Harezlak J, Farlow MR, Unverzagt FW. White matter alterations in early-stage Alzheimer's disease: A tract-specific study. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring. 2019;11:576-87.
13. Luo C, Li M, Qin R, Chen H, Yang D, Huang L, Liu R, Xu Y, Bai F, Zhao H. White matter microstructural damage as an early sign of subjective cognitive decline. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020;11:378.
14. Bosch B, Arenaza-Urquijo EM, Rami L, Sala-Llonch R, Junqué C, Solé-Padullés C, Peña-Gómez C, Bargalló N, Molinuevo JL, Bartrés-Faz D. Multiple DTI index analysis in normal aging, amnestic MCI and AD. Relationship with neuropsychological performance. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33(1):61-74.
15. Wei Y-C, Hsu C-CH, Huang W-Y, Chen Y-L, Lin C, Chen C-K, Lin C, Shyu Y-C, Lin C-P. White matter integrity underlies the physical-cognitive correlations in subjective cognitive decline. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:700764.
16. Lazar M. Working Memory: How Important Is White Matter? Neuroscientist. 2017;23(2):197-210. doi: 10.1177/1073858416634298. PubMed PMID: 30231842.
17. Zhang H, Schneider T, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Alexander DC. NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage. 2012;61(4):1000-16. Epub 20120330. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.072. PubMed PMID: 22484410.
18. Fu X, Shrestha S, Sun M, Wu Q, Luo Y, Zhang X, Yin J, Ni H. Microstructural white matter alterations in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Neuroradiol. 2020;30(3):569-79.
19. Mustafi SM, Gandhi PK, Risacher SL, West JD, Tallman EF, O'Neill DP, Farlow MR, Unverzagt FW, Apostolova LG, Saykin AJ. IC‐P‐175: Hybrid Diffusion Imaging (HYDI) of White Matter Changes in Older Adults With Subjective Cognitive Decline (SCD): Assessment of Orientation Dispersion and Axonal Density. Alzheimer's & Dementia. 2016;12:P127-P9.
20. Viviano RP, Hayes JM, Pruitt PJ, Fernandez ZJ, van Rooden S, van der Grond J, Rombouts SA, Damoiseaux JS. Aberrant memory system connectivity and working memory performance in subjective cognitive decline. NeuroImage. 2019;185:556-64.
21. Wechsler D. Wechsler Memory Scale Third UK E. London: Harcourt Assessment; 1999.
22. Shafto MA, Tyler LK, Dixon M, Taylor JR, Rowe JB, Cusack R, Calder AJ, Marslen-Wilson WD, Duncan J, Dalgleish T. The Cambridge Centre for Ageing and Neuroscience (Cam-CAN) study protocol: a cross-sectional, lifespan, multidisciplinary examination of healthy cognitive ageing. BMC Neurol. 2014;14(1):1-25.
23. Taylor JR, Williams N, Cusack R, Auer T, Shafto MA, Dixon M, Tyler LK, Cam C, Henson RN. The Cambridge Centre for Ageing and Neuroscience (Cam-CAN) data repository: Structural and functional MRI, MEG, and cognitive data from a cross-sectional adult lifespan sample. NeuroImage. 2017;144(Pt B):262-9. Epub 20150912. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.09.018. PubMed PMID: 26375206; PMCID: PMC5182075.
24. Veraart J, Novikov DS, Christiaens D, Ades-Aron B, Sijbers J, Fieremans E. Denoising of diffusion MRI using random matrix theory. NeuroImage. 2016;142:394-406. Epub 20160811. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.08.016. PubMed PMID: 27523449; PMCID: PMC5159209.
25. Veraart J, Fieremans E, Novikov DS. Diffusion MRI noise mapping using random matrix theory. Magn Reson Med. 2016;76(5):1582-93.
26. Cordero-Grande L, Christiaens D, Hutter J, Price AN, Hajnal JV. Complex diffusion-weighted image estimation via matrix recovery under general noise models. NeuroImage. 2019;200:391-404.
27. Kellner E, Dhital B, Kiselev VG, Reisert M. Gibbs‐ringing artifact removal based on local subvoxel‐shifts. Magn Reson Med. 2016;76(5):1574-81.
28. Bautista T, O’Muircheartaigh J, Hajnal JV, Tournier J-D, editors. Removal of Gibbs ringing artefacts for 3D acquisitions using subvoxel shifts. Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine; 2021.
29. Jenkinson M, Bannister P, Brady M, Smith S. Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage. 2002;17(2):825-41.
30. Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM. FSL. NeuroImage. 2012;62(2):782-90.
31. Daducci A, Canales-Rodriguez EJ, Zhang H, Dyrby TB, Alexander DC, Thiran JP. Accelerated Microstructure Imaging via Convex Optimization (AMICO) from diffusion MRI data. NeuroImage. 2015;105:32-44. Epub 20141022. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.10.026. PubMed PMID: 25462697.
32. Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE, Watkins KE, Ciccarelli O, Cader MZ, Matthews PM. Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage. 2006;31(4):1487-505.
33. Mori S, Wakana S, Van Zijl PC, Nagae-Poetscher L. MRI atlas of human white matter: Elsevier; 2005.
34. Smith SM, Nichols TE. Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. NeuroImage. 2009;44(1):83-98.
35. Winkler AM, Ridgway GR, Webster MA, Smith SM, Nichols TE. Permutation inference for the general linear model. Neuroimage. 2014;92:381-97.
36. Pasternak O, Kubicki M, Shenton ME. In vivo imaging of neuroinflammation in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2016;173(3):200-12.
37. Calsolaro V, Edison P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: Current evidence and future directions. Alzheimer's & Dementia. 2016;12(6):719-32. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.02.010.
Figures