Artifacts and Pitfalls in MSK MR Imaging
1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
Synopsis
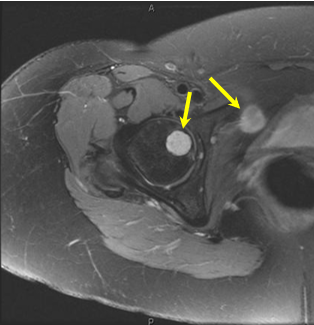
Image artifacts are commonly encountered in musculoskeletal MRI, and can lead to difficulties in correct image interpretation. While some artifacts are very obvious in an image, and the challenge then becomes one of ‘reading around’ the artifact, others can be more subtle and could be easily misinterpreted as a pathology. Understanding the source of an artifact can help to minimize its prevalence during set-up/scanning, or to differentiate artifact from genuine pathology when present in an image. This interactive talk will present a range of common (and some not-so-common) image artifacts, and discuss their source and strategies to minimize their impact.
- by the patient themselves - involuntary motion, magnetic susceptibility-induced distortions of the magnetic field, the inherent electrical properties of tissue
- from equipment malfunction - faulty RF coils or scanner electronics, damaged magnet room Faraday cage, faulty MR Conditional electronic devices (pumps, anesthesia workstations, physiological monitoring equipment) located in the magnet room, magnet room environmental conditions (temperature, humidity)
- from poor operator technique – patient preparation and set-up within RF coil and/or scanner, imaging sequence choice and/or prescription, RF coil choice
While some artifacts are very obvious in an image, and the challenge then becomes one of ‘reading around’ the artifact, others can be more subtle and could be easily misinterpreted as a pathology. Understanding the source of an artifact can help during scanning to minimize its prevalence in the resulting image or possibly to remove it altogether. For artifacts already present in an image, this understanding can also help to differentiate artifact from genuine pathology, thereby minimizing the potential for a misdiagnosis. This interactive talk will present a range of common (and not-so-common) artifacts and solicit suggestions from the audience as to their source and possible mitigation strategies.
Learning Outcomes
1. Identify common image artifacts encountered in MSK MRI
2. Understand the source of each artifact
3. Understand strategies which can be used to remove or minimize the prevalence of the artifact
Acknowledgements
I would like to acknowledge my colleagues Drs Frick and Amrami, and physics assistants Renee, Jenna, Ian and Pam for contributing some interesting artifact images.References
1. Singh DR, Chin MS, Peh WC. Artifacts in musculoskeletal MR imaging. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2014 Feb;18(1):12-22. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1365831. Epub 2014 Feb 10. PMID: 24515878.
2. Roth E, Hoff M, Richardson ML, Ha AS, Porrino J. Artifacts Affecting Musculoskeletal Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Their Origins and Solutions. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2016 Sep-Oct;45(5):340-6. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Feb 8. PMID: 26948320.
3. Vanhoenacker F, De Vos N, Van Dyck P. Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Knee. J Belg Soc Radiol. 2016;100(1):99. Published 2016 Nov 19. doi:10.5334/jbr-btr.1206
4. Elizabeth M. Lee, El-Sayed H. Ibrahim, Nancy Dudek, et al, Improving MR Image Quality in Patients with Metallic Implants. RadioGraphics 2021 41:4, E126-E137
5. Goh CK, Peh WC. Pictorial essay: pitfalls in magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2012 Nov;63(4):247-59. doi: 10.1016/j.carj.2011.02.005. Epub 2011 Nov 3. PMID: 22054700.