Clinical Thoracic MRA
Kimberly Kallianos1
1UCSF, United States
1UCSF, United States
Synopsis
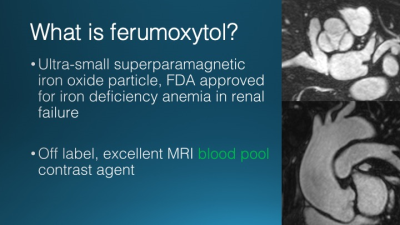
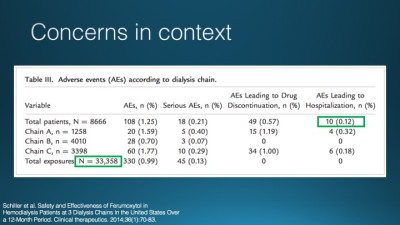
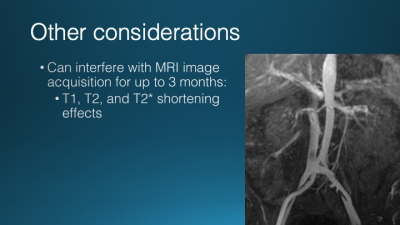
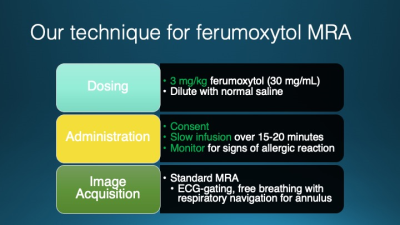
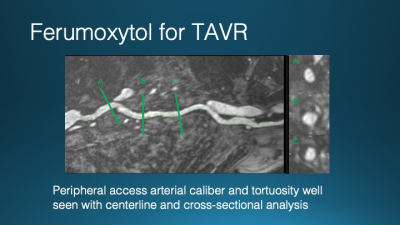
Computed tomography angiography (CTA) has been the test of choice for thoracic vascular imaging. The iodinated contrast required, however, increases the risk of renal dysfunction in patients with pre-existing renal failure, which is a common comorbidity in patients undergoing vascular imaging. Clinical thoracic MRA may be performed without contrast, with gadolinium-based contrast, and with ferumoxytol, and iron-based contrast agent. Each of these approaches has unique benefits and limitations particularly in the imaging of patients with renal failure. Clinical indications, benefits, and risks of each approach will be discussed in this talk.