Magnetotheranostics
Xiaoyuan Chen1
1National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
1National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
Synopsis
Theranostics is a fast-growing field due to demands for new, efficient therapeutics which could be precisely delivered to the target site using multimodal imaging with enhancing auxiliary actions. In this talk we discuss theranostic nanoplatforms containing magnetic nanoparticles along with other components. Magnetic nanoparticles allow for both diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities. We focus on the most important design strategies to achieve optimal theranostic effects as well as the roles of different components included in theranostics.
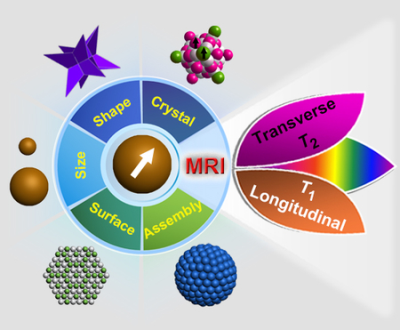
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have been extensively explored
as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. Recent progress in probing
MRI relaxivity of MNPs based on structural features at the molecular and atomic
scales is reviewed, namely, the structure-relaxivity relationships, including
size, shape, crystal structure, surface modification, and assembled structure
will be discussed. Assembly of MNPs from single particles to clustered
structures is a simple yet highly effective approach to enhance T2 relaxivity
of MNPs (assembly state, diffusion coefficient, multidomain structure, and
local magnetic field inhomogeneity). We will then highlight an activatable inflammation
magnetic resonance imaging (aiMRI) approach to stratify radiotherapy response,
which allows for early prediction of the therapeutic outcomes in cancer
radiotherapy. We will also describe the use of iron oxide nanoparticle for
Fenton-like reaction to produce tumor-specific singlet oxygen for chemodynamic therapy
of cancer.