5049
High-resolution whole-brain diffusion MRI at 7 Tesla using 63-channel signal reception1Center for Magnetic Resonance Research, Radiology, Medical School, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States
Synopsis
There has been an increasing interest to acquire high-resolution diffusion MRI at ultrahigh field (≥7 Tesla) due to the increased SNR and improved parallel imaging performance. To fully capitalize on the benefit of ultrahigh field, it is desirable to image with many receiver coils. In this study, we acquired slice-accelerated whole-brain 1.05-mm isotropic diffusion images on an FDA-approved 7 Tesla scanner (Siemens Terra) using a homemade 63-channel head RF array with various slice and in-plane accelerations. We found that the use of 63 channels can achieve higher acceleration factors (up to 9-fold acceleration in total) while maintaining the image quality.
Purpose
To demonstrate how the use of a 63-channel receiver RF array can acquire high-resolution whole-brain diffusion MRI (dMRI) using high acceleration factors at 7 Tesla (7T).Methods
Data acquisitionHuman studies were conducted on a 7T Terra (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) equipped with 64 receive channels and a whole-body gradient (70 mT/m maximum strength and 200 T/m/s maximum slew rate). Four healthy subjects who signed a consent form approved by the local Institutional Review Board were scanned using a homemade single-channel transmit and 63-channel receive RF head coil (HM1Tx63Rx), with the receive elements being self-decoupled loops [1, 2].
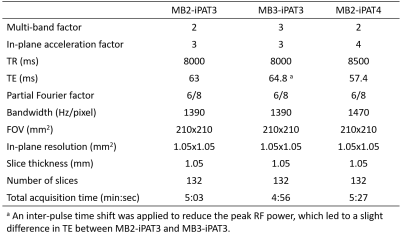
All dMRI data were obtained at 1.05-mm isotropic resolutions with single-shell q-space sampling (b-value=1000 s/mm2) and with a pair of 24 images (including 3 interspersed b0 images), each obtained using opposite phase encoding directions. Three imaging protocols (relevant imaging parameters being reported in Table 1) were optimized to investigate different slice- and in-plane acceleration combinations: 1) MB2-iPAT3 (2-fold slice and 3-fold in-plane acceleration, which was used in the original 7T Human-Connectome-Project (HCP) diffusion acquisition [3]), 2) MB3-iPAT3, and 3) MB2-iPAT4. Diffusion images were reconstructed online using the split-slice-GRAPPA algorithm [4] and SENSE-1 coil combination [5].
Image processing
Diffusion preprocessing was performed following the HCP pipelines [6], in which FSL’s topup [7] and eddy [8] routines were combined to correct for head motion and geometric EPI distortions. The preprocessed data were used to fit a diffusion tensor model to estimate such metrics as fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD).
Region-specific tensor fitting errors were also evaluated for a total of 10 brain regions of interests (ROI), including 9 anatomic regions defined by the MNI structural atlas [9] plus the whole brain.
Results
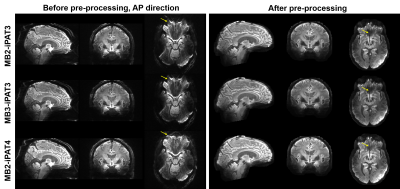
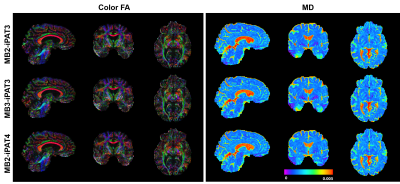
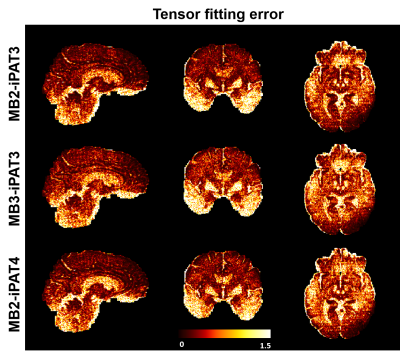
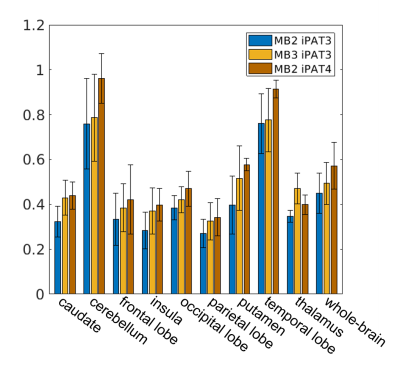
High-resolution dMRI was successfully obtained using all three protocols (Fig. 1) even with a net acceleration factor of 8 (MB2-iPAT4) or 9 (MB3-iPAT3). As expected, the images obtained with iPAT4 presented lower distortion than those obtained with iPAT3, especially in the presence of large off resonance effects (e.g., in the frontal lobe).Likewise, high-resolution FA and MD maps (Fig. 2) were obtained for all three protocols. Although visually the tensor fitting error maps were similar (Fig. 3), further quantitative analysis showed that increasing acceleration elevated tensor fitting errors. In particular, the whole-brain fitting error on average was increased by 9.8% for MB3-iPAT3 and 27.3% for MB2-iPAT4, when compared with MB2-iPAT3.
Discussion and Conclusion
We have demonstrated that a custom 63-channel receive coil can be used to acquire high-resolution whole-brain dMRI data at 7T. Our results show that the image quality can be preserved even when pushing the net acceleration up to 9-fold. This ability to increase acceleration is expected to benefit high-resolution dMRI because increasing in-plane acceleration can reduce image distortion and echo time (thus increasing SNR) and increasing slice acceleration can improve SNR efficiency.Due to the SAR limitation, the TR of the MB3-iPAT3 protocol was set to the same as with MB2-iPAT3. Part of our future work is to incorporate parallel-transmission into the data acquisition to reduce both SAR and RF inhomogeneities [10]. In addition, we will investigate how our 63-channel receive coil would compare to the commercial Nova 32-channel receive coil.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grants U01 EB025144, and P41 EB015894.References
[1] N. Tavaf, R.L. Lagore, S. Jungst, S. Gunamony, J. Radder, A. Grant, S. Moeller, E. Auerbach, K. Ugurbil, G. Adriany, P.F. Van de Moortele, A self-decoupled 32-channel receive array for human-brain MRI at 10.5 T, Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (2021).
[2] X.Q. Yan, J.C. Gore, W.A. Grissom, Self-decoupled radiofrequency coils for magnetic resonance imaging, Nature Communications 9 (2018).
[3] A.T. Vu, E. Auerbach, C. Lenglet, S. Moeller, S.N. Sotiropoulos, S. Jbabdi, J. Andersson, E. Yacoub, K. Ugurbil, High resolution whole brain diffusion imaging at 7T for the Human Connectome Project, NeuroImage 122 (2015) 318-331.
[4] S.F. Cauley, J.R. Polimeni, H. Bhat, L.L. Wald, K. Setsompop, Interslice leakage artifact reduction technique for simultaneous multislice acquisitions, Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 72(1) (2014) 93-102.
[5] S.N. Sotiropoulos, S. Moeller, S. Jbabdi, J. Xu, J.L. Andersson, E.J. Auerbach, E. Yacoub, D. Feinberg, K. Setsompop, L.L. Wald, T.E.J. Behrens, K. Ugurbil, C. Lenglet, Effects of image reconstruction on fiber orientation mapping from multichannel diffusion MRI: Reducing the noise floor using SENSE, Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 70(6) (2013) 1682-1689.
[6] M.F. Glasser, S.N. Sotiropoulos, J.A. Wilson, T.S. Coalson, B. Fischl, J.L. Andersson, J. Xu, S. Jbabdi, M. Webster, J.R. Polimeni, D.C. Van Essen, M. Jenkinson, The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project, NeuroImage 80(0) (2013) 105-124.
[7] J.L.R. Andersson, S. Skare, J. Ashburner, How to correct susceptibility distortions in spin-echo echo-planar images: Application to diffusion tensor imaging, NeuroImage 20(2) (2003) 870-888.
[8] J.L.R. Andersson, S.N. Sotiropoulos, An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging, NeuroImage 125 (2016) 1063-1078.
[9] J. Mazziotta, A. Toga, A. Evans, P. Fox, J. Lancaster, K. Zilles, R. Woods, T. Paus, G. Simpson, B. Pike, C. Holmes, L. Collins, P. Thompson, D. MacDonald, M. Iacoboni, T. Schormann, K. Amunts, N. Palomero-Gallagher, S. Geyer, L. Parsons, K. Narr, N. Kabani, G. Le Goualher, D. Boomsma, T. Cannon, R. Kawashima, B. Mazoyer, A probabilistic atlas and reference system for the human brain: International Consortium for Brain Mapping (ICBM), Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 356(1412) (2001) 1293-322.
[10] X.P. Wu, E.J. Auerbach, A.T. Vu, S. Moeller, C. Lenglet, S. Schmitter, P.F. Van de Moortele, E. Yacoub, K. Ugurbil, High-resolution whole-brain diffusion MRI at 7T using radiofrequency parallel transmission, Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 80(5) (2018) 1857-1870.
Figures