4958
Intranasal Insulin Enhances Resting Neurovascular Fluctuations in Type 2 Diabetes1State University of New York at Binghamton, Binghamton, NY, United States, 2Department of Neurology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, ME, United States, 3Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, ME, United States
Synopsis
We aimed to investigate the effect of intranasal insulin (INI) on cognition, balance, and brain neurovascular activity in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) participants of the MemAID trial. Cognition, balance, and brain neurovascular fluctuations - amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF) were measured in 11 subjects before and after 24-week treatment with INI or placebo. INI treatment significantly increased ALFF in the medial-frontal region. The ALFF increases at the end-of INI treatment were associated with improved balance. These findings suggest that INI may increase brain neurovascular activity in T2DM in the regions related to balance control and sustained attention.
Introduction
T2DM alters cognition1-4 and balance5. Resting-state functional MR imaging (rsfMRI) is a powerful tool for evaluating spontaneous brain activity6. The ALFF map from rsfMRI quantifies the intensity of neurovascular fluctuation at a single voxel level7. ALFF are diminished in T2DM as compared to healthy subjects8-10. We have demonstrated that a single INI dose acutely improves visuospatial memory11 and resting-state connectivity12. We investigated the long-term effects of INI on ALFF and the relationship of INI-induced ALFF changes with changes of cognition and balance in the MemAID trial13.Methods
Eleven T2DM participants (eight INI, three placebo) completed the baseline and end-of-treatment scans after 24 weeks using a GE Discovery MR750 3T scanner. Insulin/placebo was delivered using the ViaNase™ electronic atomizers (Kurve Technology, Inc. Lynnwood, WA, USA). Participants administered 40 IU (0.4mL) of human insulin (rDNA origin; Novolin® R, Novo Nordisk Inc., Bagsværd, Denmark) or placebo (0.4 mL bacteriostatic sodium chloride 0.9% solution) intranasally once daily before breakfast. Novolin® R was used off-label14.The MRI protocol included a localizer, 3D T1-weighted BRAVO images, and BOLD rsfMRI images (TR: 2s, 240 image volumes). Participants completed cognitive measure of sustained attention (Rapid Visual Information Processing-A (RVPA, range 0 to 1, worse to better) and balance test with eyes open (EO Total Sway Area).ALFF maps were derived from BOLD fMRI images. The first six image volumes were discarded to remove the signals before equilibrium. The remaining 234 image volumes were then realigned for head motion correction, corrected for slice timing differences, and spatially normalized to the MNI space. Six rigid-body motion parameters and linear trend were regressed out to reduce effects of head motion and scanner drift. The BOLD data were then filtered with band-pass filter of (0.01- 0.1 Hz). Time series of each voxel were Fourier transformed to frequency domain. The ALFF measure at each voxel was calculated as the averaged square root of the power in the filtered frequency range. The individual ALFF maps were divided by the global mean ALFF value within the brain.
ALFF maps of eight INI-treated subjects between baseline and end-of-treatment were compared using a paired t test. The association between ALFF changes and cognition/balance changes from the baseline to end-of-treatment was evaluated with a general linear regression model. Because of small number of subjects potentially violating normality tests, we adopted nonparametric tests for robust statistical evaluation on a voxel-by-voxel basis using Statistical nonparametric Mapping (SnPM). To further increase the robustness of linear regress analyses, we utilized the rank-based analyses. The voxel-level significance threshold was set for p < 0.005. Five-thousand random permutations were performed to generate the cluster-level statistics. The cutoff cluster size with FWE of 5% was used to correct for multiple comparisons. Post-hoc regional analyses were performed to evaluate the INI vs. placebo effects.
Results & Discussion
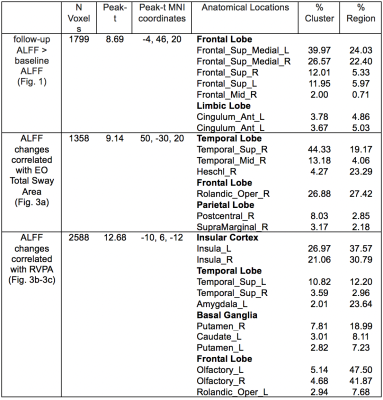
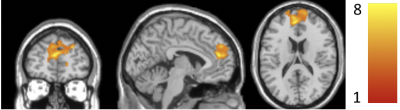
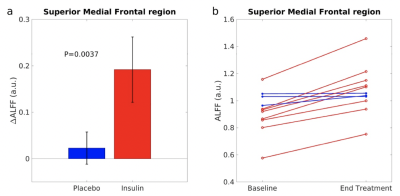
ALFF increased significantly from baseline to the end-of-treatment in the superior medial frontal (SMF) region (Fig. 1). Table 1 shows the specific cluster statistics. In this region, INI-treated T2DM subjects had larger ALFF increases compared to those with T2DM-Placebo (p=0.0037, Fig. 2a). ALFF increased in all INI-treated subjects in the SMF region, while decreased in placebo-treated subjects (Fig. 2b). The SMF region with INI-increased ALFF is consistent with INI-induced cerebral blood flow (CBF) increases15. T2DM has been associated with reduced ALFF10 and reduced CBF16 in the SMF region. These results suggest that INI can improve neurovascular activity in the region affected by T2DM.ALFF increases in the superior/middle temporal (SMT) region and insular region were associated with improved balance (smaller EO Total Sway Area) (Fig. 3a) but decreased levels of sustained attention (lower RVPA values) (Fig. 3b-3c; Table 1), respectively. Regional analyses showed a significant correlation between changes in ALFF and cognition/balance variables after adjusting age and gender (Fig. 4). Positive association of ALFF with balance levels in the SMT region may be associated with a potentially enhanced neuronal signaling from the INI-increased neural activity in the temporal region to the cerebellar balance control system. The insular region in which ALFF was negatively associated with attention levels is consistent with previously reported increased ALFF in the anterior cingulate region (constitutes salience network with insular region)8. The insular association suggests that INI can reduce overactive insular activity that modulates attention levels to salient stimuli17,18.
Conclusion
Intranasal insulin alters brain neurovascular activity in regions related to attention processing and balance control. Intranasal insulin may prove to be an effective intervention to improve functional outcomes in T2DM but larger studies are needed to confirm these results.Acknowledgements
www.clinicaltrials.gov NCT2415556; NIH-NIDDK 1R01DK103902; ISS-001033 Novo-Nordisk, Inc.; NERP15031 Medtronic Inc.References
1. Diabetes C, Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes I, Complications Study Research G, Jacobson AM, Musen G, Ryan CM, Silvers N, Cleary P, Waberski B, Burwood A, Weinger K, Bayless M, Dahms W, Harth J. Long-term effect of diabetes and its treatment on cognitive function. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(18):1842-52. Epub 2007/05/04. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa066397. PubMed PMID: 17476010; PMCID: PMC2701294.
2. Cukierman T, Gerstein HC, Williamson JD. Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes--systematic overview of prospective observational studies. Diabetologia. 2005;48(12):2460-9. Epub 2005/11/12. doi: 10.1007/s00125-005-0023-4. PubMed PMID: 16283246.
3. Xu WL, Qiu CX, Wahlin A, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L. Diabetes mellitus and risk of dementia in the Kungsholmen project: a 6-year follow-up study. Neurology. 2004;63(7):1181-6. Epub 2004/10/13. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000140291.86406.d1. PubMed PMID: 15477535.
4. Tan ZS, Beiser AS, Fox CS, Au R, Himali JJ, Debette S, Decarli C, Vasan RS, Wolf PA, Seshadri S. Association of metabolic dysregulation with volumetric brain magnetic resonance imaging and cognitive markers of subclinical brain aging in middle-aged adults: the Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(8):1766-70. Epub 2011/06/18. doi: 10.2337/dc11-0308. PubMed PMID: 21680719; PMCID: PMC3142014.
5. Xie YJ, Liu EY, Anson ER, Agrawal Y. Age-Related Imbalance Is Associated With Slower Walking Speed: An Analysis From the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2017;40(4):183-9. Epub 2016/06/25. doi: 10.1519/JPT.0000000000000093. PubMed PMID: 27341325; PMCID: PMC5182195.
6. Mantini D, Perrucci MG, Del Gratta C, Romani GL, Corbetta M. Electrophysiological signatures of resting state networks in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(32):13170-5. Epub 2007/08/03. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700668104. PubMed PMID: 17670949; PMCID: PMC1941820.
7. Zang YF, He Y, Zhu CZ, Cao QJ, Sui MQ, Liang M, Tian LX, Jiang TZ, Wang YF. Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev. 2007;29(2):83-91. Epub 2006/08/22. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2006.07.002. PubMed PMID: 16919409.
8. Cui Y, Jiao Y, Chen YC, Wang K, Gao B, Wen S, Ju S, Teng GJ. Altered spontaneous brain activity in type 2 diabetes: a resting-state functional MRI study. Diabetes. 2014;63(2):749-60. Epub 2013/12/20. doi: 10.2337/db13-0519. PubMed PMID: 24353185.
9. Xia W, Wang S, Sun Z, Bai F, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Wang P, Huang Y, Yuan Y. Altered baseline brain activity in type 2 diabetes: a resting-state fMRI study. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013;38(11):2493-501. Epub 2013/06/22. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.05.012. PubMed PMID: 23786881.
10. Wang CX, Fu KL, Liu HJ, Xing F, Zhang SY. Spontaneous brain activity in type 2 diabetics revealed by amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations and its association with diabetic vascular disease: a resting-state FMRI study. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e108883. Epub 2014/10/02. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108883. PubMed PMID: 25272033; PMCID: PMC4182760.
11. Novak V, Milberg W, Hao Y, Munshi M, Novak P, Galica A, Manor B, Roberson P, Craft S, Abduljalil A. Enhancement of vasoreactivity and cognition by intranasal insulin in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(3):751-9. Epub 2013/10/09. doi: 10.2337/dc13-1672. PubMed PMID: 24101698; PMCID: PMC3931384.
12. Zhang H, Hao Y, Manor B, Novak P, Milberg W, Zhang J, Fang J, Novak V. Intranasal insulin enhanced resting-state functional connectivity of hippocampal regions in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2015;64(3):1025-34. Epub 2014/09/25. doi: 10.2337/db14-1000. PubMed PMID: 25249577; PMCID: PMC4338591.
13. Galindo-Mendez B, Trevino JA, McGlinchey R, Fortier C, Lioutas V, Novak P, Mantzoros CS, Ngo L, Novak V. Memory advancement by intranasal insulin in type 2 diabetes (MemAID) randomized controlled clinical trial: Design, methods and rationale. Contemp Clin Trials. 2020;89:105934. Epub 2020/01/11. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2020.105934. PubMed PMID: 31923471; PMCID: PMC7242142.
14. Novo Nordisk Medical, Inc. Novolin R (insulin human injection- Prescribing Information and Safety. Updated 11/2019.
15. Novak V, Mantzoros CS, Novak P, McGlinchey R, Dai W, Lioutas V, Buss S, Fortier CB, Khan F, Becerra LA, Ngo L. Memory Advancement with Intranasal Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes: Randomized control. The 81st Annual Meeting of American Diabetes Assocation, June 2021. 2021.
16. Dai W, Duan W, Alfaro FJ, Gavrieli A, Kourtelidis F, Novak V. The resting perfusion pattern associates with functional decline in type 2 diabetes. Neurobiol Aging. 2017;60:192-202. Epub 2017/10/11. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.09.004. PubMed PMID: 28992987; PMCID: PMC5687828.
17. Uddin LQ. Salience processing and insular cortical function and dysfunction. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015;16(1):55-61. Epub 2014/11/20. doi: 10.1038/nrn3857. PubMed PMID: 25406711.
18. Menon V, Uddin LQ. Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function. Brain Struct Funct. 2010;214(5-6):655-67. Epub 2010/06/01. doi: 10.1007/s00429-010-0262-0. PubMed PMID: 20512370; PMCID: PMC2899886.
Figures