4938
CAMWARE: Cascaded Multi-level Wavelet Refine Neural Network for Accelerated Whole-brain MR Vessel Wall Imaging1Department of Radiology, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Department of Bioengineering, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 3Department of Neurology, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 4Department of Radiation Oncology, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 5Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States
Synopsis
3D MR vessel wall imaging (VWI) is a non-invasive imaging modality for directly assessing intracranial arterial wall diseases. A typical intracranial VWI protocol requires 6-12 minutes per scan to obtain adequate spatial coverage and resolution. Such a long scan time hinders widespread use of VWI in clinical settings. We have developed a novel intracranial vessel-dedicated CAscaded Multi-level WAvelet REfine (CAMWARE) network that enables a VWI scan within 4 minutes. The proposed network achieved significant improvement in vessel wall delination over conventional compressed sensing reconstruction, and several state-of-the-art deep neural networks, such as U-Net and multi-level wavelet U-Net.
Introduction
3D MR vessel wall imaging (VWI)1 is a non-invasive, “looking-beyond-the-lumen” imaging method that can directly probe intracranial arterial wall diseases. However, the needs for large spatial coverage and submillimeter spatial resolution mandate a long acquisition time (e.g. 6-12 min per scan)2-5, making the technique suffer from low throughput, poor patient tolerance, and high likelihood of scan failure. Recently, convolutional neural networks (CNN) have shown promising results on imaging acceleration in a wide variety of MR applications6-8. In this work, we propose a novel intracranial vessel-dedicated CAscaded Multi-level WAvelet REfine (CAMWARE ) network that enables a whole-brain VWI scan within 4 min.Methods
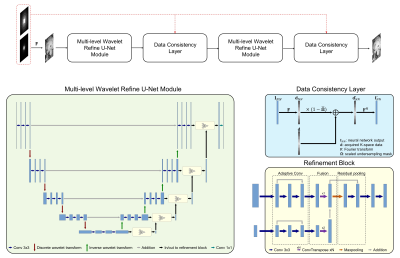
Problem formulation: Similar to previous studies for CNN-based MR imaging acceleration, an unconstrained optimization problem can be formulated as: $$\arg\min_{\mathbf{I}}\left\|\mathbf{I}-C(\mathbf{I_{u}}|\mathbf{\Theta})\right\|_{2}^{2}+\lambda\|\boldsymbol{\Omega} \mathbf{F}\mathbf{I}-\mathbf{d}\|_{2}^{2}$$where $$${\mathbf{I}}$$$ denotes complex-valued MR images, $$${\mathbf{d}}$$$ represents undersampled measurements in k-space, $$${\mathbf{I}_{u}}$$$ is the zero-filled reconstruction of $$${\mathbf{d}}$$$, $$$C(\mathbf{I_{u}}|\mathbf{\Theta}): \mathbf{I_{u}} \mapsto \mathbf{I}$$$ is a mapping function conditioned on CNN parameter $$$\mathbf{\Theta}$$$, and $$${\Omega}$$$ and $$${\textbf{F}}$$$ represent undersampling pattern and Fourier encoding operators, respectively.Network design: To solve the above problem, instead of treating the CNN reconstruction and data fidelity as two separate terms, a better choice is to incorporate the data fidelity in the learning stage. This is achieved by introducing a data consistency (DC) layer7, which replaces the k-space values of the reconstruction in with the originally acquired values, at the end of the CNN. CAMWARE adopts a U-Net structure as the backbone CNN architecture (Figure 1). To ensure a decent network performance on fine vessel wall structures (0.5 ± 0.1 mm), we modify U-Net in two aspects. (a) Pooling and deconvolution operations, which are adopted in conventional U-Net to enlarge receptive field and alter resolution of feature maps, are replaced by discrete wavelet transform and inverse wavelet transform, respectively9. (b) Multi-path refinement building block is added to fuse coarse features with fine-grained low-level features to restore sharp vessel wall boundaries10. We concatenate two “CNN + DC” blocks, such that the latter one acts as an extra step to reduce the learning errors of the former block11.
Data preparation: A total of 69 whole-brain VWI datasets, including 43 pre-contrast and 26 post-contrast scans, were acquired on a 3T system (Skyra, Siemens) with a standard 20-channel head-neck coil. The imaging protocol included: FOV=248x229x132 mm3, matrix size=448x414x240, 0.55 mm isotropic resolution, GRAPPA acceleration of 2x in the phase-encoding direction, 12.1 min acquisition time. Coil-combined complex-valued images reconstructed directly on the scanner were saved as the ground-truth, and thus was considered as a single-coil scenario. A variable density Poisson-disc undersampling mask was retrospectively applied to the k-space data generated by Fourier transforming the complex-valued images to simulate undersampled k-space which corresponded to an acceleration factor 6.5 or a 4-min acquisition. Data augmentation was applied including randomly rotation and flipping to counter overfitting.
Experiments: We split the 69 VWI sets into 57 for training, 6 for validation and 6 for testing, respectively. CAMWARE was compared to zero-filled reconstruction, compressed sensing (CS) based on projection onto convex sets (POCS) reconstruction12, state-of-art deep neural network reconstructions including U-Net13 and multi-level wavelet U-Net9. All neural networks were trained with 2D transverse slices using a combination of structural similarity index (SSIM) and mean absolute error (MAE) losses with Adam optimizer. The performances were evaluated with SSIM and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR).
Results
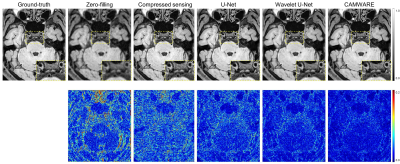
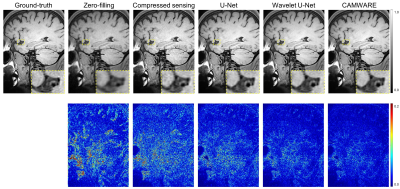
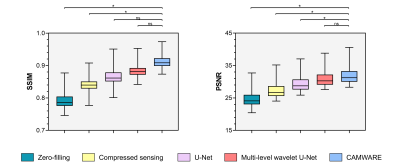
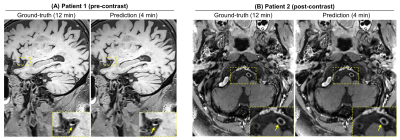
The qualitative comparisons as well as corresponding error maps for all different imaging acceleration methods with an acceleration factor 6.5 are shown in Figure 2 and 3. The CAMWARE model achieved SSIM of 0.9125 ± 0.0206 and PSNR of 31.8922 ± 2.5393. Comparisons of these metrics among different methods are displayed in Figure 4. All three deep learning models outperformed conventional zero-filled and CS reconstructions. CAMWARE faithfully reconstructed images with smaller errors and more accurate anatomical details compared to the ground-truth, indicated by the error maps and the zoom-in images. Figure 5 shows vessel wall images from two ischemic stroke patients. The pre-contrast hyper-intense plaque on the middle cerebral artery (Figure 5A) and post-contrast wall enhancement on the vertebral artery (Figure 5B) are depicted comparably by the proposed model (4 min) with respect to the ground-truth (12 min).Discussion
In this work, we proposed a CAMWARE network that can reconstruct high-quality 0.55 mm isotropic-resolution whole-brain vessel wall images with 6.5x undersampled in k-space data. The performance of the proposed approach is superior to other methods including compressed-sensing and deep neural networks. Our major innovations include: (a) preserving low-frequency details by incorporating discrete wavelet transform; (b) refining low-resolution features with fine-grained features; (c) adding data consistency layers to enforce data fidelity; (d) cascading two “CNN + DC” blocks to let the latter one acts as an extra step to reduce the learning errors of the former block. A recently optimized and widely used whole-brain VWI protocol requires 8 min per scan4. With the novel deep learning method, a whole-brain VWI scan can further be accelerated to 4 min, thus allowing for complete VWI investigation (both pre- and post-contrast scans) within 10 min.Conclusion
In this work, we proposed a novel intracranial vessel dedicated CAMWARE network that holds the potential to enable 4-min whole-brain VWI.Acknowledgements
This work is supported by NIH/NHLBI R01 HL147355.References
1. Mandell, D. M., Mossa-Basha, M., Qiao, Y., Hess, C. P., Hui, F., Matouk, C., ... & Mikulis, D. J. (2017). Intracranial vessel wall MRI: principles and expert consensus recommendations of the American Society of Neuroradiology. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 38(2), 218-229.
2. Qiao, Y., Steinman, D. A., Qin, Q., Etesami, M., Schär, M., Astor, B. C., & Wasserman, B. A. (2011). Intracranial arterial wall imaging using three‐dimensional high isotropic resolution black blood MRI at 3.0 Tesla. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 34(1), 22-30.
3. Zhang, L., Zhang, N., Wu, J., Zhang, L., Huang, Y., Liu, X., & Chung, Y. C. (2015). High resolution three dimensional intracranial arterial wall imaging at 3 T using T1 weighted SPACE. Magnetic resonance imaging, 33(9), 1026-1034.
4. Fan, Z., Yang, Q., Deng, Z., Li, Y., Bi, X., Song, S., & Li, D. (2017). Whole‐brain intracranial vessel wall imaging at 3 T esla using cerebrospinal fluid–attenuated T1‐weighted 3 D turbo spin echo. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 77(3), 1142-1150.
5. Yang, Q., Deng, Z., Bi, X., Song, S. S., Schlick, K. H., Gonzalez, N. R., ... & Fan, Z. (2017). Whole‐brain vessel wall MRI: A parameter tune‐up solution to improve the scan efficiency of three‐dimensional variable flip‐angle turbo spin‐echo. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 46(3), 751-757.
6. Sriram, A., Zbontar, J., Murrell, T., Zitnick, C. L., Defazio, A., & Sodickson, D. K. (2020). GrappaNet: Combining parallel imaging with deep learning for multi-coil MRI reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 14315-14322).
7. Schlemper, J., Caballero, J., Hajnal, J. V., Price, A. N., & Rueckert, D. (2017). A deep cascade of convolutional neural networks for dynamic MR image reconstruction. IEEE transactions on Medical Imaging, 37(2), 491-503.
8. Eun, D. I., Jang, R., Ha, W. S., Lee, H., Jung, S. C., & Kim, N. (2020). Deep-learning-based image quality enhancement of compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging of vessel wall: Comparison of self-supervised and unsupervised approaches. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1-17. 9. Liu, P., Zhang, H., Lian, W., & Zuo, W. (2019). Multi-level wavelet convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access, 7, 74973-74985.
10. Lin, G., Milan, A., Shen, C., & Reid, I. (2017). Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 1925-1934).
11. Quan, T. M., Nguyen-Duc, T., & Jeong, W. K. (2018). Compressed sensing MRI reconstruction using a generative adversarial network with a cyclic loss. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 37(6), 1488-1497.
12. Liu, J., & Wu, D. (2011, September). Joint POCS method with compressive sensing theory for super-resolution image reconstruction. In 2011 3rd International Conference on Awareness Science and Technology (iCAST) (pp. 99-102). IEEE.
13. Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., & Brox, T. (2015, October). U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (pp. 234-241). Springer, Cham.
Figures