4729
Diffusion-weighted MRI evaluation of kidney tumor: Comparison of small field-of-view and conventional EPI techniques1Department of Radiology,The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Wuhan, China, 3MR Application, Siemens Healthineers, Changsha, China, 4MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany
Synopsis
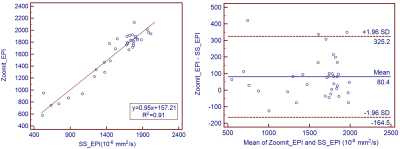
Image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of conventional single-shot spin-echo echo-planar imaging (SS-EPI) and prototype small field-of-view EPI (Zoomit_EPI) diffusion-weighted imaging in kidney tumor were compared. Results showed that Zoomit_EPI had better image quality, including fewer distortion artifacts and blurring (p < 0.01), and clearer edges of the lesions. ADC value of Zoomit_EPI had a good correlation with those of SS-EPI (R2 = 0.91), but Zoomit_EPI had significantly larger ADC than SS_EPI with 80.4*10-6 mm2/s.
Introduction
Distortions in the phase-encoding direction increase with larger fields-of-views in the phase-encoding direction and with longer echo spacing for diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) using echo planar imaging (EPI) technique. Conventional abdominal DWI therefore often suffers from distortion artifacts. Small field-of view echo planar imaging (Zoomit_EPI) acquires fewer k-space lines and therefore uses shorter EPI echo train length, leading to less distortions. In this study, we compared Zoomit_EPI and conventional single shot EPI (SS_EPI) for DWI with matched scan time in the evaluation of renal cancer through qualitative image quality, lesion detection, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values.Materials and Methods:
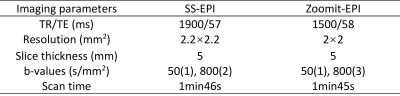
This prospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital. Thirteen patients (n=13, 5 females, age = 53 +/- 4.6 years) previously diagnosed with renal cancer were recruited, and informed written consent was obtained from all patients. All patients underwent renal MR examinations, including conventional coronal T1w, T2w, SS_EPI, and a prototype Zoomit_EPI DWI sequence, on a 3T MRI scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with 18-channel abdominal phase array coil and 32-channel Tim spinal array coil. Sequence parameters for SS_EPI and Zoomit_EPI are listed in Table 1. Two blinded radiologists with 5-7 years of experience assessed the image quality in terms of image blur, sharpness of boundaries, distortion artifacts, and overall image quality using a 5-point Likert scale. For quantitative analysis, three regions of interest (ROI) were drawn on the tumor, right, and left renal healthy tissue for the same location of SS_EPI and Zoomit_EPI, respectively. The mean ADC value of each ROI was calculated. Paired t-test, Pearson coefficient, and Bland-Altman analysis were used to assess the difference, correlation, and agreement of ADC between SS_EPI and Zoomit_EPI methods. p value <0.05 was considered statically significant.Results
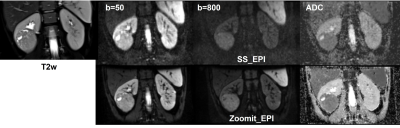
Image quality scores are shown in Table 2. Zoomit_EPI image quality scores were significantly higher than those of SS_EPI (p<0.01). Zoomit_EPI also showed less blur, increased sharpness of boundaries, and fewer distortion artifacts (Figure 1). ADC values of SS_EPI and Zoomit_EPI were highly correlated (R2=0.91, p<0.05). Bland-Altman analysis showed that ADC values of Zoomit_EPIs were higher than that of SS_EPI, with a bias of 80.4 ×10-6 s/mm2. This difference between ADC values was statistically significant as determined by paired-sample t-test (p<0.05).Discussion
Results indicate that Zoomit_EPI can significantly improve image quality compared with conventional SS_EPI. Less blur, sharper boundaries, and fewer distortions were observed from Zoomit_EPI, consistent with findings in previous studies performed in the pancreas, prostate, and kidney.1-3 In addition, because Zoomit_EPI had higher resolution and more averages compared with SS_EPI in the same scan time, DWI images with b=800 s/mm2 for Zoomit_EPI improved appearance compared with SS_EPI images.The findings of good correlation with significant bias between techniques was inconsistent with previous studies,1,2 which found no significant difference between the two methods. However, in a previous prostate cancer study using Zoomit_EPI, ADC tended to be higher in Zoomit_EPI, though without statistical significance.3 The reason for our findings may be that the ADC map of SS_EPI had less homogeneity and more regions with low ADC, meanwhile, complex averaging in Zoomit _EPI may increase the ADC value.
Conclusions
Zoomit_EPI DWI technique showed significant improvements in image quality compared to conventional SS_EPI DWI, and it may be useful for the detection of kidney lesions.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. He YL, Hausmann D, Morelli JN, et al. Renal zoomed EPI-DWI with spatially-selective radiofrequency excitation pulses in two dimensions, European Journal of Radiology. 2016; 85:1773–1777.
2. Riffel P, Michaely HJ, Morelli JN, et al. Zoomed EPI-DWI of the Pancreas Using Two-Dimensional Spatially-Selective Radiofrequency Excitation Pulses. PLoS ONE. 2014; 9(3): e89468.
3. Brendle C, Martirosian P, Schwenzer NF, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in the assessment of prostate cancer: Comparison of zoomed imaging and conventional technique. European Journal of Radiology. 2016;85:893–900.
Figures