4686
Learned Subspace Model Enables Ultrafast Neonatal Brain MR Imaging1School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, United States, 3Department Radiology, The Fifth People’s Hospital of Shanghai, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Fast imaging is essential in neonatal brain MRI. Deep learning-based methods can provide high acceleration rates but their performance is instable when limited training data are available. Subspace model-based approach could reduce the dimensionality of imaging and improve reconstruction stability. This work presents a novel method to integrate neonate-specific subspace model and model-driven deep learning, making stable and ultrafast neonatal MR imaging possible. The feasibility and potential of the proposed method have been demonstrated using in vivo data from four medical centers, producing very encouraging results. With further development, the proposed method may provide an effective tool for neonatal imaging.
Introduction
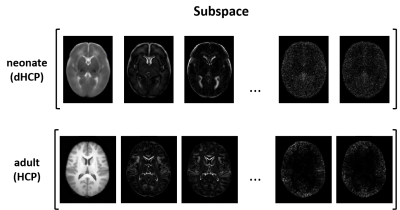
Neonatal brain MR imaging is important for the assessment of early brain development and injury [1][2]. Acquisition of high-resolution images is essential to reduce the partial volume effect but will lead to long scanning time, which increases the possibility of motion artifacts and suffers from reduced signal-to-noise ratio [3]. Therefore, fast neonatal brain MR imaging is critical, which could provide more flexibility in data acquisition to improve image resolution and contrast as well [4]. There have been several strategies to accelerate neonatal MR imaging, including parallel imaging [5], simultaneous multisection imaging [6], compressed sensing [7], and deep learning [8]. Deep learning-based methods provided additional accelerations by taking advantage of the prior image information in training data. But given the high-dimensionality of image learning, the lack of large training data might lead to instability to various sampling patterns and number of encodings [9]-[11]. Subspace modeling-based approach has shown great promise in reducing the dimensionality of imaging and improving reconstruction stability [12]-[15]. Nevertheless, the subspace features could vary considerably across different populations. As shown in Fig. 1, the spatial features of neonatal brain subspace (based on dHCP dataset [16]) are significantly different from those of adult brain subspace (based on HCP dataset [17]). This work presents a learned subspace model to adaptively combine the spatial features of neonatal brain image subspace to further accelerate neonatal MRI. The synergistic interaction of the subspace model with a deep network enables them to capture prior information effectively for reconstruction of high-quality neonatal brain images from very sparse data. The proposed method has been validated using both the dHCP dataset and testing data from four independent medical centers, yielding very encouraging results. With further development, the proposed method may provide an effective tool for neonatal brain imaging.Method
Problem formulationA key problem in neonatal brain MR imaging is to estimate an underlying MR image $$$\rho$$$ from highly undersampled k-space measurements $$$d$$$. In this work, we formulated the problem as solution of the following optimization problem with a subspace constraint:
$$\min_{\alpha,\ \rho}\frac{1}{2}||d-\Omega\mathcal{F}\rho||_2^2+||\mathcal{D}\rho||_1\ \ \ \ \ (1)\\s.t.\ \ \rho=\Phi\alpha$$
Here $$$\mathcal{F}$$$ represents Fourier transform, and $$$\Omega$$$ is a sampling operator. The subspace constraint $$$\rho=\Phi\alpha$$$ forces the desired image $$$\rho$$$ to be a linear combination of spatial basis $$$\Phi$$$ with spatial weighting coefficients $$$\alpha$$$. The spatial basis $$$\Phi$$$ capture the normal features of neonatal brain images, and the spatial coefficients $$$\alpha$$$ capture novel features of a specific neonatal data set. The subspace model significantly reduces the number of degrees-of-freedom, thus improving reconstruction accuracy. The projection onto convex sets (POCS) algorithm [18] was used to solve the above-constrained optimization problem by alternate projections between subspace, proximity and data consistency:
$$\begin{cases}\text{Subspace projection:}\ \ \ \rho_0=\Phi\alpha, \ \alpha=(\Omega\mathcal{F}\Phi)^*d\\\text{Proximity projection:}\ \ \ \rho_n=\mathcal{D}^T\text{soft}(\mathcal{D}\rho_{n-1},\ \lambda)\ \ \ \ \ (2)\\\text{Consistency projection:}\ \ \ \rho_n=\text{DC}(\rho_n, d)\\\end{cases}
$$
Learned subspace network
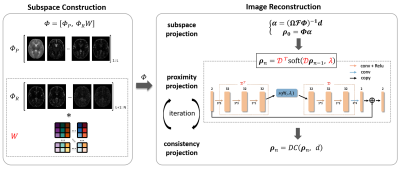
To improve computational efficiency, the optimization process was unrolled into a deep neural network, as shown in Fig. 2. The proposed method contains two components: (1) subspace construction and (2) image reconstruction, and both are learnable. The constructed subspace $$$\Phi$$$ contains a principal subspace $$$\Phi_P$$$ and a weighted residual subspace $$$\Phi_RW$$$, where the weight matrix $$$W$$$ is learned by a neural network. Then, the learned subspace was used for image reconstruction, which is unrolled from the iterative procedures in the POCS algorithm. The synergistic interaction makes the construction of the subspace to “resonate” with the network reconstruction, so that the data-adaptive subspace can be better adapted to the reconstruction of neonatal brain images.
Dataset
Our training data were obtained from the dHCP dataset [16] and 780 neonatal brain T2-weighted images from 28 to 44 weeks were used. Each image was reconstructed by an aligned SENSE method [19] with motion correction [20]. Additional data from subjects scanned at Shanghai Children’s Medical Center, Shanghai Fifth People’s Hospital, Wuhan Union Hospital, China and Washington University (HCP Young Adult) [17], USA, were used for testing.
Results and discussion
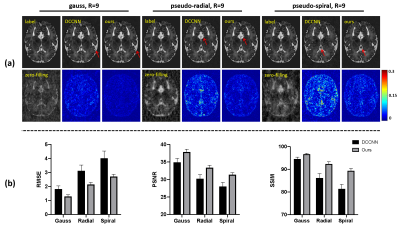
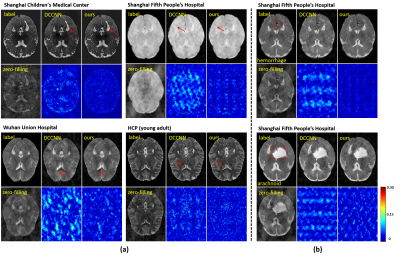
The proposed method was compared with a state-of-the-art deep learning-based method DCCNN [21]. As shown in Fig. 3, at a 9-fold acceleration, the proposed method achieved noticeably better reconstruction, both qualitatively and quantitatively. Our proposed method captured the tiny image features marked by the red arrows.To demonstrate the generalization capability of the proposed method, the trained model was tested on multi-center data, as shown in Fig. 4. Our proposed method produced reliable reconstructions from data collected from both healthy subjects (Fig. 4 (a)) and patients (Fig. 4 (b)).
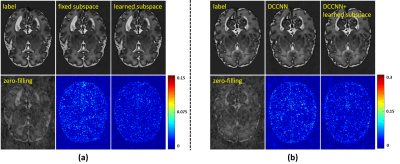
Fig. 5 (a) illustrates the effectiveness of subspace learning. Compared with a fixed (pre-learned) subspace, the proposed data-adaptive subspace produced better reconstructions with less artifacts. The learned subspace is flexible, which can be easily embedded in other deep models to improve reconstruction as shown in Fig. 5 (b).
Conclusion
This work combines subspace learning with deep learning to accelerate neonatal brain MR imaging. The effectiveness, stability and flexibility of the proposed method have been shown. With further development, the proposed method may provide an effective tool for neonatal imaging studies. Our reconstruction algorithm may prove useful for solving other image reconstruction problems as well.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Science Foundation of China (No.61671292, 81871083 and 62001293); Shanghai Jiao Tong University Scientific and Technological Innovation Funds (2019QYA12); Key Program of Multidisciplinary Cross Research Foundation of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (YG2021ZD28).References
[1]. Li, G., Wang, L., Yap, P. T., Wang, F., Wu, Z., Meng, Y., ... & Shen, D. (2019). Computational neuroanatomy of baby brains: A review. NeuroImage, 185, 906-925.
[2]. Levine, D., Barnes, P. D., Robertson, R. R., Wong, G., & Mehta, T. S. (2003). Fast MR imaging of fetal central nervous system abnormalities. Radiology, 229(1), 51-61.
[3]. Hillenbrand, C. M., & Reykowski, A. (2012). MR imaging of the newborn: a technical perspective. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Clinics, 20(1), 63-79.
[4]. Kozak, B. M., Jaimes, C., Kirsch, J., & Gee, M. S. (2020). MRI techniques to decrease imaging times in children. Radiographics, 40(2), 485-502.
[5]. Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, et al. Sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med 1999;42(5):952–62.
[6]. Larkman, D. J., Hajnal, J. V., Herlihy, A. H., Coutts, G. A., Young, I. R., & Ehnholm, G. (2001). Use of multicoil arrays for separation of signal from multiple slices simultaneously excited. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 13(2), 313-317.
[7]. Lustig, M., Donoho, D., & Pauly, J. M. (2007). Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 58(6), 1182-1195.
[8]. Wang, S., Su, Z., Ying, L., Peng, X., Zhu, S., Liang, F., ... & Liang, D. (2016, April). Accelerating magnetic resonance imaging via deep learning. In 2016 IEEE 13th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI) (pp. 514-517). IEEE.
[9]. Guan, Y., Li, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2020). A Further Analysis of Deep Instability in Image Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Sydney, Australia.
[10]. Antun V , Renna F , Poon C , et al. On instabilities of deep learning in image reconstruction and the potential costs of AI, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2020; 117(48): 30088–30095.
[11]. Knoll F , Hammernik K , Kobler E , et al. Assessment of the generalization of learned image reconstruction and the potential for transfer learning, Magn. Reson. Med., 2019; 81(1): 116–128.
[12]. Liang, Z. P. (2007, April). Spatiotemporal imagingwith partially separable functions. In 2007 4th IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging: from nano to macro (pp. 988-991). IEEE.
[13]. Lam, F., & Liang, Z. P. (2014). A subspace approach to high‐resolution spectroscopic imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 71(4), 1349-1357.
[14]. Li, Y., Lam, F., Clifford, B., & Liang, Z. P. (2017). A subspace approach to spectral quantification for MR spectroscopic imaging. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 64(10), 2486-2489.
[15]. Lam, F., Li, Y., Guo, R., Clifford, B., & Liang, Z. P. (2020). Ultrafast magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging using SPICE with learned subspaces. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 83(2), 377-390.
[16]. Makropoulos, A., Robinson, E. C., Schuh, A., Wright, R., Fitzgibbon, S., Bozek, J., ... & Rueckert, D. (2018). The developing human connectome project: A minimal processing pipeline for neonatal cortical surface reconstruction. Neuroimage, 173, 88-112.
[17]. Van Essen, D. C., Ugurbil, K., Auerbach, E., Barch, D., Behrens, T. E., Bucholz, R., ... & WU-Minn HCP Consortium. (2012). The Human Connectome Project: a data acquisition perspective. Neuroimage, 62(4), 2222-2231.
[18]. Bauschke, H. H., & Borwein, J. M. (1996). On projection algorithms for solving convex feasibility problems. SIAM review, 38(3), 367-426.
[19]. Cordero-Grande, L., Teixeira, R. P. A., Hughes, E. J., Hutter, J., Price, A. N., & Hajnal, J. V. (2016). Sensitivity encoding for aligned multishot magnetic resonance reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2(3), 266-280.
[20]. Cordero‐Grande, L., Hughes, E. J., Hutter, J., Price, A. N., & Hajnal, J. V. (2018). Three‐dimensional motion corrected sensitivity encoding reconstruction for multi‐shot multi‐slice MRI: application to neonatal brain imaging. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 79(3), 1365-1376.
[21]. J. Schlemper, J. Caballero, J.V. Hajnal, A. Price, D. Rueckert, “A Deep Cascade of Convolutional Neural Networks for Dynamic MR Image Reconstruction”, IEEE TMI, DOI: 10. 1109/TMI.2017.2760978 (2017).
Figures