4613
Evaluate myocardial microcirculation in pediatric myocarditis patients with free breathing intravoxel incoherent motion MR sequence1Department of Magnetic Resonance, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, Lanzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Xi’an, China
Synopsis
To explore the possibility of application of free breathing intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging in pediatric myocarditis patients, we utilized diaphragmatic navigation technique to detect heart rate and improved the probability of scanning success. Eight pediatric myocarditis patients and ten healthy volunteers were enrolled. The study confirmed that the IVIM imaging method with free breathing condition was acceptable and achievable. Besides, compared with healthy children, the microcirculation of myocarditis patients was impaired, and pseudo-diffusion coefficient (Dfast) and perfusion fraction (f) were significantly lower.
Introduction
Multi-b-value based diffusion weighted imaging technique is the basic conception of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) theory1. IVIM imaging can non-invasively and quantitatively assess myocardial microcirculation and water diffusion without contrast agents. Viral myocarditis is a common complication of systemic viral infection, which is normally occur in children. The clinical symptoms of viral myocarditis are varied with varying severity, and the severe cases may cause fulminant cardiac shock or even cardiac death. As a result, early diagnosis of acute myocarditis has significantly clinical importance and patients can receive standardized treatment in time. In this study, IVIM technique was used to detect microcirculation in pediatric myocarditis patients under the condition of free breathing.Material and method
Ten healthy volunteers (age range: 3months~12y) and eight pediatric myocarditis patients (age range: 4y-11y) were enrolled. All subjects were scanned using 3.0T MR (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, the netherlands) with a 16 channel phase-array cardiac coil. IVIM was performed at the free breathing by diaphragmatic navigation from Left ventricle apex to basal slices using 9 b value (0,20,50,80,100,120,200,300,500 s/mm2). The imaging parameters were as follows: FOV was set to 310×310mm, number of slice was 3, slice thickness was 8mm, total scanning time was 2 minutes. The original IVIM images were transmitted to the post-processing software Medical Imaging Interaction Toolkit (MIKT, https://www.mitk.org), and the double exponential model was used to get IVIM related parameter maps: tissue diffusivity (Dslow), pseudo-diffusion coefficient (Dfast) and f (perfusion fraction). Two senior radiologists with at least 8 years’ experience in cardiac MR diagnosis were completed IVIM parameters calculation of myocardium independently. They drew the region of interest (ROI) of myocardium manually three times to obtain the averaged Dslow, Dfast and f values, the ROI was placed at the mid-wall area. Difference of myocardial microcirculation between healthy children and myocarditis patients was analyzed by non-parametric Mann–Whitney U test. All statistical analyses were performed by using SPSS software.Results
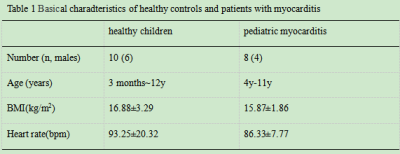
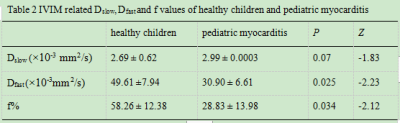
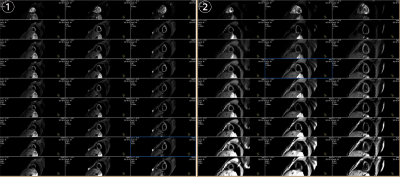
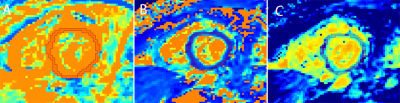
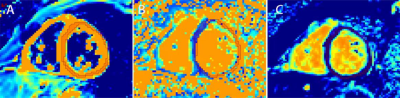
Basical characteristics of study population, as shown in Table 1. The IVIM technique is feasible to assess myocardial microcirculation in children under free respiration, the signal of myocardium shows very well, original images of was shown in Fig1. The Dfast and f values of pediatric myocarditis patients was significantly lower than that of healthy children (P <0.05), as shown in Table 2, Fig 2 and Fig 3.Disscusion
In this study, IVIM scanning was performed under free breathing, which could provide a valuable method for myocarditis patients who did not control themselves to keep the breath holding, such as infancy. Our results demonstrated that compared with health controls,microcirculation of pediatric myocarditis patients was impaired, which may be due to edema of myocardial cell. In clinical, endocardial biopsy is the gold standard for the diagnosis of acute myocarditis, but its sensitivity is extremely low, and it is an invasive method to evaluate the disease2. Echocardiography can observe cardiac structure and function, but left ventricular function of many acute myocarditis is normal in the early stage, dysfunction may occur when chronic or severe myocarditis3. Cardiac troponin is very sensitive to myocardial injury, but has no specificity for inflammation, and lack of information about the lesion site4. However, IVIM technology can non-invasively observe myocardial microcirculation with no contrast agent5, which has important clinical and diagnostic value for early detection of acute myocarditis, and can receive standardized treatment in time and improve prognosis.Conclusion
IVIM with free breathing is a promising method that can noninvasively evaluate the situation of myocardial microcirculation in children with myocarditis and can be used for early diagnosis and treatment of acute myocarditis, which has important clinical value.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Bihan D L. et al. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging[J]. Radiology, 1988, 168.1. Noel RR. Viral myocarditis [J].Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2016, 28(4):383-389.
2. Donnie Cameron, Vassilios S Vassiliou, David M Higgins, et al. Towards accurate and precise T1 and extracellular volume mapping in the myocardium: a guide to current pitfalls and their solutions [J]. MAGMA, 2018, 31(1):143-163.
3.Silvio A, Nigel M. Coagulation, protease activated receptors and viral myocarditis [J]. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 2014, 7(2):203-211.
4. Mou A, Zhang C, Li M, et al. Evaluation of myocardial microcirculation using intravoxel incoherent motion imaging[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2017, 46(6):1818-1828.
Figures