4584
Characterization of mouse cerebrovascular reactivity using task-free resting-state fMRI1Department of Ophthalmology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 2Neuroscience Institute, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States, 3Department of Radiology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States
Synopsis
The recent development of relative cerebrovascular reactivity (rCVR) mapping derived from task-free resting-state blood-oxygenation-level-dependent fMRI resolves issues of experimental complications from hypercapnic challenge or pharmacological administrations required in conventional CVR mapping. While human clinical rCVR studies have begun, there lacks rCVR characterization in healthy adult rodents before it can be applied to preclinical models of neuropathology for translational research. This study demonstrated the feasibility of rCVR mapping using resting-state fMRI at 7 Tesla in mice. The results also revealed potential rCVR lateralization in cortical regions and heterogenous vascularization along the septotemporal axis of the hippocampus.
Introduction
Cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) is the response of cerebral blood vessels to vasoactive stimuli. It closely relates to the health of the vasculature and is a key parameter for studying cerebrovascular diseases such as stroke, small vessel disease, and dementia1,18. However, conventional CVR mapping requires hypercapnic challenge2,3 or pharmacological interventions such as acetazolamide injection4 , presenting an obstacle for routine clinical and preclinical use. The recent development of measuring relative CVR (rCVR) using task-free, resting-state blood-oxygenation-level-dependent (BOLD) fMRI attempts to address these issues, with rCVR maps in close resemblance to conventional CVR maps under gas challenge5,13. While several human clinical rCVR studies5,13 have begun and several rodent models of cerebrovascular diseases are widely available9-11, rCVR characterization for rodents has been lacking, obscuring its feasibility for preclinical research. In this study, we used whole-brain resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) to both show the feasibility of rCVR mapping in rodents, and characterize rCVR in various regions of the healthy adult mice. For characterization, we compared rCVR between the left and right cortical regions to determine if CVR lateralization may be present in rodents similar to functional lateralization as suggested in a growing number of studies6,7, 12. The rCVR between the ventral and dorsal hippocampus was also compared given the vascular and functional heterogeneity along the septotemporal axis of the hippocampus8,22.Method
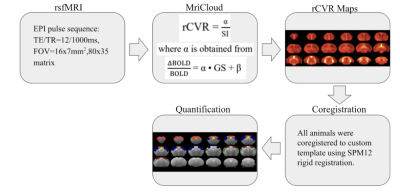
rsfMRI images were obtained from 13 male C57BL/6J mice aged 14 weeks old, using a 7-Tesla Bruker scanner and a transmit-only birdcage coil in combination with an actively decoupled receive-only cryo-surface coil. A single-shot gradient-echo echo-planar-imaging (GE-EPI) pulse sequence was used with TE/TR=12/1000ms, FOV=16x7mm2, 80x35 matrix, 30 contiguous 0.5-mm axial slices, and 600 volumes. rCVR maps were generated using MriCloud (braingps.mricloud.org/rs-cvr) followed by co-registration using SPM12 (www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/). rCVR in different cortical brain areas including the visual cortex (VC), auditory cortex (AC), somatosensory cortex (SS), motor cortex (MC) and cingulum (Cg), as well as the ventral/dorsal hippocampus (vHP/dHP) were quantified using regions-of-interest (ROIs) analysis (Figure 1). Results are compared using paired sample t-tests and presented as mean±SEM.Results
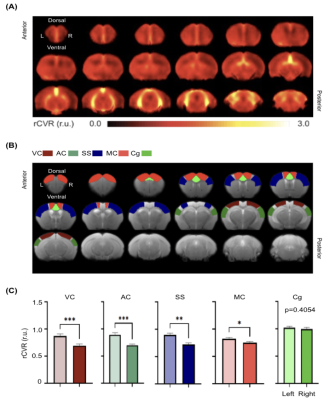
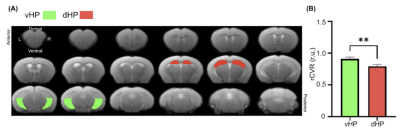
Averaged rCVR maps were shown in Figure 2. When comparing between the left and right hemispheres of the neocortex, rCVR values were significantly higher in the left hemisphere for VC (0.87±0.04 relative unit (r.u.); p<0.001), AC (0.89±0.04 r.u.; p<0.001), SS (0.90±0.03 r.u.; p<0.01), and MC (0.82±0.03 r.u.; p<0.05), except for Cg (1.02±0.03 r.u.; p=0.41) relative to the right hemisphere (VC: 0.69±0.03 r.u.; AC: 0.70±0.02 r.u.; SS: 0.72±0.03 r.u.; MC: 0.75±0.02 r.u.; Cg: 1.00±0.03 r.u.).The rCVR of the vHP and dHP was also compared to assess the vascular heterogeneity along the septotemporal axis of the hippocampus. The vHP (0.91±0.03 r.u.; p<0.01) showed a higher vHP than the dHP (0.79±0.03 r.u.; Figure 3).
Discussion
Feasibility of rodent rCVR mapping
The rCVR maps presented in this study closely resemble conventional CVR maps in rodents using hypercapnic challenges16,17, demonstrating the feasibility of task-free rodent rCVR mapping without gas challenge.Rodent rCVR Characterizations
rCVR lateralization in the neocortex
While increasing studies have suggested the presence of structural and functional lateralization in rodents6,7,12,18-20, it is unclear whether rodent CVR is lateralized. In this study, higher rCVR was observed in the left hemisphere for all sensory and motor cortical regions measured, signifying lateralization of vascular reserve in rodents5, 13. An asymmetric rCVR agrees with a previous study that demonstrates an asymmetric regional cerebral blood flow in mice21. Recent studies on structural asymmetry also exhibit an asymmetric vascular system in rodents14,15 and a larger left hemisphere than the right hemisphere in mice20. A higher rCVR uniformity in the left hemisphere could thus indicate a higher vascularization needed for the left hemisphere.Vascular heterogeneity in the hippocampus
Previous evidence in rodents suggested a higher vulnerability of the dHP to hypoxia relative to the vHP23. Our whole-brain rsfMRI study indicated a lower rCVR in the dHP relative to the vHP, suggesting a lower vascular reserve in the dHP. This in vivo rodent characterization agrees with the heterogeneous vascularization along the septotemporal axis of the hippocampus demonstrated using ex vivo photomicrography8.Conclusion
In this study, we demonstrated the feasibility to map rCVR in mice using task-free rsfMRI. The characterization of a higher rCVR in the left hemisphere of the sensory and motor cortical regions compared to the right hemisphere suggested lateralization of vascular reserve in the neocortex of adult mice, whereas the higher rCVR in the ventral hippocampus compared to the dorsal hippocampus suggested vascular heterogeneity along the septotemporal axis of the hippocampus.Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health P30-CA016087, P41-EB017183, R01-EY028125 and UF1-NS107680 (Bethesda, Maryland); BrightFocus Foundation G2019103 (Clarksburg, Maryland); Research to Prevent Blindness/Stavros Niarchos Foundation International Research Collaborators Award (New York, New York); and an unrestricted grant from Research to Prevent Blindness to NYU Langone Health Department of Ophthalmology (New York, New York).References
Haller, S., Bonati, L. H., Rick, J., Klarhöfer, M., Speck, O., Lyrer, P. A., Bilecen, D., Engelter, S. T., & Wetzel, S. G. (2008). Reduced cerebrovascular reserve at co2bold MR imaging is associated with increased risk of periinterventional ischemic lesions during carotid endarterectomy or stent placement: Preliminary results1. Radiology, 249(1), 251–258. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2491071644
Geranmayeh, F., Wise, R. J. S., Leech, R., & Murphy, K. (2015). Measuring vascular reactivity with breath-holds after stroke: A method to aid interpretation of group-level bold signal changes in longitudinal fmri studies. Human Brain Mapping, 36(5), 1755–1771. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22735
Yezhuvath, U. S., Lewis-Amezcua, K., Varghese, R., Xiao, G., & Lu, H. (2009). On the assessment of cerebrovascular reactivity using hypercapnia bold MRI. NMR in Biomedicine, 22(7), 779–786. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1392
Ma, J., Mehrkens, J. H., Holtmannspoetter, M., Linke, R., Schmid-Elsaesser, R., Steiger, H.-J., Brueckmann, H., & Bruening, R. (2007). Perfusion MRI before and after acetazolamide administration for assessment of cerebrovascular reserve capacity in patients with symptomatic internal carotid artery (ICA) occlusion: Comparison with 99mTc-ECD SPECT. Neuroradiology, 49(4), 317–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0193-x
Golestani, A. M., Wei, L. L., & Chen, J. J. (2016). Quantitative mapping of cerebrovascular reactivity using resting-state bold fmri: Validation in healthy adults. NeuroImage, 138, 147–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.05.025
Li, Q., Bian, S., Liu, B., Hong, J., Toth, M., & Sun, T. (2013). Establishing brain functional laterality in adult mice through unilateral gene manipulation in the embryonic cortex. Cell Research, 23(9), 1147–1149. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2013.106
Kim, S., Mátyás, F., Lee, S., Acsády, L., & Shin, H.-S. (2012). Lateralization of observational fear learning at the cortical but not thalamic level in mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(38), 15497–15501. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1213903109
Grivas, I., Michaloudi, H., Batzios, C., Chiotelli, M., Papatheodoropoulos, C., Kostopoulos, G., & Papadopoulos, G. C. (2003). Vascular network of the rat hippocampus is not homogeneous along the septotemporal axis. Brain Research, 971(2), 245–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(03)02475-2
Komotar, R. J., Kim, G. H., Sughrue, M. E., Otten, M. L., Rynkowski, M. A., Kellner, C. P., Hahn, D. K., Merkow, M. B., Garrett, M. C., Starke, R. M., & Connolly, E. S. (2007). Neurologic assessment of somatosensory dysfunction following an experimental rodent model of cerebral ischemia. Nature Protocols, 2(10), 2345–2347. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.359
Gartshore, G., Patterson, J., & Macrae, I. M. (1997). Influence of ischemia and reperfusion on the course of brain tissue swelling and blood–brain barrier permeability in a rodent model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. Experimental Neurology, 147(2), 353–360. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1997.6635
Boychuk, J. A., Adkins, D. A. L., & Kleim, J. A. (2010). Distributed versus focal cortical stimulation to enhance motor function and motor map plasticity in a rodent model of ischemia. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair, 25(1), 88–97. https://doi.org/10.1177/1545968310385126
Levy RB;Marquarding T;Reid AP;Pun CM;Renier N;Oviedo HV; (n.d.). Circuit asymmetries underlie functional lateralization in the mouse auditory cortex. Nature communications. Retrieved November 2, 2021, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31239458/.
Liu, P., Liu, G., Pinho, M. C., Lin, Z., Thomas, B. P., Rundle, M., Park, D. C., Huang, J., Welch, B. G., & Lu, H. (2021). Cerebrovascular reactivity mapping using resting-state bold functional MRI in healthy adults and patients with moyamoya disease. Radiology, 299(2), 419–425. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2021203568
Xiong, B., Li, A., Lou, Y., Chen, S., Long, B., Peng, J., Yang, Z., Xu, T., Yang, X., Li, X., Jiang, T., Luo, Q., & Gong, H. (2017). Precise cerebral vascular atlas in stereotaxic coordinates of Whole Mouse Brain. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2017.00128
Kuchinka, J. (2017). Morphometry and variability of the Brain Arterial Circle in chinchilla (Chinchilla Laniger, Molina). The Anatomical Record, 300(8), 1472–1480. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.23566
Long, J. A., Watts, L. T., Li, W., Shen, Q., Muir, E. R., Huang, S., Boggs, R. C., Suri, A., & Duong, T. Q. (2015). The effects of perturbed cerebral blood flow and cerebrovascular reactivity on structural MRI and behavioral readouts in mild traumatic brain injury. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 35(11), 1852–1861. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2015.143
Ono, Y., Morikawa, S., Inubushi, T., Shimizu, H., & Yoshimoto, T. (1997). T2*-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of cerebrovascular reactivity in rat reversible focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Research, 744(2), 207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(96)01079-7
Tsai, K.-J., Yang, C.-H., Lee, P.-C., Wang, W.-T., Chiu, M.-J., & Shen, C.-K. J. (2009). Asymmetric expression patterns of brain transthyretin in normal mice and a transgenic mouse model of alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience, 159(2), 638–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.12.045
Carlson, J. N., & Glick, S. D. (1989). Cerebral lateralization as a source of interindividual differences in behavior. Experientia, 45(9), 788–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01954054
Spring, S., Lerch, J. P., Wetzel, M. K., Evans, A. C., & Henkelman, R. M. (2010). Cerebral asymmetries in 12-week-old C57BL/6J mice measured by magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage, 50(2), 409–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.043
Apostolova, I., Wunder, A., Dirnagl, U., Michel, R., Stemmer, N., Lukas, M., Derlin, T., Gregor-Mamoudou, B., Goldschmidt, J., Brenner, W., & Buchert, R. (2012). Brain perfusion SPECT in the mouse: Normal pattern according to gender and age. NeuroImage, 63(4), 1807–1817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.08.038
Tanti, A., & Belzung, C. (2013). Neurogenesis along the septo-temporal axis of the hippocampus: Are depression and the action of antidepressants region-specific? Neuroscience, 252, 234–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.017
Ashton, D., Van Reempts, J., Haseldonckx, M., & Willems, R. (1989). Dorsal-ventral gradient in vulnerability of CA1 hippocampus to ischemia: A combined histological and electrophysiological study. Brain Research, 487(2), 368–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(89)90842-1
Figures