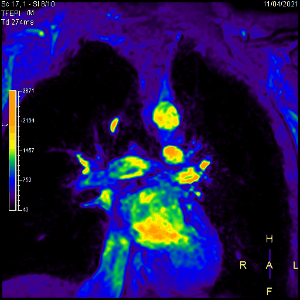
4547
High-resolution flow-sensitive CINE imaging visualizing valve, chamber, and regurgitant flow1Department of Radiological Services, Tokyo Woman's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 2Department of Diagnostic imaging & Nuclear Medicine, Tokyo Woman's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan
Synopsis
Cardiac bSSFP CINE imaging is widely used in clinical practice for function and morphological evaluation, but we often experienced situations where it is difficult to visually evaluate blood flow and valves. TFEPI is a flow-sensitive imaging method and can be expected to evaluate blood flow and valves. In this study, we investigate the clinical usefulness of Flow sensitive CINE Imaging using TFEPI.
Introduction
Congenital heart disease patients with valvular disease and healthy volunteers underwent conventional cine and a flowCardiac balanced SSFP (bSSFP) CINE imaging is commonly used as a standard method for function and morphological evaluation. bSSFP shows excellent results in functional evaluation, but have yet visualize heart valve and abnormal flow due to valve stenosis or regurgitation. 2D flow TFEPI based on modified Lock-Locker technique is a screening tool of valve regurgitation, the phase variance was emphasized, and the regurgitant flow was successfully visualized. It is feasible and useful for pulmonary regurgitation evaluation as a method (1). We have developed a flow sensitive CINE imaging using Compressed SENSE TFEPI (CS-TFEPI) with even higher temporal resolution and report the clinical usefulness.Methods
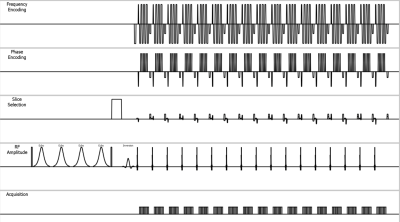
Congenital heart disease patients with valvular disease and healthy volunteers underwent conventional cine and a flow-sensitive cine imaging on a 3.0T MR system(Ingenia, Philips Healthcare). Flow sensitive CINE imaging with breath-hold and retrospective cardiac gating, FOV=250mm, pixel size=2.0*2.0mm, slice thickness=8mm,CS-SENSE=1.9,EPI factor=3, TFE factor=2,flip angle=15,number of heart phase=100,TR=5.5ms,TE=2.3ms,NSA=1, and acquisition time=10~12sec (Fig. 1). bSSFP CINE imaging with breath-hold and retrospective cardiac gating, FOV=250mm, pixel size=2.0*2.0mm,slice thickness=8mm, CS-SENSE=2.8,TFE factor=4,flip angle=50,number of heart phase=100,TR=2.8ms,TE=1.39ms,NSA=1, and acquisition time=10~12sec.Results & Discussion
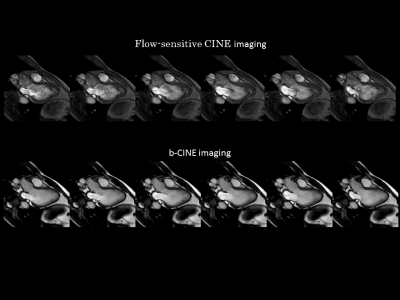
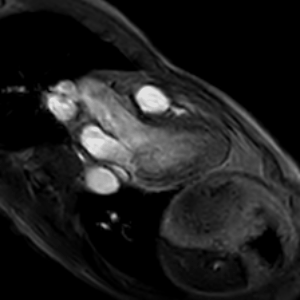
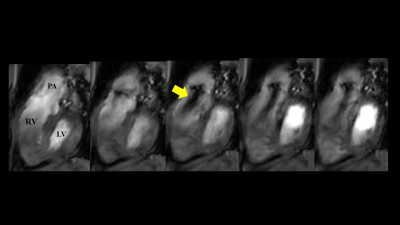
Figure 2 shows the representative images of conventional bSSFP CINE and Flow-sensitive CINE imaging. In bSSFP CINE, the blood signal becomes uniform, which makes it difficult to evaluate the flow. Flow-sensitive CINE, on the other hand, made it possible to observe the flow of blood flowing into and out of the left ventricle. In the Flow-sensitive CINE with 3ch view, it was possible to observe the movement of the valve as well as to depict the flow. By increasing the temporal resolution, it was possible to grasp the hemodynamics in the left chamber (Fig. 3). In the Flow-sensitive CINE imaging clearly show pulmonary regurgitation in the right ventricular outflow tract, which usually has many artifacts on conventional cine images due to postoperative changes (Fig. 4). It is also possible to observe the flow of left and right PA (Fig. 5).Conclusion
Flow-sensitive CINE imaging using TFEPI could visualize flow and valve movement. It is useful for structural heart disease, and is also excellent in evaluating valvular disease after repair of congenital heart disease. Being able to observe blood flow, which was not so visible with conventional bSSFP CINE, is expected to provide new images for various heart diseases.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
(1)Gulsin GS, Singh A, McCann GP. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in the evaluation of heart valve disease. BMC Med Imag 2017 Dec 29;17(1):67
(2)Yumi shiina,et al. Semi-quantification of pulmonary regurgitation in congenital heart disease using 2D flow magnetic resonance imaging at 3.0 T with modified Look-Locker sequence.International Journal of Cardiology Congenital Heart Disease 4 (2021)
(3)Zoghbi WA, Adams D, Bonow RO, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, Grayburn PA, Hahn RT, Han Y, Hung J, Lang RM, Little SH, Shah DJ, Shernan S, Thavendiranathan P, Thomas JD, Weissman NJ. Recommendations for noninvasive evaluation of native valvular regurgitation: a report from the American society of echocardiography developed in collaboration with the society for cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2017 Apr;30(4):303–71.
Figures