4524
Monitoring mild cognitive impairment of workers exposed to occupational aluminum based on quantitative susceptibility mapping1Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
Synopsis
In this work, we presented a study which investigated the diagnostic value of quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) of occupational aluminum (Al) workers, we found that QSM might be a reliable neuroimaging marker for the diagnosis of MCI.
INTRODUCTION
Early detection of mildcognitive impairment(MCI) will gain more time to take individualized symptomatic treatment, prevent MCI from progressing to Alzheimer’s disease(AD).Reports have shown Al has neurotoxicity and it is a potential risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases including MCI and AD. Therefore, long-term exposure to Al will be harmful to cognitive function of workers and cause the occurrence of MCI. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) is a novel MRI postprocessing technique developed on the basis of SWI, which allows quantification of the spatial distribution of tissue magnetic susceptibility in vivo. Recently, only a few studys related to applying QSM to study MCI and there are inconsisitent results. Current research on QSM in diagnosing MCI of occupational Al workers is even rarer. Therefore, this study aims to explore the diagnostic value of QSM in MCI of occupational Al workers, and analyze the correlation between QSM values, MoCA scores and plasma Al concentrantion, providing new ideas for early determination of MCI and assessment of the severity of cognitive decline.METHODS
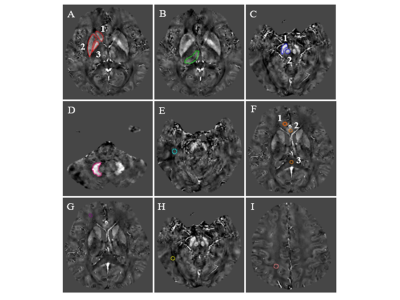
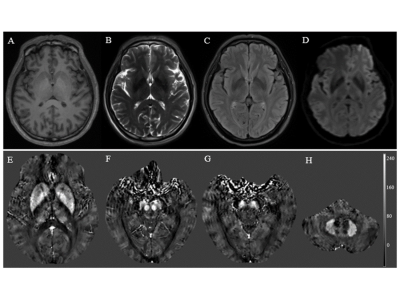
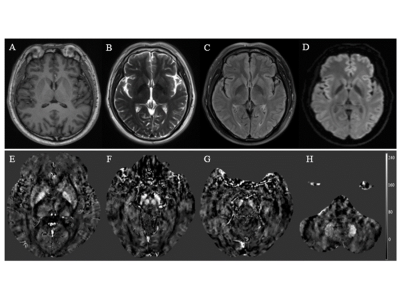
The basic data of 53 workers in an Al factory were collected and they were divided into MCI group and normal control (NC) group by Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scores. All of them were tested for plasma Al concentration MRI scan. The QSM values of many areas in brain were delineated and measured. Two independent sample t-tests or non-parametric test were used to compare the parameter values between groups. Spearman correlation analysis was performed between QSM values, MoCA scores and plasma Al concentration. The receiver operating characteristic curve and z test was performed to assess diagnostic efficacy and the best parameter value.RESULTS
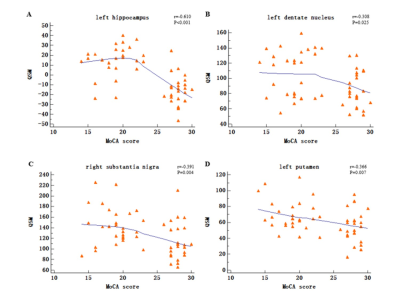
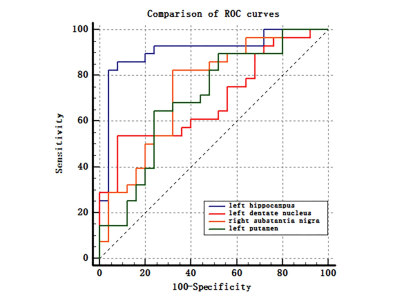
The prevalence rate of MCI in retired Al potroom workers (18.2%) was three times greater than NC group (5.7%). Plasma Al concentration of MCI group was higher than that of NC group (P=0.057). QSM values of left hippocampus, left dentate nucleus, right substantia nigra and left putamen in MCI group were higher than that of NC group (P<0.05), and left hippocampus had the best diagnostic efficacy. QSM values were negatively correlated with MoCA scores. No correlation was found between QSM values and plasma Al concentration (P>0.05).DISCUSSION
Occupational Al workers represent a special group with high risk of progressing cognitive decline. Accurate and timely intervention are the key to prevent the progression of MCI.The present study showed left hippocampus had the best diagnostic efficacy compared with left dentate nucleus, right substantia nigra, and left putamen. Previous study showed that cognitive functions of retired Al workers declined after prolonged exposure to Al. The present study found that QSM values were negatively correlated with MocA score, it can be seen that with the impairment of cognitive function, the QSM values of MCI patients gradually increases. Moreover, the magnetic susceptibility value seems to clarify the severity of cognitive function impairment, so it is speculated that the QSM value of hippocampus may be a new imaging marker for evaluating the cognitive function of occupational workers.
This study also found that QSM values of hippocampus, dentate nucleus, and putamen were slightly prominent on the left side, while substantia nigra showed more obvious changes on the right side, indicating that the changes of magnetic susceptibility of bilateral hemispheres are not necessarily simultaneous. Other studies have also obtained the same results. As we all know, individuals have a dominant hemisphere, and the thinking activity and metabolism of dominant hemisphere are significantly greater than that of the other side. When the metabolic rate increases, the distribution of magnetic substances may be affected, resulting in the asymmetry of susceptibility values of bilateral hemispheres.
The plasma Al concentration of MCI group was higher than that of NC, and the P value has a clear tendency to significance (P=0.057), and there was no correlation between QSM values and plasma Al concentration. This is different from the results of previous studies. These indicate that the differences of individual variations such as Al intake and metabolism levels can cause different results. Although Al has neurotoxicity, for MCI workers who had been exposed to Al for a long time, the pathological mechanism seems not be related to plasma Al concentration and Al deposition in brain tissue. The changes of brain tissue of MCI patients are still between normal aging and AD, the pathological changes are so slight that it is difficult to identify clinically. Furthermore, the sample size of this study is relatively small, and plasma Al concentration of the sample fluctuates widely, which may affect the results of the study.The QSM value measured in present research is caused by Al overload or iron overload or the result of the combination of two metal, no definite conclusion could be drawn, the detailed mechanism remains to be further explored.
CONCLUSION
QSM might be a reliable neuroimaging marker for the diagnosis of MCI and could assess the severity of MCI. The left hippocampus showed the best diagnostic efficacy. The plasma Al concentration of MCI group was higher than that of NC, the correlation between QSM parameters and plasma Al concentration was not found, the detailed damage mechanism remains to be further explored.Acknowledgements
Acknowledgment
The authors want to thank the Shanxi Medical University, participants who took part in the study and data collection.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (81771824 and 81971593 to Hui Zhang; 81701681 and 82071893 to Yan Tan; 81971592 to Xiao-chun Wang; the Precision Medicine Key Innovation Team Project (YT1601 to Hui Zhang); the Youth Innovation Fund (YC1426 to Yan Tan); Fund Program for the Scientific Activities of Selected Returned Overseas Professionals in Shanxi Province (20200003 to Yan Tan); the Youth Project of Applied Basic Research Project of Shanxi Province (201801D221403 to Guoqiang Yang); Science and Technology Innovation Project of University in Shanxi Province (2019L0440 to Guoqiang Yang).
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics and Human Committees of Shanxi Medical University.
Consent to participate
All participants voluntarily participated and signed an informed consent form.
Consent for publication
All authors provide consent for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Availability of data and material
The data for this study are not publicly available because the First Clinical Medical Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, the center from which the data were collected, does not agree to make the data publicly accessible. Further inquiry about data sharing maybe directed to Prof. Yan Tan, tanyan123456@sina.com.
References
Figures