4326
Feasibility of 3D breath hold MRCP: Prospective Comparison With parallel imaging technique and compressed sensing method
Zhiyong Chen1, Yunjing Xue1, Bin Sun1, and Yang Song2
1Radiology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers Ltd, Shanghai, China, Shanghai, China
1Radiology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers Ltd, Shanghai, China, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
The modified 3D-BH-PI-MRCP technique allowing direct exciting the area of interest, could not only decrease the slice number but also could eliminate folding artifacts.
Objectives
Objectives: the purpose of the present study was to evaluate the clinical feasibility of the modified 3D breath-hold MRCP with parallel imaging (3D-BH-PI-MRCP) using a spatially selective radiofrequency (RF) excitation pulse in patients with suspected pancreaticobiliary diseases. Moreover, we also compared its image quality with those of the original 3D-BH-PI-MRCP with a nonselective exciting pulse and the 3D breath hold compressed sensing MRCP (3D-BH-CS-MRCP).Methods
Methods: Between January 2021and July 2021, 106 patients prospectively underwent modified 3D-BH-PI-MRCP, original 3D-BH-PI-MRCP and 3D-BH-CS-MRCP at 3T in this study. The Friedman test was performed to compare the contrast, signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR), and contrast-noise-ratio (CNR), overall image quality, and duct visualization among the three protocols.Results
Results: The contrast ratio, SNR and CNR of the CBD differed significantly among the three sequences (P<0.001). Compared with the 3D-BH-CS-MRCP protocol, the overall imaging quality of the two 3D-BH-PI-MRCP was higher but not significantly different. The scores for the anterior and posterior branches visualization were significantly higher in the original 3D-BH-PI-MRCP compared to the 3D-BH-CS-MRCP, but were no significant differences between the modified 3D-BH-PI-MRCP and the 3D-BH-CS-MRCP.Conclusions
Conclusions: The modified 3D-BH-PI-MRCP with a spatially selective radiofrequency (RF) excitation pulse could provide comparable image quality to the original 3D-BH-PI-MRCP and the 3D-BH-CS-MRCP during a single breath hold (22 seconds), and showed improved SNR and superior visualization of the pancreaticobiliary tree. Clinical Impact: The modified 3D-BH-PI-MRCP technique allowing direct exciting the area of interest, could not only decrease the slice number but also could eliminate folding artifacts.Acknowledgements
The authors thank the members of Magnetic Resonance team at Fujian Medical University Union Hospital and Siemens Healthineers for technical support.References
1. Cai, L.; Yeh, B.M.;Westphalen, A.C.; Roberts, J.;Wang, Z.J. 3D T2-weighted and Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced 3D T1-weighted MR cholangiography for evaluation of biliary anatomy in living liver donors. Abdom. Radiol. 2016, 42, 842–850. 2. Nakaura, T.; Kidoh, M.; Maruyama, N.; Kawahara, T.; Namimoto, T.; Sakai, Y.; Harada, K.; Yamashita, Y. Usefulness of the SPACE pulse sequence at 1.5T MR cholangiography: Comparison of image quality and image acquisition time with conventional 3D-TSE sequence. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 1014–1019. 3. Zhang J, Israel GM, Hecht EM, et al. Isotropic 3D T2-weighted MR cholangiopancreatography with parallel imaging: feasibility study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2006;187:1564–1570. 4. Asbach P, Dewey M, Klessen C, et al. Respiratory-triggered MRCP applying parallel acquisition techniques. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006; 24:1095–1100. 5. Masui T, Katayama M, Kobayashi S, et al. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: comparison of respiratory-triggered three dimensional fast-recovery fast spin-echo with parallel imaging technique and breath-hold half-Fourier two-dimensional single-shot fast spin-echo technique. Radiat Med 2006;24:202–209. 6. Nandalur KR, Hussain HK, Weadock WJ, et al. Possible biliary disease: diagnostic performance of high-spatial-resolution isotropic 3D T2-weighted MRCP. Radiology. 2008; 249:883–890. 7. Chen Z, Sun B, Duan Q, et al, Three-dimensional breath-hold MRCP using SPACE pulse sequence at 3 T: comparison with conventional navigator-triggered technique, AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019;213(6):1247-1252. 8. Zhu L, Xue H, Sun Z et al. Modified breath-hold compressed-sensing 3D MR cholangiopancreatography with a small field-of-view and high resolution acquisition: clinical feasibility in biliary and pancreatic disorders. J Magn Reson Imaging 2018;48:1389–1399 9. Mannes I, Dallongeville A, Badat N, Beaussier H, Chatellier G, Zins M. Breath-hold compressed-sensing 3D MR cholangiopancreatography compared to free-breathing 3D MR cholangiopancreatography: prospective study of image quality and diagnostic performance in pancreatic disorders. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2020;45:1082–1091. 10. Morikatsu Yoshida, Takeshi Nakaura, Taihei Inoue, et al., Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography with GRASE sequence at 3.0T: does it improve image quality and acquisition time as compared with 3D TSE, Eur. Radiol2018; 28:2436–2443. 11. Seo N, Park MS, Han K, et al. Feasibility of 3D navigator-triggered magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography with combined parallel imaging and compressed sensing reconstruction at 3 T. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;46:1289–1297. 12. Zhu L, Wu X, Sun Z, et al. Compressed-sensing accelerated 3-dimensional magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: application in suspected pancreatic diseases. Invest Radiol. 2018;53:150–157. 13. Yoon JH, Lee SM, Kang HJ, et al. Clinical feasibility of 3-dimensional magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography using compressed sensing: comparison of image quality and diagnostic performance. Invest Radiol. 2017;52:612–619. 14. Yokoyama K, Nakaura T, Iyama Y et al. Usefulness of 3D hybrid profile order technique with 3T magnetic resonance cholangiography: comparison of image quality and acquisition time. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;44:1346–1353. 15. Nam JG, Lee JM, Kang HJ et al. GRASE Revisited: breath-hold three-dimensional (3D) magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography using a Gradient and Spin Echo (GRASE) technique at 3 T. Eur Radiol. 2018;28:3721-8. 16. Ryo Itatani, Tomohiro Namimoto, Shinichiro Kusunoki et al. Usefulness of the short-echo time cube sequence at 3-T magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: prospective comparison with the conventional 3-dimensional fast spin-echo sequence. J Comput Assist Tomogr. Jul-Aug 2016;40(4):551-6. 17. Yoen H, Lee JM, Lee SM et al. Comparisons between image quality and diagnostic performance of 2D- and breath-hold 3D magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography at 3T. Eur Radiol 2021 Apr 21.doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07968-w. 18. He M, Xu J, Sun Z, Wang S, et al. Comparison and evaluation of the efficacy of compressed SENSE (CS) and gradient- and spin-echo (GRASE) in breath-hold (BH) magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Mar;51(3):824-832. 19. Chen Z, Sun B, Xue Y, et al. Comparing compressed sensing breath-hold 3D MR cholangiopancreatography with two parallel imaging MRCP strategies in main pancreatic duct and common bile duct. Eur J Radiol. 2021 Sep;142:109833.Figures
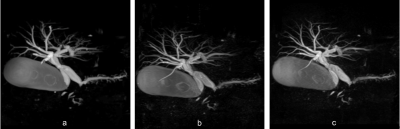
The mean SNR, Contrast ratio and CNR of
common bile duct (CBD) for 3D-BH-CS-MRCP (a) were 21.85, 0.98, 30.69; for
original 3D-BH-PI-MRCP (b) were 6.62, 0.92, 9.16; modified 3D-BH-PI-MRCP (c)
were 14.0, 0.91, 19.1, respectively. Maximum intensity projection images of the
three breath-hold MRCPs showed dilation of pancreaticobiliary tree.
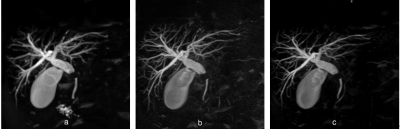
Compared with 3D-BH-CS-MRCP(a), original
3D-BH-PI-MRCP (b) and modified 3D-BH-PI-MRCP (c) revealed intrahepatic ductal
with better ductal visibility and main pancreatic duct with similar image
quality.
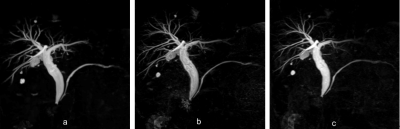
Original 3D-BH-PI-MRCP (b) exhibited
slightly higher image sharpness of the anterior branches, posterior branches,
segment 2 and 3 branches of intrahepatic bile duct than modified 3D-BH-PI-MRCP
(c) although the results were not significant, and significantly superior than
3D-BH-CS-MRCP(a).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2022/4326