4324
Banding artifacts reduction for brachial plexus (BP) imaging Using RF phase cycling balanced FFE technique combined with compressed SENSE1Department of Radiology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Banding artifacts are frequently observed in brachial plexus imaging, particularly within the spinal canal, with the balanced FFE sequence (b-FFE) at 3.0T due to increased influence of higher magnetic field inhomogeneity compared with clinical 1.5T. In this work we propose using a RF phase cycling technique with b-FFE (namely b-FFE-XD) to reduce the banding artifacts in clinical. This design RF phase limits the intravoxel dephasing of scan object voxels, therefore the artifacts caused by field inhomogeneity decrease. Meanwhile, the compressed SENSE technique was adopted to reduce the scan time. Results demonstrated successful removal of banding artifacts with the proposed technique.
Synopsis
Banding artifacts are frequently observed in brachial plexus (BP) imaging, particularly within the spinal canal, with the balanced FFE sequence (b-FFE) at 3.0T due to increased influence of higher magnetic field inhomogeneity compared with clinical 1.5T. In this work we propose using a RF phase cycling technique with b-FFE (namely b-FFE-XD) to reduce the banding artifacts in clinical. This design RF phase limits the intravoxel dephasing of scan object voxels, therefore the artifacts caused by field inhomogeneity decrease than that of b-FFE. Meanwhile, the compressed SENSE technique was adopted to reduce the scan time. Results demonstrated successful removal of banding artifacts with the proposed technique.Summary of main findings
The combination of b-FFE-XD with compressed SENSE techniques can effectively reduce banding artifacts in BP imaging at clinical 3T MR scanners without extending scan time.Introduction
It remains clinically challenging to diagnose disfunctions in brachial plexus (BP), particularly within spinal canal, due to its complex anatomy, which provides sensory and motor innervation to the ipsilateral shoulder, chest, and hand [1-2]. Despite the use of balanced fast field echo (b-FFE) technique, this sequence is prone to magnetic field inhomogeneity and is frequently disturbed by banding artifacts with increased severity at 3.0T. This study proposed a RF phase-cycling technique as an addition to the conventional b-FFE sequence (b-FFE-XD hereafter) to suppress the potential banding artifacts in brachial plexus imaging. In addition, compressed SENSE was implemented in our study to reduce imaging time.Method
Ten healthy volunteers (4 women, and 6 men, mean age, 53.30±8.73 years; age range, 31-64 years) underwent B-FFE-XD and B-FFE scans (Coronal orientation) at 3.0T (Ingenia Elition, Philips healthcare, Best, the Netherlands) on the brachial plexus with a body coil for RF transmitting and an anterior coil for signal receiving. The detailed acquisition parameters for both sequences were kept the same, listed in Table1 as below, except that a RF phase cycling scheme ([0,180+1*X, 2*X, 180+3*X,4*X,…], where X=n*360/NSA, and n is the nth average) was applied to the excitation pulse for b-FFE-XD sequence. Images were evaluated independently by two radiologists (>3 years radiology experience) in terms of overall image quality, banding artifact suppression, and diagnostic certainty using a 5-point scale criteria (5 for the best result, the scoring system was listed in Table2). Reduction factor of compressed SENSE was set as 1.5 to accelerate the scan speed. Consistency of the evaluation results between the two observers were assessed using intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) in SPSS (IBM). If the consistency was good, the scores would be averaged, then performed the subsequent analysis. The scores of the two sequences were compared using a Wilcoxon signed-rank test with a significance threshold of P < 0.05.Results
Effective banding artifact suppression without prolonged scan time was achieved by B-FFE-XD combined with compressed SENSE , representative images shown in Figure 1. Good agreement was achieved between the scoring of the two observers, and the ICCs of banding reduction and overall imaging quality scores were 0.786 ad 0738 (both P<0.001), respectively. The scores on ‘black band artifact’ and on ‘overall image quality’ were both significantly higher of b-FFE-XD than that of b-FFE (4.75±0.55 v.s. 3.10±0.64, 4.30±0.66 v.s. 4.10±0.79, respectively, both P<0.05), as shown in Table3.Discussion and Conclusion
Our results demonstrated the promising clinical application of the proposed RF phase cycling scheme for brachial plexus imaging with compressed SENSE, which yielded improved image quality and reduced banding artifacts compared to the conventional b-FFE technique without extension of scan time.Acknowledgements
NoReferences
[1] Arvind Vijayasarathi, algun H. Chokshi. MRI of the brachial plexus: A practical review. Applied Radiology. 2016; 9-18.
[2] Alberto Tagliafico, Giulia Succio, etc. MR imaging of the brachial plexus: comparison between 1.5-T and 3-T MR imaging: preliminary experience. Skeletal Radiology. 2011;40:717-724.
Figures
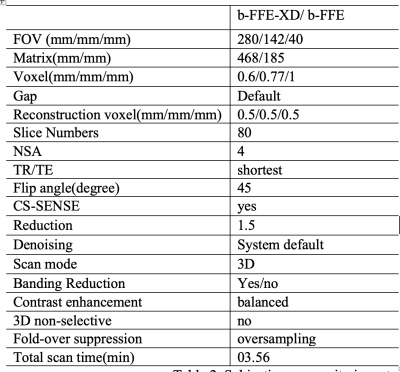
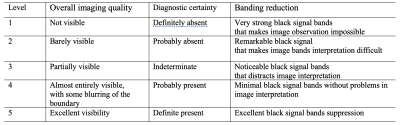

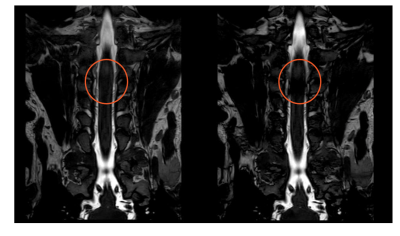
Figure 1.A healthy volunteer, 31-year-old male. Banding artifacts were indicated in the red circles of BP imaging, which showed less black banding artifacts in Left image than that of Right.
Left: B-FFE-XD image of the BP within spinal canal in coronal direction.
Right: B-FFE image of the BP within spinal canal in coronal direction