4319
A comparison study of novel and conventional diffusion weighted imaging techniques in subjective and objective evaluation of the pancreas1Radiology, Xiangya Hospital Central South University, Changsha, China, 2GE heathcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Based on field-of-view optimized and constrained undistorted single shot (FOCUS) combined with multiplexed sensitivity-encoding (MUSE) techinique, a new diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequence was developed in our study (named FOCUS MUSE-DWI). Our aim is to assess FOCUS MUSE-DWI’ reliability with comparison to single-shot DWI (ss-DWI), FOCUS-DWI and MUSE-DWI with the evaluation of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) repeatability, surrogate signal-to-noise ratio (sSNR) and image quality. FOCUS MUSE-DWI can provide sufficient sSNR and excellent image quality, best ADC repeatability in above four DWIs. It suggests that FOCUS MUSE-DWI is a reliability technique and should be recommended for the clinical application of pancrentic DWI.
Synopsis
Based on field-of-view optimized and constrained undistorted single shot (FOCUS) combined with multiplexed sensitivity-encoding (MUSE) techinique, a new diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequence was developed to delineate panrease in our study (named FOCUS MUSE-DWI). Our aim is to assess FOCUS MUSE-DWI’ reliability with comparison to single-shot DWI (ss-DWI), FOCUS-DWI and MUSE-DWI with the evaluation of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) repeatability, surrogate signal-to-noise ratio (sSNR) and image quality. FOCUS MUSE-DWI can provide sufficient sSNR and excellent image quality, best ADC repeatability in above four DWIs. It suggests that FOCUS MUSE-DWI is a reliability technique and should be recommended for the clinical application of pancrentic DWI.Introduction and Purpose
DWI is an essential MRI sequence in diagnostic pancrease imaging. It is non-invasive and easy to perform without the need for contrast administration. In the clinical utility of DWI, ADC is a vital quantitative imaging parameter and key therapeutic biomarker for differentiating benign from malignant lesions and predicting therapeutic response, which can be affected by many factors, such as sSNR and artifacts from physiologic motion (breathing and gastrointestinal peristalsis). Thus, the reliability of ADC measurements is essential to the assessment of treatment effect on those patients with pancrease disease. This study aimed to compare the reliability of FOCUS MUSE-DWI with ss-DWI, FOCUS-DWI and MUSE-DWI in clinical utility via systematically estimating the repeatability of ADC measurements, sSNR and image quality.Methods
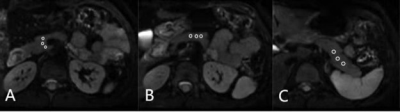
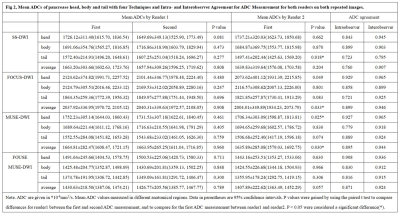
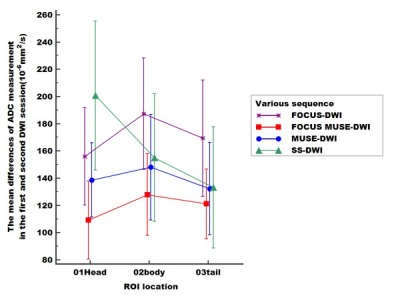
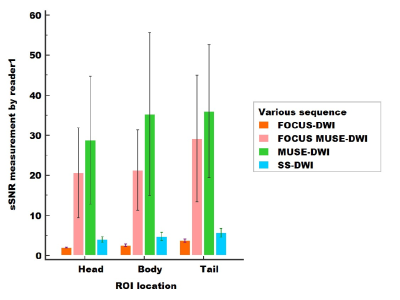
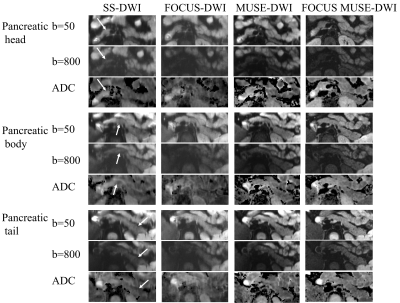
This prospective study was approved by our institutional review board-approved. Pancrentic DWIs ( b = 50, 800 s/mm2 ) were performed in 33 healthy volunteers (13 males and 20 females, 23.8±1.6 years old) on 3.0 T MRI (Signa Premier, GE Healthcare, USA) using ss-DWI, FOCUS-DWI, MUSE-DWI and FOCUS MUSE-DWI. The scan parameters were kept the same as much as possible in four DWIs and all DWI sequences were scanned twice with an interval of 10 minutes. ADC and sSNR were measured with three nonoverlapping approximately 16-mm² circular regions of interest (ROI)1 in three anatomic locations of pancrease (head, body and tail) (Fig 1). Image quality (4-point scale for each of severity of artifacts, sharpness of boundaries, interslice signal homogeneity and overall image quality)2 was also assessed. The sequence with the optimal clinical utility was determined by systematically comparing the ADC repeatability, sSNR and image quality. Individual reliability and inter-rater repeatability of ADC values were compared using a paired t-test or non-parametric wilcoxon signed rank depending on data normality and analyzed with intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). An ICC over 0.80 represents a good agreement. To visual display for ADC repeatability, the Bland-Altman method was used to compare the 95 % confidence interval (limits of agreement [LOAs]) and the mean absolute difference in ADC values between the first and second DWI scans. All sSNRs were compared using the Friedman test. Differences were considered significant when P values are less than 0.05.Results
Among the four sequences, FOCUS MUSE-DWI had the most reliable intra-observer agreement (intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC): 0.816−0.918; all P > 0.05) and interobserver agreement (ICC: 0.912−0.936; all p > 0.05) (Fig 2). ADC value of FOCUS MUSE-DWI had the best repeatability in the three anatomy locations (mean ADC absolute differences: 109.07–127.82 ×10 −6 mm 2 /s, limits of agreement (LOA): 25.57- 29.04 ×10 −6 mm 2 /s) (Fig 3). Also, FOCUS MUSE-DWI had the highest sSNR (Reader 1: 20.58 ± 31.67 (pancrease head), 21.25 ± 28.36 (pancrease body), 29.19 ± 44.53 (pancrease tail); Reader 2: 21.01 ± 32.06 (pancrease head), 21.15 ± 28.68 (pancrease body), 30.64 ± 48.17 (pancrease tail)) in three representative sections except for MUSE-DWI (Fig 4). Furthermore, FOCUS MUSE-DWI had a better image quality than ss-DWI and MUSE-DWI (P < 0.05) and similar image quality with FOCUS-DWI in the severity of artifacts, sharpness of boundaries, interslice signal homogeneity and overall image quality (Fig 5).Discussion and conclusion
Our study showed FOCUS MUSE-DWI possesses the better reproducibility for ADC values than the others on 3.0 T MRI. In our study, FOCUS MUSE-DWI gained a better image quality than ss-DWI and MUSE-DWI (P < 0.05) and had similar image quality to FOCUS DWI. FOCUS technique can reduce the influence of gastrointestinal peristalsis beyond the scanning field of vision on the image and improve the image quality of pancreas by reducing FOV in the phase direction. MUSE technique can tailor matrix with two to three segments in phase direction without additional navigator echo and achieve high spatial resolution and high SNR. In addition, FOCUS MUSE-DWI, besides MUSE-DWI, had the highest sSNR in three representative locations of pancrease. Overall, FOCUS MUSE-DWI can potentially be a reliable DWI technique in clinical diagnosis of pancrease.Acknowledgements
Funding: The work was supported by the Hunan Science and Technology Department Plan Project (grant number 2018XK2304), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 82071895) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant number: 2019M652807, Beijing, China).References
1, Xiao-Hua Ye, Jia-Yin Gao, Zheng-Han Yang et,al. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Reproducibility of the Pancreas Measured at Different MR Scanners Using Diffusion-Weighted Imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014 Dec;40(6):1375-1381.
2. Chao Ma, Yan-jun Li, Chun-shu Pan, et.al. High resolution diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas using reduced field of view single-shot echo-planar imaging at 3 T. Magnetic Resonance Imaging 32 (2014) 125–131.
Figures