4277
Intravoxel incoherent motion imaging for the differentiating early breast adenosis from sclerosing adenosis1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, daLian, China, 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, dalian, China, 3philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Sclerosing adenosis (SA) of the breast is the late development stage of breast adenosis which is difficult to diagnose. Because its imaging manifestations are similar to malignant lesions of the breast, which often needs pathological diagnosis. Intravoxel incoherent motion(IVIM ) imaging is an MR method to separate diffusion and perfusion effects by fitting a double exponential model of signal attenuation and can accurately display the diffusion movement of water molecules. This study confirmed that some parameters of IVIM can be used in the identification of early breast adenosis and SA. Therefore, IVIM is of great value in the diagnosis of breast adenosis.
Introduction
Studies have shown that the existence of sclerosing adenosis (SA) can increase the risk of cancer, some radiologist have misdiagnosis it as precancerous lesions (1, 2). it is difficult to diagnose because its imaging manifestations are similar to breast malignant diseases.Therefore, it is particularly important to early diagnose and distinguish it from breast adenosis. MRI is a non-invasive, well-differentiated, and radiation-free imaging technology of examination, which can effectively and accurately evaluate the blood perfusion of breast tumor tissue, and it has a unique advantage in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast tumors (3). Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) is a non-injection MRI technology, which can accurately display the diffusion of water molecules and microcirculation perfusion information of lesions, and further display the microscopic information of lesions. At present, the research on quantitative parameters of IVIM mainly focuses on the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions (1, 4). This study will explore the diagnostic value of IVIM quantitative parameters in breast adenosis.METHODS
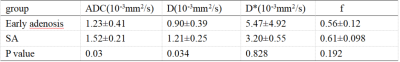
Twenty-five patients with breast adenosis(the age range was 27-61 years)were included in the study. All patients were scanned using a 3.0 T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, the Netherlands) with a seven-channel bilateral phased-array breast coil. IVIM was undertaken with 19 b-values(0, 20, 30, 50, 80, 100, 120,150,180,200, 300, 500, 800, 1000, 1200, 1500, 1800, 2000, 2500s/mm2). Based on the histopathology results, patients were divided into group 1 with early adenosis (n=13) and group 2 with SA (n=12). IVIM parameters such as Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), true diffusion coefficient (D), pseudo-diffusion coefficient (D*), perfusion fraction (f ), were calculated. Data were compared using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test when lacking a normal distribution. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Using pathological results of breast lesions as the gold standard, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of ADC, D, D∗, and f value when differentiating early adenosis and SA lesions.RESULTS
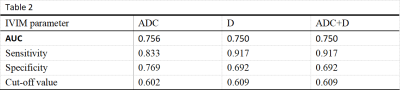
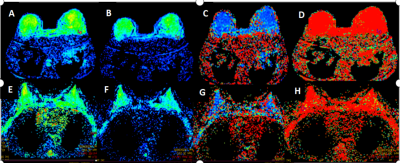
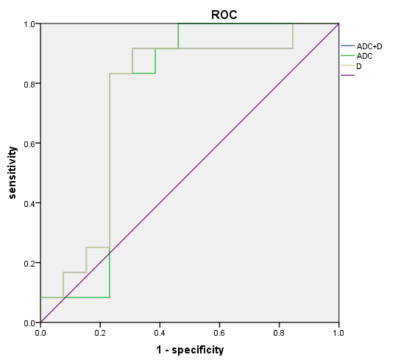
In this study, 25 patients with breast adenosis were analyzed retrospectively. Two experienced imaging doctors outlined the lesions and obtained the IVIM parameter values (ADC, D, D *, f), with a good consistency (ICC>0.75) (Fig. 1).The ADC value, D value, and f value of SA were significantly higher than those of early breast adenosis, and there was a significant difference in ADC and D value between the two groups (P<0.05), and there was no significant difference in D* and f value (Table 1). The AUC and optimal thresholds of ADC value and D value were 0.756, 0.750, and 0.602, 0.609, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity reached 0.833, 0.769 and 0.917, 0.692, respectively (Table. 2). When ADC value and D value were combined to diagnose SA, the sensitivity and specificity were not increased(Fig.2).DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
The noninvasive examination is very useful for the evaluation of auxiliary diagnosis and treatment plans. IVIM can provide more useful information than traditional DWI, and also provides effective auxiliary diagnostic value for breast adenosis. In our study, the ADC value and D value of IVIM quantitative parameters provide useful diagnostic value for the diagnosis of early breast adenosis and sclerosing adenosis. This study is still in the initial exploration stage, and we hope to provide more valuable diagnostic information in the future.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] ZHANG YP, DONG G, GENG H, et al.The diagnostic value of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging in the differential diagnosis between adenosis of the breast and breast cancer.J Pract Radio,2017;33(4):533-537.
[2] Bao-Hua Yu, Shao-Xian Tang, Xiao-Li Xu, et al.Breast carcinoma in sclerosing adenosis: a clinicopathological and immunophenotypical analysis on 206 lesions. J Clin Pathol 2018;0:1-8.
[3] Youn I, Choi SH, Choi YJ, et al. Contrast enhanced digital mammography versus magnetic resonance imaging for accurate measurement of the size of breast cancer. Br J Radiol 2019; 92: 20180929.
[4] MA YC, SHAN DD, WEI J,et al. Application of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in differential diagnosis and molecular subtype analysis of breast cancer. Am J Transl Res 2021;13(4):3034-3043.
Figures