4273
Diffusion and IVIM MR imaging-based virtual elastography for the differentiation between invasive ductal carcinoma and fibroadenoma1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China
Synopsis
Preoperative accurate differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors is very important to avoid unnecessary surgical treatment. This study aims to evaluate the potential efficacy of the virtual elastography (vMRE) method in the differential diagnosis of IDC and FA, and help guide clinical management. Our results suggested that mean virtual stiffness obtained by this vMRE method can accurately distinguish the hardness difference between FA and IDC.
Introduction
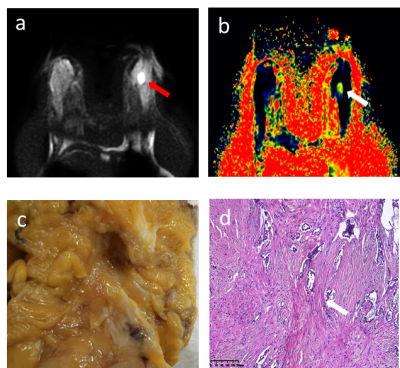
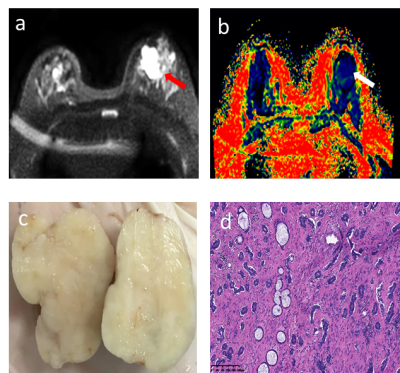
Breast invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) and fibroma (FA) sometimes have similar imaging findings and are difficult to distinguish. It is widely that the hardness of breast tumor depends on the degree of proliferation of myofibroblasts (MFS). Invasive ductal carcinoma and fibroma show different hardness. Magnetic resonance elastography relies on the propagation of mechanically induced shear waves[1]. However, the method lacks in image resolution and this may limit the visibility of small tumors and focal regions of increased tissue stiffness in larger tumors. Also, the method relies on additional hardware for induction of breast vibrations. Thus, a novel and non-invasive method that relies on a clinically available MRI sequences with high speed and image resolution, this so called virtual elastography (vMRE) has an intrinsically high sensitivity to the viscoelastic property of the tissue. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the potential efficacy of the vMRE method in the differential diagnosis of IDC and FA.Methods
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee and informed consents were obtained from all participants. Fifty-seven patients with suspected breast tumors underwent the vMRE-method. All the MRI examinations were performed on a 3.0T MRI scanner (Signa HDXT, GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, USA) with a 16-channel breast coil. The vMRE-method were acquired by EPI echosequence (TR/TE, 7800ms/82ms; FA, 15; slice thickness, 4mm; FOV, 320mm; matrix, 128×128;b= 10、20、30、40、50、80、100、150、200、500、800、1000、2000s/mm2). Data analysis The ADC value was performed using the mean signal intensity based on the regions of interest (ROIs). vMRE-images, reflecting tissue stiffness were reconstructed. From these images, the mean virtual stiffness values over the tumor body were extracted; Diffusion weighted images of the lower b-value (Slow, b value = 200 s/mm2) and those of the higher b-value (Shigh, b value = 1000 s/mm2) were used to estimate the virtual shear stiffness [2,3]: virtual shear stiffness = a·ln (Slow/Shigh) + b. The scaling (a) and the shift (b) factors were separately set to −9.8 and 14 according to the previous calibration studies [2,3]. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUCs) of the mean virtual stiffness and ADC value were further compared by non-parametric test.Results
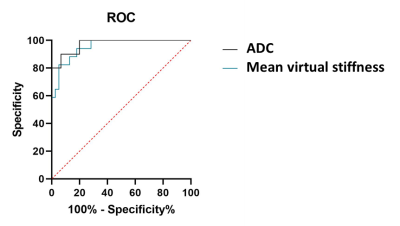
The 57 patients (17 fibroadenoma, mean age of 38.6 years old, range 23~55 years; 39 IDC, mean age of 44.1 years old, range 29~62 years) were finally recruited in this study. No significant differences were observed between fibroadenoma and IDC groups in terms of mean tumor’s maximal diameter, and lesion location. The vMRE value between the two groups was statistically significant (p<0.001), the cut-off value was 5.519. The AUC of mean virtual stiffness value was 0.955, and it was similar to the AUC of ADC value (0.961).Discussion
Intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging, through a calibration of sADC200–1000 with standard MR elastography, can be converted quantitatively into shear modulus without using mechanical vibrations to provide information on the degree of breast issue; these virtual elastograms require only two b values to be acquired and processed [2]. This study demonstrated that the vMRE-method has the potential to improve the differential diagnosis of IDC and FA due to IDC has a higher degree of myofibroblast proliferation. Previous study indicated that evaluation of pituitary adenomas consistency in preparation for surgery seems to be feasible using the vMRE-method [3]. Non-Gaussian diffusion is believed to arise from diffusion barriers, such as cell membranes in fibrotic tissue. Hence, vMRE method could potentially provide a better understanding of microstructural tissue changes in breast associated with disease pathology and enable fast and detailed evaluation of the tumor stiffness.Conclusion
Diffusion and intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging-based virtual elastography has more diagnostic performance than DWI assessment in distinguishing IDC from FA, which could be widely used in clinical routine practice.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shanxi National Science Foundation (2020JQ-518)References
[1]. Sack I, Beierbach B, Hamhaber U, et al. Non-invasive measurement of brain viscoelasticity using magnetic resonance elastography[J]. NMR Biomed, 2008, 21(3):265–271.
[2]. Le Bihan D, Ichikawa S, Motosugi U. Diffusion and intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging–based virtual elastography: a hypothesis-generating study in the liver[J]. Radiology, 2017, 285(2): 609-619.
[3]. Lagerstrand K , Gaedes N , Eriksson S , et al. Virtual magnetic resonance elastography has the feasibility to evaluate preoperative pituitary adenoma consistency[J]. Pituitary, 2021,24(4):530-541.
Figures