4234
Reliability Assessment of IVIM Imaging with Different b-values in Evaluating Myometrium Invasion of Endometrial Cancer1Department of Radiology, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Tianjin, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Beijing, China
Synopsis
The incidence of Endometrial Carcinoma (EC) has occupied the first place among malignant tumors of the female reproductive system. This study aims to explore the reliability of different b-values of IVIM-MRI in evaluating the myometrial invasion of endometrial cancer using advanced ZOOMit technique. The results showed that group A was the highest, group B was the second, and group C was the lowest in evaluating consistency and repeatability of D value, D* value and fp value. It indicated diagnostic is related to b values combinations of IVIM imaging for EC.
Introduction
The incidence of endometrial carcinoma (EC) has occupied the first place among malignant tumors of the female reproductive system [1]. Recently, Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM)MRI has attracted the attention of the oncology community due to its relationship with microperfusion. However, IVIM-MRI has some controversy in clinical practice, because there is no standard reference protocol, especially how to select the b value in the image acquisition process. Currently, IVIM is mostly used for cervical cancer in female pelvic cavity[2, 3], and there are few studies on EC. The purpose of this study is to explore the reliability of different b-values combinations of IVIM-MRI in evaluating the myometrial invasion of EC, and advanced ZOOMit technique was used in the imaging process, aiming at the problem of image distortion caused by traditional echo-planar imaging (EPI).Materials and Methods
69 patients with EC were preoperatively recruited, all participants had written informed consent before examination. All data was collected on a 3T MR scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) through a 16-element abdominal coil array. Advanced ZOOMit imaging technique was used which dynamically reduced the phase field of view caused by EPI distortion. The parameters are as follows: TR/TE =4100/75ms, FOV=190×106mm2, matrix =56×100, slice thickness=3mm with zero spacing, b-values = 0、20、40、80、120、200、400、800、1200、1600s/mm2. For further analysis, the b-values are divided into three groups, group A: b-values = 0, 20, 40, 80, 120, 200, 400, 800, 1200, 1600s/mm2, group B: b-values = 0, 20, 40, 80, 120, 200, 400, 800s/mm2 and group C: b-values = 0, 20, 40, 80, 120, 200, 400s/mm2. SPSS 26 and Medcalc15 statistical software were used for data analysis. Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) was used to evaluate the consistency and repeatability of parameter measurement.Results and Discussion
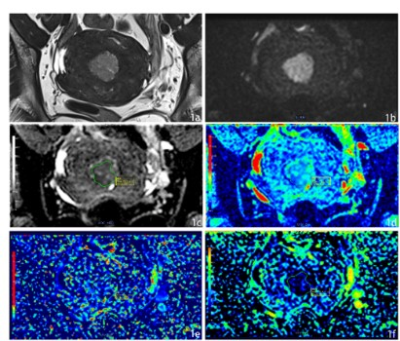
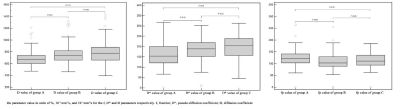
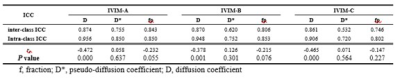
69 patients all obtained high quality images using advanced ZOOMit imaging. Fig.1 showed T2W, DWI, ADC, D mapping, D* mapping, fp mapping of a 54-year-old patient with EC. ICC of D value D* and fp value in A, B, and C group was shown in Table 1. The results showed that group A was the highest, group B was the second, and group C was the lowest. The ICC values of D* value measured by the doctors between the different groups showed medium except for group C, and the ICC values of other parameters measured by the doctors intra- and inter-class showed well. In view of the consistency and repeatability of the measurement results, this study took the average of the first measurement results of two physicians for further analysis. The results showed that the differences in IVIM parameters D, D*, and f values among groups A, B, and C were statistically significant (p value<0.001), and parameters differed statistically between group A and group B, group A and group C (p value<0.05), and there was no significant difference between group B and group C (p value>0.05).Conclusion
EC diagnosis is related to the b-values combinations of IVIM MRI. The parameter of D value is stable, and it can objectively evaluate myometrial invasion of endometrial cancer; the clinical application value of the parameters D* value and f value remains to be further explored.Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank all the participants in this study.References
[1] LORTET-TIEULENT J, FERLAY J, BRAY F, et al. International Patterns and Trends in Endometrial Cancer Incidence, 1978-2013 [J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2018, 110(4): 354-61.[2]PERUCHO J A U, WANG M, VARDHANABHUTI V, et al. Association between IVIM parameters and treatment response in locally advanced squamous cell cervical cancer treated by chemoradiotherapy [J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(10): 7845-54. [3] XU C, DU S, ZHANG S, et al. Value of integrated PET-IVIM MR in assessing metastases in hypermetabolic pelvic lymph nodes in cervical cancer: a multi-parameter study [J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(5): 2483-92.
Figures