4203
DKI and IVIM for Assessment of Rectal Cancer: Correlations between Imaging Parameters and Tumor Tissue Composition1Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China, 2MR scientific Marketing, Diagnostic Imaging, Siemens Healthineers Ltd, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
It is important to combine histopathological and non-invasive imaging measurements to assess tumor components and predict tumor invasiveness to define disease treatment and prognostic assessment. In this study, we assessed the relationships between DKI and IVIM parameter measurements and the corresponding tumor tissue composition, regardless of the status of the malignant tumor. To this end, we selected a range of tissue parameters informative for important biological properties of the tumor, such as Ki-67, the tumor: stroma ratio, CD34 etc.
To correlate non-invasive quantitative diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) and intravoxel incoherent motion-derived (IVIM) parameters with rectal cancer composition assessed by the expression of caudal-type homeobox 2 (CDX-2), Vimentin (VIM) and CD34 on resected tissues, as well as the tumor stroma ratio (TSR) and the results of H&E and Masson staining.
Materials and Methods
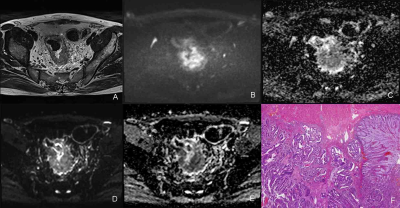
A prospective study of 26 patients with rectal cancer were included in this study. All patients underwent magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, including DKI and IVIM at a 3 T scanner(Magnetom Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with a 18 channel coil. Oblique axial DKI with b values of 0, 700, 1400, 2100 sec/mm2 (with no. of averages=1, 2, 8, 8, respectively) and IVIM with b values of 0, 20, 50, 70, 150, 400 and 800 sec/mm2 were performed using a single-shot echo-planar imaging sequence with similar parameters. Primary tumor was harvested and fixed for H&E, immunohistochemistry and Masson staining.
Results
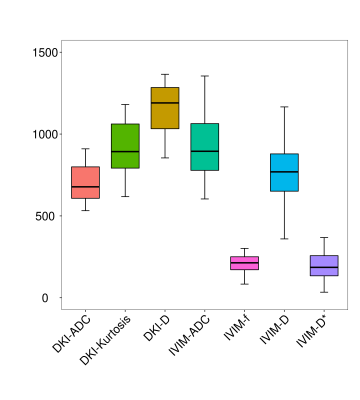
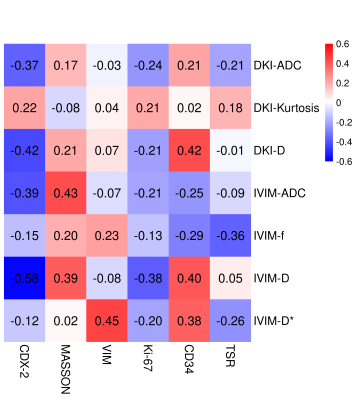
Here, we document a number of correlations between non-invasive MR imaging parameters and the composition of rectal cancer tissue after resection. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC)DKI exhibited a weak negative correlation with CDX-2 (r=-0.367, P=0.068) whereas MKDKI showed a moderate negative correlation with this marker (r=-0.422, P=0.04) and a moderate positive correlation with CD34 (r=0.421, P=0.041). ADCIVIM exhibited a moderate positive correlation with Masson staining (r=0.426, P=0.048) and a weak negative correlation with CDX-2 (r=-0.394, P=0.007). The fIVIM was weakly negatively correlated with the TSR (r=-0.364, P=0.088). DIVIM showed a moderate negative correlation with CDX-2 (r=-0.58, P=0.005) and a moderate positive correlation with CD34 (r=0.403, P=0.063). DIVIM showed a weak negative correlation with Ki-67 (r=-0.378, P=0.075) and a weak positive correlation with Masson (r=0.39, P=0.072). Finally, D*IVIM showed a moderate positive correlation with VIM (r=0.445, P=0.033) and a weak positive correlation with CD34 (r=0.38, P=0.073).
Conclusion
The present prospective study linked DKI and IVIM to tissue structure assessed by histopathology after rectal resection. By comparing DKI and IVIM parameters and histological sections, this work revealed correlations between MRI parameters and the composition of rectal cancer tissue. Thus, this study documents the use of DKI and IVIM values to non-invasively establish tumor biological properties in rectal cancer.
Acknowledgements
NoReferences
1. Hectors SJ, Semaan S, Song C, Lewis S, Haines GK, Tewari A, Rastinehad AR, Taouli B. Advanced Diffusion-weighted Imaging Modeling for Prostate Cancer Characterization: Correlation with Quantitative Histopathologic Tumor Tissue Composition-A Hypothesis-generating Study. Radiology. 2018 Mar;286(3):918-928. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017170904. Epub 2017 Nov 8. PMID: 29117481.
2. Zhu L, Pan Z, Ma Q, Yang W, Shi H, Fu C, Yan X, Du L, Yan F, Zhang H. Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Study of Rectal Adenocarcinoma Associated with Histopathologic Prognostic Factors: Preliminary Findings. Radiology. 2017 Jul;284(1):66-76. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016160094. Epub 2016 Dec 5. PMID: 27929929.
Figures