3822
Comparison of T1 mapping from StarVIBE and conventional variable flip angle in abdomen: a preliminary study1Department of Radiology,The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Wuhan, China,, Wuhan, China
Synopsis
The purpose of this study to assess image quality and T1 value value between variable flip angle (VFA-T1) and StarVIBE (StarVIBE-T1) methods using breath-holding and free breathing, respectively. Compared with VFA-T1 method, StarVIBE-T1 had better image quality, including overall image quality, blurring, and clearer edge of lesions, especially for the patients without breath-holding. The T1 values from the two methods had high correlation and moderate agreement.
Introduction
MR-based TI mapping is a promising diagnostic tool which can quantitatively measure and characterize tissues, and also can quantify extracellular volume fraction (ECV) through T1 mapping of pre- and post- contrast enhancement. T1 mapping and ECV are usually used in assessments of tumor and fibrosis in whole body, such as renal cell carcinoma,1 liver fibrosis,2 cardiovascular disease.3 In previous studies, the T1 mapping methods, such as conventional variable flip angle T1 mapping (VFA-T1) and look-locker inversion recovery (MOLLI), require the patients to hold breaths. However, some patients have difficulty in breath holds, which may produce poor quality images unusable in clinical diagnosis. Due to the radial acquisitions, StarVIBE is a promising method for organs susceptible to respiratory motion or swallowing movements, such as esophagus,4 liver5, kidney, and lung6, with free breathing. In this study, we aimed to assess the feasibility of T1 mapping from StarVIBE in patients with kidney cancer through comparisons with VFA-T1 using image quality and T1 values with breath-holding and free breathing, respectively.Methods
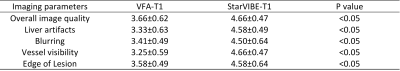
This prospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital. Six patients with renal cancer were recruited, and the signed informed written consent of all patients were obtained. All patients underwent renal MR examinations on a 3T MR scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with 18-channel abdominal phase array coil and 32-channel Tim spinal array coil, and the scan sequences included conventional T1w, T2w, VFA-T1 and StarVIBE-T1 in pre- and post- contrast enhancement. The parameters of the two T1 mapping methods are listed in Table 1. The image quality, including overall quality, blur, sharpness of boundaries, vessel visibility, were assessed using 5-point Likert scale by two blinded radiologists with 5-7 years’ experience. Four regions of interest (the tumor, right and left renal healthy tissue, liver healthy tissue) were drawn on the same location and as near as possible for the corresponding VFA-T1 and starVIBE-T1 maps. The mean T1 value of each ROI was calculated. T-test was used to assess the difference for image quality, and Pearson correlation coefficient and Bland-Altman analysis for correlation and agreement of T1 value between the VFA-T1 and StarVIBE-T1 methods, respectively. The p value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results
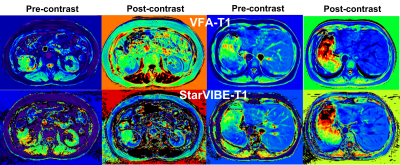
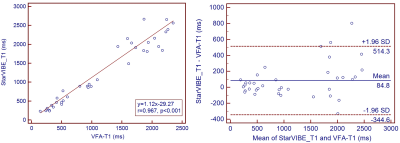
Table 2 shows the qualitative image quality scores of VFA-T1 and StarVIBE-T1 methods. The image quality scores of StarVIBE-T1 for any items were significantly greater than those of VFA-T1 (p<0.01). StarVIBE-T1 showed better overall image quality, less blur, more small vessels, and sharpness of boundaries, as shown in Figure 1. The T1 values of StarVIBE-T1 and VFA-T1 had high corrections (r=0.967, p<0.001) and good agreement between the two methods (2/48 out the 95% limited agreement interval). Bland-Altman analysis showed that the T1 value of StarVIBE-T1 was higher than VFA-T1 with a bias of 84.8 ms.Discussion:
In our study, we found that starVIBE-T1 method significantly improved the image quality compared with conventional VFA-T1 method. For the patient who can’t breathe hold well, the VFA-T1 failed to diagnose in clinic, but StarVIBE-T1 still produced good quality images. Although the StarVIBE-T1 permits free breathing, almost no respiratory motion artifacts in the liver and kidney regions were observed. The artifacts were automatically removed out of the tissues for the radial acquisition. For T1 quantitative analysis, there was a very high correlation (Pearson coefficient r=0.96, p<0.001), but the agreement was moderate. The main reason is that the data from all the patients were included due to our small sample size, but the VFA-T1 had more respiratory motion artifacts for certain patients, which might cause the large difference. In the future, we will recruit more patients and try to decrease the effects of the poor quality images on the T1 value.Conclusions
StarVIBE-T1 technique is useful for the detection of kidney lesions with free breathing, especially for the patients who can’t breathe hold.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Lisa C. Adams, Philipp J, Bernhard R, et al. Assessment of the extracellular volume fraction for the grading of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: first results and histopathological findings. 2019, European Radiology, 29(11):5832-5843.
2. Kim JE, Kim HO, Bae K, et al. T1 mapping for liver function evaluation in gadoxetic acid–enhanced MR imaging: comparison of look-locker inversion recovery and B1 inhomogeneity–corrected variable flip angle method. 2018, European Radiology, 29(7):3584-3594.
3. Lin L, Li X, Shen K, et al. The prognostic value of T1 mapping and late gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in patients with light chain amyloidosis. 2018, Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 20(1):2.
4. Wang Z, Guo J, Qin J, et al. Accuracy of 3-T MRI for Preoperative T Staging of Esophageal Cancer After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, With Histopathologic Correlation. 2019, American Journal of Roentgenology, 212:1–8.
5. Frenk NE, Montesi SB, Chen T, et al. Free-breathing radial 3D fat-suppressed T1-weighted gradient echo sequence: a viable alternative for contrast-enhanced liver imaging in patients unable to suspend respiration. Magn Reson Imaging. 2020, 69:16-21.
6. Kumar S, Rai R, Stemmer A, et al. Feasibility of free breathing Lung MRI for Radiotherapy using non-Cartesian k-space acquisition schemes. 2017, Br J Radiology, 90(1080):20170037.