3800
Higher reliability and validity of Wavelet-based ALFF of resting-state fMRI: evidence from multicenter eyes open and eyes closed databases
1Center for Cognition and Brain Disorders, The Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, China, 2Institute of Psychological Sciences, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, China, 3Zhejiang Key Laboratory for Research in Assessment of Cognitive Impairments, Hangzhou, China, 4Unit of Psychiatry, Department of Public Health and Medicinal Administration, & Institute of Translational Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Macao SAR, China, 5Centre for Cognitive and Brain Sciences, University of Macau, Macao SAR, China, 6Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Macao SAR, China, 7MR Research, GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 8Institute of Sports Medicine and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu, China
Synopsis
Using multi-center resting-state fMRI databases under eyes closed (EC) and eyes open (EO), this study systematically investigated the intra- and inter-scanner reliability and validity of Wavelet-mALFF across multiple frequency bands. We found that Wavelet-mALFF outperformed FFT-mALFF in terms of intra- and inter-reliability and validity, particularly in the higher frequency band slow-2 (0.1992-0.25 Hz), where db2-mALFF is the top performer in Wavelet-mALFF. We propose that instead of FFT-ALFF, db2-ALFF can be employed to measure the spontaneous oscillations of local brain activity in future studies.
Introduction
The amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) has been widely employed in analyzing the local spontaneous oscillation of a single voxel, which can be obtained by fast Fourier transform (FFT-ALFF) 1. and wavelet transform (Wavelet-ALFF) 2. In contrast to the periodic sine function decomposition of FFT, mother wavelet functions of irregular shape may be preferable for simulating biological data 3. In addition to the sensitivity and reproducibility discussed in the previous article 2, a more systematic consideration of wavelet-ALFF and FFT-ALFF is required.Methods
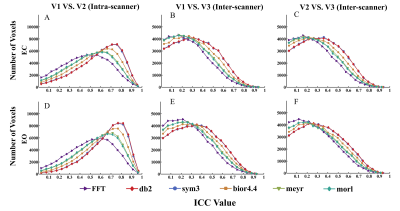
This study group collected nine resting-state fMRI datasets in the eyes closed (EC) and eyes open (EO) resting states (open access at https://www.nitrc.org/projects/eceo_rsfmri_9/) 4-7, with datasets 1-3 collected from the same cohort of participants over three visits (V1, V2, V3), with V1 and V2 performed on a GE 3T scanner and V3 on a Siemens 3T scanner. FFT-ALFF and Wavelet-ALFF were calculated for each dataset based on five parent waves (i.e. db2, bior4.4, morl, meyr, and sym3) for the conventional band (0.0117-0.0781 Hz) and five frequency sub-bands: slow 6 (0-0.0117 Hz), slow 5 (0.0117-0.00273 Hz), slow 4 (0.0273-0.0742 Hz), slow 3 (0.0742-0.1992 (0.1992-0.25 Hz). The intra- (V1 vs. V2) and inter-scanner (V2 vs. V3, V1 vs. V3) test-retest reliability were calculated using the Intra-Class Correlation Coefficient (ICC). Both FFT-mALFF and Wavelet-mALFF were used to conduct meta- and mega-analyses of the differences between EC and EO.Results
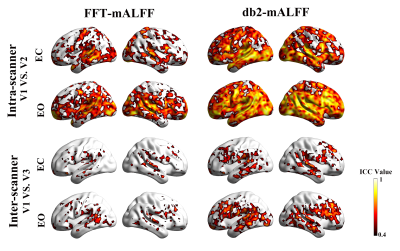
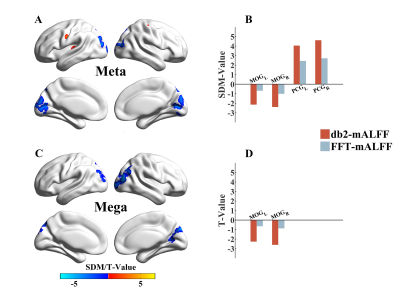
We found that Wavelet-mALFF had greater inter- and intra-scanner reliability and validity than FFT-mALFF, notably db2-mALFF in the higher frequency band slow-2 (0.1992-0.25 Hz) (Figure 1-2). Furthermore, both mega- and meta-analyses revealed that Wavelet-mALFF had better validity than FFT-mALFF in most conditions, particularly in slow-2 (0.1992-0.25 Hz), where the db2-mALFF observed much more robust differences between EC and EO in the sensorimotor cortex and MOG (Figure 3).Discussion
Wavelet-mALFF is superior to FFT-mALFF in terms of reliability and validity, particularly in the higher frequency slow-2 (0.1992-0.25 Hz), where the db2-mALFF is the most robust measure for identifying spontaneous local activity. The superiority of db2-mALFF might be explained by the shape of its basis function, which is quite similar to the hemodynamic resonance function (HRF) 8-10. These findings suggest that the db2-mALFF might be a valuable metric for detecting functional alternations in brain disorders in a single voxel.Conclusion
Since db2-mALFF outperformed FFT-mALFF in terms of reliability and validity, this study recommends that db2-mALFF be employed instead of FFT-ALFF to detect spontaneous regional brain activity in future studies.Acknowledgements
None.References
1. Y. F. Zang, Y. He, C. Z. Zhu, et al. Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev-Jpn. 2007;29(2):83-91.
2. F. F. Luo, J. B. Wang, L. X. Yuan, et al. Higher Sensitivity and Reproducibility of Wavelet-Based Amplitude of Resting-State fMRI. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:224.
3. P. Lio. Wavelets in bioinformatics and computational biology: state of art and perspectives. Bioinformatics. 2003;19(1):2-9.
4. B. K. Yuan, J. Wang, Y. F. Zang, et al. Amplitude differences in high-frequency fMRI signals between eyes open and eyes closed resting states. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 2014;8:503.
5. L. X. Yuan, J. B. Wang, N. Zhao, et al. Intra- and Inter-scanner Reliability of Scaled Subprofile Model of Principal Component Analysis on ALFF in Resting-State fMRI Under Eyes Open and Closed Conditions. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:311.
6. Q. H. Zou, B. K. Yuan, H. Gu, et al. Detecting Static and Dynamic Differences between Eyes-Closed and Eyes-Open Resting States Using ASL and BOLD fMRI. Plos One. 2015;10(3):e0121757.
7. D. Liu, Z. Dong, X. Zuo, et al. Eyes-open/eyes-closed dataset sharing for reproducibility evaluation of resting state fMRI data analysis methods. Neuroinformatics. 2013;11(4):469-476.
8. I. D. Dinov, J. W. Boscardin, M. S. Mega, et al. A wavelet-based statistical analysis of fMRI data. Neuroinformatics. 2005;3(4):319-342.
9. L. D. Lewis, K. Setsompop, B. R. Rosen, et al. Fast fMRI can detect oscillatory neural activity in humans. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(43):79-85.
10. M. K.
van Vugt, P. B. Sederberg & M. J. Kahana. Comparison of spectral analysis
methods for characterizing brain oscillations. J Neurosci Meth.
2007;162(1-2):49-63.
Figures