3793
Acceleration of T2-weighted head Multivane imaging by compressed sensing
Na Liu1, Wei Qing Song1, Jie Liang Lin2, Nan Wang1, Lian ai Liu1, and Wei Yan Miao1
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Da Lian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, BeiJing, China
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Da Lian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, BeiJing, China
Synopsis
Multivane (MV) imaging, based on the blade rotating acquisition in k space, is a novel sequence for motion reduction imaging. The MV acquisition percentage is critical parameter in MV imaging for balanced image quality and scan time. This study aims to assess the performance of compressed sensing for accelerated T2-weighted head MV imaging under altered MV acquisition percentages. Results indicated that scan time of head Multivane (MV) T2WI was significantly reduced by compressed sensing (CS) without reduced image quality.
Synopsis
Multivane (MV) imaging, based on the blade rotating acquisition in k space, is a novel sequence for motion reduction imaging. The MV acquisition percentage is critical parameter in MV imaging for balanced image quality and scan time. This study aims to assess the performance of compressed sensing for accelerated T2-weighted head MV imaging under altered MV acquisition percentages. Results indicated that scan time of head Multivane (MV) T2WI was significantly reduced by compressed sensing (CS) without reduced image quality.Summary of Main Findings
Scan time for head MV T2WI was reduced significantly by CS without obvious reduction in image quality. Images acquired with combination of the CS factor 3 and the MV percentage of 260 showed adequate performance in both subjective and objective evaluations, thus recommended for routine MR scans.Introduction
Multivane (MV) is a recently introduced technique for motion reduction in MRI using rotating blades in the k-space, which is capable of detection and correction of affects introduced by low frequency in-plane motion in the center k-space for each blade, thus reduced motion artifacts in images [1]. MV percentage refers to the total area of rotating acquisition of blades in this acquisition mode of windmill compared to the area collected in the Cartesian manner when fully filling the k space[2]. The higher MV percentage tends to be associated with the better image quality, but also the longer scan time. The compressed sensing (CS) technique has now been widely used for scan time reduction in MRI through the sparse data sampling, while ensuring the image quality to meet the diagnostic requirements. The purpose of this study is to explore the best combination of MV percentage and CS acceleration factor (AF) for fast and motion-robustness head T2-weighted imaging (T2WI).Materials and methods
Data from 12 healthy subjects were included (6 females, 31.25±12.47 years). All subjects underwent the conventional and MV T2WI on a 3.0 T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands). MV T2WI adopted a routine clinical setup using a SENSE acceleration factor 2, and the CS AF of 2, 3 and 4 were used with combination of different MV percentages (160,210,260 or 310). Detailed parameters were shown in Table 1. Regions of interest were placed manually at both sides of the Centrum semiovale, tail-shaped nucleus at the maximum level, press part of corpus callosum, cerebrospinal fluid by an experienced radiologist for the measurement of signal to noise ratio (SNR) and contrast to noise ratio (CNR). The SNR and CNR were repeated measured for twice with the averaged values for further analyses. Two experienced observers used a five-point scoring method to subjectively evaluate the quality of images (the scoring system was listed in Table 2). The Kappa test was adopted to evaluate the consistency of the scores from the two radiologists. If the consistency was in good agreement, the corresponding images would be adopted for further analysis by senior physicians. The Frideman test was used to assess the difference of SNR, CNR and score among all sequences. This study has been approved by the local IRB.Results
The scores by the two observers were in good agreement (Kappa = 0.762). There was no statistical differences in the subjective scores of each sequence (P>0.05, Table 3). For sequences with the same CS factor, the SNR and CNR tended to be increased with the increased of MV percentage but without significantly difference (P>0.05). For sequence with the same MV percentage, the SNR and CNR tended to be reduced with the increase of CS factors without significantly difference (P>0.05). For the sequence with similar scan times, the combination of CS-AF3 and MV percentage of 260 showed the highest SNR and CNR (P>0.05, Table 4).Conclusions
Scan time for head MV T2WI could be reduced significantly by CS without obvious reduction in image quality. Images acquired with the combination of the CS factor 3 and the MV percentage of 260 showed adequate performance in both subjective and objective evaluations, thus recommended for routine MR scans.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Kang, KA,Kim, YK ,Kim, E, et al. T2-Weighted Liver MRI Using the MultiVane Technique at 3T: Comparison with Conventional T2-Weighted MRI. Korean J Radiol.2015 ;16(5) :1038-46 2. Sodhi, KS ,Bhatia, A ,Lee, EY. Prospective Evaluation of Free-Breathing Fast T2-Weighted MultiVane XD Sequence at 3-T MRI for Large Airway Assessment in Pediatric Patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol.2021 04 ;216(4) :1074-1080Figures
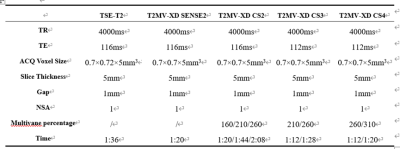
Scan parameters of each sequence
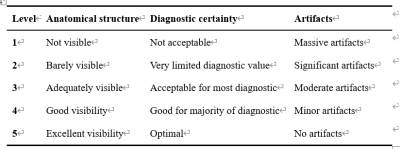
Subjective score
criteria system

Objective statistical
results
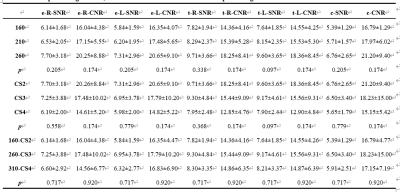
Comparison of objective SNR and CNR measurements among sequences with
the same CS factor but changed MV percentages; comparison of objective SNR and
CNR measurements among sequences with the same MV percentage but changed CS
factors and comparison of objective SNR and CNR measurements among sequences
with similar scan times: the CS-AF2 combined with MV percentage of 160, the
CS-AF3 combined with MV percentage of 260, and the CS-AF4 combined with MV
percentage of 310
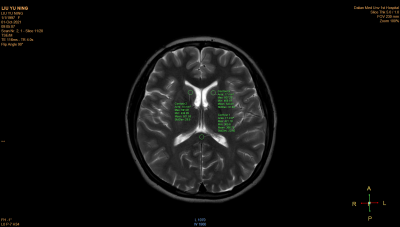
Figure1,Male, 24 years old, healthy volunteer.
Use ROI to measure SI and SD on tail-shaped nucleus at the maximum level, press
part of left and right corpus callosum.
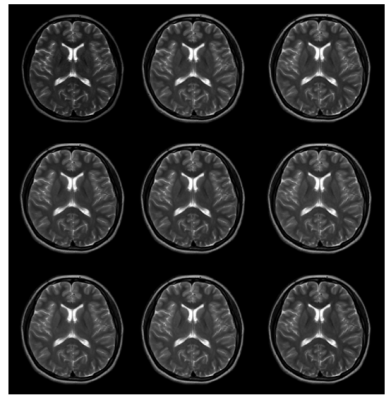
Figure2,Male,
24 years old, healthy volunteer. From left to right, the sequences are:
conventional T2WI, MV-SENSE2,T2MVXD:160,210,260 multivane percentage combined
with CS2; 210,260 MV percentage combined with CS3; 260,310 multivane percentage
combined with CS4.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2022/3793