3784
Sex-related Changes in GABA+ Signaling in the Right Thalamus in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis through Acupuncture Stimulation1Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Center for Biomedical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2School of Medical Information Engineering, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei, China
Synopsis
This study aimed to investigate GABA variation between KOA patients and healthy people without therapy and how GABA changes through acupuncture stimulation. MEGA-PRESS sequence was used to detect GABA signaling in the right thalamus before and after acupuncture stimulation on EX-LE5 acupoint of the left leg. Our study demonstrated a sex-related GABA+/Cr difference in patients with KOA chronic pain, proving the quantitative sex differences in human pain processing. Moreover, the therapeutic effect of acupuncture stimulation was positively proved and quantified by measuring GABA+/Cr.
Introduction
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a common disease in middle-aged and elderly people. KOA patients suffer from long-term chronic pain.[1] One meta-analysis study shows that the global prevalence of KOA is 16.0% in people over 15 and 22.9% in people over 40. However, the prevalence in women (21.7%) is much higher than that in men (11.9%) at all ages.[2] A previous study has reported different modulating of GABA signaling in gray matter between female and male rats with chronic pain.[3]Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system[4] and the key neurometabolite in the physiology of chronic pain[5-8]. Nociceptive inputs can be transmitted from the spinal cord to the thalamus, which is GABAergic.[9] Acupuncture is an effective therapy to relieve the chronic pain of KOA[10-12], but the neural mechanisms of chronic pain of KOA and the therapeutic effect are still unclear. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate GABA variation between KOA patients and healthy people without therapy and how GABA changes through acupuncture stimulation. Due to the low concentration of GABA itself and spectra overlapping of metabolites with much higher concentration[13, 14], we used MEGA-PRESS sequence to examine GABA signaling, in which 2 editing pulses were performed to resolve GABA signaling.
Besides, sex was considered in our study because of the different prevalence in different sexes.
Materials and Methods
16 KOA patients (PA) (11 female, age 60.63 ± 8.43) were recruited from the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine (AUCM), and 18 healthy controls (HC) (12 female, age 56.33 ± 9.44) were recruited from the local community (Figure 1). All participants were scanned on a GE Discovery MR750 (GE Healthcare, USA) 3T MRI scanner using an 8-channel head coil. Acupuncture stimulation was performed on EX-LE5 acupoint of the left leg for 6 min 50 s by doctors from AUCM. 3 PA and 4 HC did not undergo therapy because of fear of acupuncture, lacking MRS data after stimulation.MRS/MRI protocol includes 3D T1 BRAVO (TR/TE = 8.16/3.18 ms, FA = 12°, FOV = 256 mm × 256 mm, matrix = 256 × 256, slice thickness = 1 mm, number of slices = 170) for brain anatomical structure. A MEGA-PRESS sequence, programmed using GE EPIC, was performed before and after stimulation, respectively. Voxel of interest (VOI) of MRS was set to the right thalamus (3 × 3 × 3 cm3). Basic parameters of MEGA-PRESS are as follow: TR/TE = 2000/68 ms, phase cycle = 8, total number of scans = 256 (128 OFF/ON alternated), spectral bandwidth = 5000 Hz, number of points = 4096, scan duration = 9 min 20 s. The parameters of editing pulses are as follows: SLR RF design, pulse duration = 17 ms, pulse bandwidth (FWHM) = 66 Hz, transmit frequency of OFF/ON spectra = 7.46/1.9 ppm.
MRS VOI was rebuilt based on MRI/MRS raw data by AFNI[15, 16]. MRS data were processed using Gannet[17] to resolve GABA signaling, labeled GABA+ in the rest of this study due to co-editing influence from macro-molecules. Moreover, the GABA+/Cr ratio is used to avoid individual measurement errors. Representative examples of VOI placement and GABA spectra are shown in Figure 2.
Results
GABA+/Cr of both KOA PA and HC before acupuncture stimulation were grouped by sex. Detailed statistical information of sub-groups (Figure 1). A two-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was conducted to investigate the GABA+/Cr level changes among the 4 sub-groups above. There was a significant interaction effect (F (1, 30) = 15.5000, p = 0.0005). However, both main factors, sex difference (F (1, 30) = 0.8168, p = 0.3733) and whether subject has KOA or not (F (1, 30) = 0.0002, p = 0.9894), had no significant effects. Further two-tailed unpaired T-tests reported that GABA+/Cr level of KOA PA was significantly higher than HC in males (FDR corrected, P = 0.0162, Figure 3), whereas GABA+/Cr level of KOA PA was significantly lower than HC in females (FDR corrected, P = 0.0162, Figure 3).To analyze the therapeutic effect of acupuncture, we performed two-tailed paired T-tests between pre-acupuncture and post-acupuncture in the 4 sub-groups independently. In males, GABA+/Cr level in KOA PA tended to decrease after acupuncture (Decreased Mean = 0.0193, P = 0.0622) (Figure 4a), whereas GABA+/Cr level in HC had no significant trend (P = 0.7265) (Figure 4b). In females, GABA+/Cr level in KOA PA tended to increase after acupuncture (Increased Mean = 0.0133, P = 0.0617) (Figure 4c), whereas GABA+/Cr level in HC had no significant trend (P = 0.2873) (Figure 4d).
Discussion and conclusion
Our study demonstrated a sex-related GABA+/Cr difference in patients with KOA chronic pain, proving the quantitative sex differences in human pain processing. Moreover, there were different reactions to acupuncture stimulation between different sexes. According to the results, GABA+/Cr level of male KOA PA decreased after acupuncture stimulation, which tended to the level of male HC before stimulation. Similarly, GABA+/Cr level of female KOA PA increased after acupuncture stimulation, which approached the level of female HC before stimulation. Therefore, the therapeutic effect of acupuncture stimulation was positively proved and quantified by measuring GABA+/Cr in the right thalamus.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81873370) and Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China (No. 2018YFC170460-4).References
[1] SHARMA L. Osteoarthritis of the Knee [J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(1): 51-9.
[2] CUI A, LI H, WANG D, et al. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies [J]. EClinicalMedicine, 2020, 29-30(100587.
[3] TONSFELDT K J, SUCHLAND K L, BEESON K A, et al. Sex Differences in GABAA Signaling in the Periaqueductal Gray Induced by Persistent Inflammation [J]. J Neurosci, 2016, 36(5): 1669-81.
[4] PETROFF O A. GABA and glutamate in the human brain [J]. Neuroscientist, 2002, 8(6): 562-73.
[5] BRIDGE H, STAGG C J, NEAR J, et al. Altered neurochemical coupling in the occipital cortex in migraine with visual aura [J]. Cephalalgia, 2015, 35(11): 1025-30.
[6] AGUILA M E, LAGOPOULOS J, LEAVER A M, et al. Elevated levels of GABA+ in migraine detected using (1) H-MRS [J]. NMR Biomed, 2015, 28(7): 890-7.
[7] CHAN Y M, PITCHAIMUTHU K, WU Q Z, et al. Relating excitatory and inhibitory neurochemicals to visual perception: A magnetic resonance study of occipital cortex between migraine events [J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(7): e0208666.
[8] PEEK A L, REBBECK T, PUTS N A, et al. Brain GABA and glutamate levels across pain conditions: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of 1H-MRS studies using the MRS-Q quality assessment tool [J]. Neuroimage, 2020, 210(116532.
[9] YEN C T, LU P L. Thalamus and pain [J]. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan, 2013, 51(2): 73-80.
[10] WANG M, LIU L, ZHANG C S, et al. Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis [J]. J Pain Res, 2020, 13(1421-9.
[11] TU J F, YANG J W, SHI G X, et al. Efficacy of Intensive Acupuncture Versus Sham Acupuncture in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial [J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2021, 73(3): 448-58.
[12] LIN L L, TU J F, WANG L Q, et al. Acupuncture of different treatment frequencies in knee osteoarthritis: a pilot randomised controlled trial [J]. Pain, 2020, 161(11): 2532-8.
[13] NEAR J, EVANS C J, PUTS N A, et al. J-difference editing of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA): simulated and experimental multiplet patterns [J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 70(5): 1183-91.
[14] MULLINS P G, MCGONIGLE D J, O'GORMAN R L, et al. Current practice in the use of MEGA-PRESS spectroscopy for the detection of GABA [J]. Neuroimage, 2014, 86(43-52.
[15] COX R W, HYDE J S. Software tools for analysis and visualization of fMRI data [J]. NMR Biomed, 1997, 10(4-5): 171-8.
[16] COX R W. AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages [J]. Comput Biomed Res, 1996, 29(3): 162-73.
[17] EDDEN R A, PUTS N A, HARRIS A D, et al. Gannet: A batch-processing tool for the quantitative analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acid-edited MR spectroscopy spectra [J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2014, 40(6): 1445-52.
Figures

Figure 1. A statistical information table of 16 KOA PA, 18 HC, and 4 sub-groups divided by KOA PA/HC and different sexes.
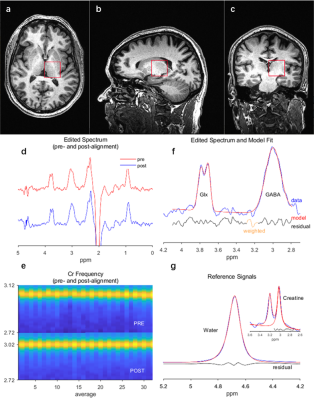
Figure 2. Representative example of MRS VOI placement and GABA spectra. (a), (b) and (c) are a participant's axial, sagittal, and coronal planes. The red lines in (a), (b), and (c) are edges of VOI placement rebuilt. (d) Representative edited spectrum and (e) Cr Frequency (pre-and post- alignment) used for spectra reference. (f) GABA+ signals and (g) reference signals fitting by Gannet. The red line is the result of Gaussian model fitting. The blue line is the processed GABA+ spectrum, and the black line is the residual difference between the fitting result and the processed spectrum.
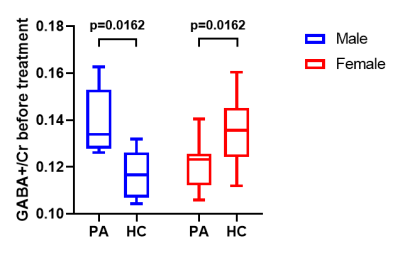
Figure 3. Results of two-way ANOVA analysis among 4 sub-groups divided by KOA PA/HC and different sexes. In males (blue), GABA+/Cr level of KOA PA was significantly higher than HC. In females (red), GABA+/Cr level of KOA PA was significantly lower than HC.
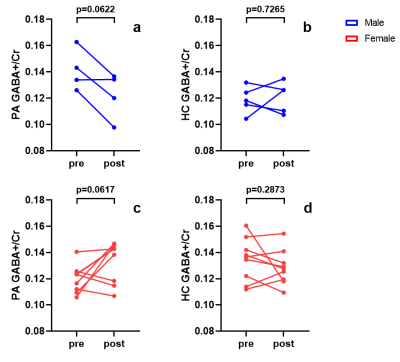
Figure 4. Results of two-tailed paired T-tests of GABA+/Cr level between pre-acupuncture and post-acupuncture in 4 sub-groups divided by KOA PA/HC and different sexes. (a) GABA+/Cr level change of male KOA PA. (b) GABA+/Cr level change of male HC. (c) GABA+/Cr level change of female KOA PA. (d) GABA+/Cr level change of female HC. Blue dots and lines show male data, red dots and lines show female data. PA: patients; HC: healthy controls; pre: pre-acupuncture; post: post-acupuncture.