3783
Evaluation of Blood Flow and Plaque Vulnerability in Carotid Artery Stenosis Focusing on Morphological and Component Characteristics1Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Tokushima University Graduate School, Tokushima, Japan, 2Graduate school of Health Science, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan, 3Faculty of Health Sciences, Institute of Medical, Pharmaceutical and Health Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, 4Global MR Applications and Workflow, GE Healthcare Japan, Hino-city, Japan, 5Department of Neurosurgery, Tokushima University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Tokushima, Japan
Synopsis
Our purpose was to assess plaque vulnerability under the influence of blood flow in terms of morphological and component characteristics using MRI.Twenty-three patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic carotid stenosis, all of whom provided informed consent, underwent 3T MRI scan (GE Healthcare). We evaluated the consistency between the flow patterns and plaque features in the carotid artery stenosis, using 4D-flow MRI and 3D-FSE-MSDE sequences. During the vulnerability analysis, it was observed that there was a negative correlation between 3D-FSE-MSDE and 4D-flow parameter (R = -0.43, P < 0.001).
Introduction & Purpose
A risk factor for ischemic stroke includes carotid artery stenosis caused by atherosclerotic plaques. The atherosclerotic plaque rupture leads to ischemic stroke. Because there are patients with symptomatic or asymptomatic stenosis, evaluating the plaque characteristics is very important before the rupture. The evaluation method using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been widely used; the three-dimensional fast spin-echo with motion-sensitized driven equilibrium (3D-FSE-MSDE) method is very useful because the imaging contrast doesn't depend on the heartbeats[1]. Recently, papers four-dimensional flow (4D-flow) MRI have been increasing to assess blood flow with the development of computers [2]. If combine hemodynamic and plaque characteristics, there is a possibility of the determination of parameters indicating the plaque risk rupture. Our purpose was to assess plaque vulnerability under the influence of blood flow in terms of morphological and component characteristics using MRI.Materials & Methods
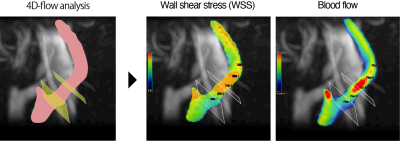
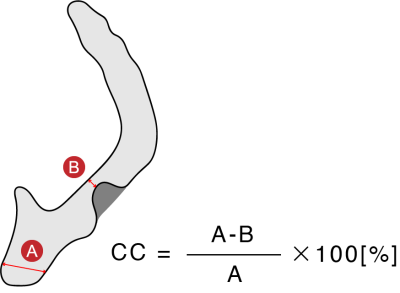
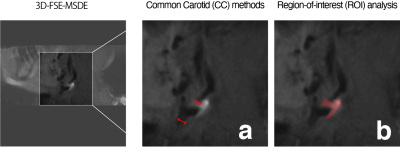
Twenty-three patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic carotid stenosis, all of whom provided informed consent, underwent 3T MRI scan (GE Healthcare). We evaluated the consistency between the flow patterns and plaque features in the carotid artery stenosis, using 4D-flow MRI and 3D-FSE-MSDE sequences. Hemodynamic parameters and wall shear stress (WSS) [3] were then assessed using the 4D-flow MRI data and dedicated flow analysis software (Circle Cardiovascular Imaging Inc). After processing, the estimated parameter values were measured by two regions of interest (ROIs), which were placed perpendicular to the vessel axis in pre-stenotic and highly stenotic regions, respectively (see Fig 1) The carotid artery stenosis on T1-weighted (T1w) 3D-FSE-MSDE sequences was assessed by the common carotid (CC) criteria (see Fig 2, Fig 3a) [4]. In addition, the ratio of the T1w or T2-weighted (T2w) signal intensities on the carotid artery stenosis regions and muscle region (T1w ratio, and T2w ratio) was calculated to assess the vulnerability of the components used in the carotid artery stenosis (see Fig 3b).Results
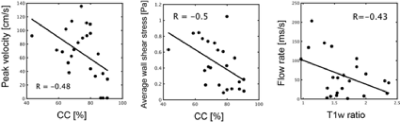
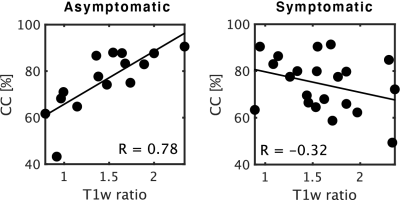
Good correlation was observed between the T1w ratio and minimum flow ratio of the pre-stenotic and highly stenotic regions, which was acquired from the time series of the cardiac cycle (R = -0.43, P < 0.001, see Fig4). However, there was no correlation between each flow parameter and the T2w ratio. Moreover, a strong correlation was observed between the T1w ration and CC in asymptomatic carotid stenosis, on the other hands, no correlation was found in symptomatic carotid stenosis (see Fig 5).Conclusion
The results obtained suggest that the plaque vulnerability may be evaluated both in terms of morphological and component information using 4D-flow MRI and 3D-FSE-MSDE sequences. Therefore, our analysis might contribute to the risk prediction of plaque rupture in carotid artery stenosis.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Balu, N. et al. Carotid plaque assessment using fast 3D isotropic resolution black-blood MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 65, 627-637 (2010).
[2] Markl M, et al. Time Resolved Three Dimensional Phase Contrast MRI. Journal of Magn Reson Imaging 2003;17:499-506. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 18, 396-396 (2003).
[3] Malek, A. Hemodynamic Shear Stress and Its Role in Atherosclerosis. JAMA 282, 2035 (1999).
[4]Rothwell, P., Gibson, R., Slattery, J. & Warlow, C. Prognostic value and reproducibility of measurements of carotid stenosis. A comparison of three methods on 1001 angiograms. European Carotid Surgery Trialists' Collaborative Group. Stroke 25, 2440-2444 (1994).