3767
Prediction of Lymphatic Vessel Space Invasion of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma Based on Enhanced MRI Radiomics Method1Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, China
Synopsis
Cervical Cancer Lymph-vascular space invasion (LVSI) is a type of cancer cells that invade into lymphatics and blood vessels.The typical symptoms are closely related to the distant metastasis of cervical cancer.The selection of treatment strategies for early cervical cancer is particularly important.This study established and verified the radiomics based on enhanced MRI to predict the preoperative LVSI status of cervical squamous cell carcinoma, which can be used as a noninvasive biomarker to better predict the LVSI status of patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma.
Introduction
To explore the predictive value of LVSI in cervical squamous cell carcinoma based on enhanced MRI radiomics method.Method
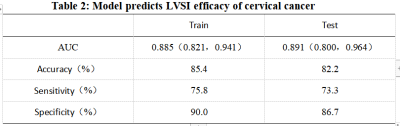
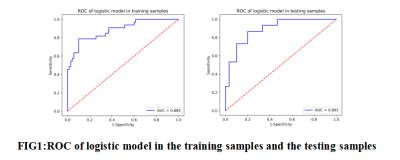
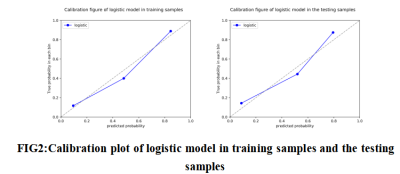
85 patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma confirmed by postoperative pathology were included in the study. Using ITK-SNAP software to manually outline the region of interest (ROI) layer by layer on the enhanced MRI image, then synthesize the tumor volume of interest (VOI), then import the AK analysis software for high-dimensional radiomics feature extraction, and use Spearman correlation Analysis and Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT) method to screen radiomics features and reduce dimensionality, and finally construct a multivariate logistic regression prediction model, and use receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of the model in the training group and the testing group .Results
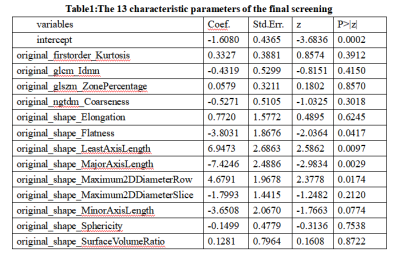
A total of 386 radiomics features were extracted,and finally 13 radiomics features with the highest correlation with the prediction of cervical cancer LVSI were screened out. The accuracy, area under the ROC curve (AUC), sensitivity and specificity of the constructed model for predicting cervical cancer LVSI in the training group were 85.4%, 0.885, 75.8% and 90.0%, respectively, in the testing group were 82.2%, 0.891, 73.3% and 86.7%.Discussion and Conclusion
Traditional imaging features and methods, such as tumor volume, maximum diameter, and functional MRI, etc., although they have certain predictive value for the preoperative LVSI status of cervical cancer, but it ignores the underlying features of the tumor [1,2]. Radiomics can extract a large number of high-dimensional features from tomographic images. It is a non-invasive method for evaluating tumor heterogeneity[3].It has certain advantages and can provide more information.Radiomics is a rapidly developing research field. Its essence is to transform various types of medical imaging picture into high-dimensional imaging feature data, and it can be combined with histology, genomics, proteomics and other data to provide a deeper level of the micro-level information ,which is quantitatively reflected in the macro-level image characteristics, to achieve a more comprehensive description of the heterogeneity of tumor tissues, and to reveal the potential associations between image data and various clinical information such as biochemistry and pathology[4,5] .In this study, the full-area multi-class radiomics feature extraction of cervical cancer was carried out, a total of 386 radiomics features in 7 categories were extracted, and the radiomics information contained in the enhanced MRI image was deeply excavated. Through Spearman correlation analysis and GBDT and other methods to reduce the dimensionality, reasonably reduce the over-fitting effect that redundant features may cause to the model, and finally screen out 13 radiomics prediction features with greater discriminative value, and establish a prediction model.Among them, 9 Shape features and 1 first-order histogram feature show good correlation in predicting the LVSI status of cervical squamous cell carcinoma, which reflects the change in the gray scale of the tumor edge displayed by MRI and the morphological effect. Predicting the status of LVSI is very important. The gray-level co-occurrence matrix is a common method to describe the texture by studying the spatial correlation characteristics of gray levels. This research extracts a gray-level co-occurrence matrix. The gray-scale run-length matrix reflects the image gray-scale information about the direction, the adjacent interval, and the magnitude of change. Among them, the long step size has a larger value on a smoother image, while the short step size has a larger value on a rougher image [6]. The heterogeneity of the tumor is often reflected in the change of the image gray level. Therefore, the features attributed to the gray-level co-occurrence matrix and gray-level run-length matrix have certain relevance to the prediction of the LVSI status of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Therefore, the objectivity and accuracy of the MRI radiomics model is reflected in this study.
In summary, this study established and verified the radiomics based on enhanced MRI to predict the preoperative LVSI status of cervical squamous cell carcinoma, which can be used as a noninvasive biomarker to better predict the LVSI status of patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma. It also provides a basis for formulating individualized treatment plans for patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma to reduce postoperative recurrence and improve the survival rate of cervical cancer patients.
Acknowledgements
NoReferences
[1] Lee MJ, Sayers AE, Drake TM,et al. Malnutrition, nutritional interventions and clinical outcomes of patients with acute small bowel obstruction: results from a national, multicentre, prospective audit. BMJ Open. 2019,9(7):e029235.
[2] Li SJ, Cheng JL, Zhang Y, et al. T2-mapping imaging to assess the pathological features of cervical cancer [J]. China Medical Imaging Technology, 2019, 35(9):136 5-1369.
[3] Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Carvalho S, van Stiphout RG, Granton P, Zegers CM, Gillies R, Boellard R, Dekker A, Aerts HJ. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2012 Mar;48(4):441-6.
[4]Mayerhoefer ME, Materka A, Langs G, et al. Introduction to Radiomics. J Nucl Med, 2020, 61(4):488-495.
[5]Lee SH, Park H, Ko ES. Radiomics in Breast Imaging from Techniques to Clinical Applications: A Review. Korean J Radiol, 2020, 21(7):779-792.
[6]Li Z, Mao Y, Huang W, et al. Texture-based classification of different single liver lesion based on SPAIR T2W MRI images. BMC Med Imaging. 2017 Jul 13;17(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12880-017-0212-x.
Figures