3737
Added Value of Isotropic High-Resolution 3D T2-weighted Imaging in Differentiation of Tis–T1 from T2 Stage in Rectal Cancers
Yu Guo1, Yu Fu1, Jiansen Li2, Lei Zhang1, Zhuo Wang1, and Huimao Zhang1
1The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
1The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
2D T2WI obtained in multi plane is recommend in preoperative assessment of rectal cancer, but 2D acquisition suffers from heavy partial volume effects. As a result, 2D T2WI cannot assess early rectal cancer stages accurately. Comparing with 2D T2WI, 3D T2WI could provide higher spatial resolution, especially the thin slice thickness, with highly reduced partial volume effects in rectal MRI. The purpose of the study was to compare the local-regional staging accuracy of the conventional 2D T2WI protocol and the 3D T2WI protocol for preoperative MR imaging in early rectal cancer patients.
Introduction
Accurate stage differentiation in early rectal cancer patients is important for the selection of appropriate surgical treatment. Local excision is recommended for stage Tis–T1 rectal tumors, while stage T2 tumors are usually treated with total mesorectal excision1-3. Multi-planar T2-weighted images (T2WI) are standardized protocols for rectal cancer staging. However, the differentiation ability of two-dimensional (2D) T2WI to distinguish stage Tis-T1 from stage T2 rectal cancer is not good enough because of its thick slice thickness and partial volume effect. Three-dimensional (3D) isotropic high resolution T2WI can achieve very thin slice thickness and allow to construct images in all planes in one scan, simplifying the scanning workflow4-5. This study aims to investigate the added diagnostic value of the isotropic high-resolution 3D T2WI protocol for preoperative MRI in early rectal cancer patients.Methods
Study Population: A total of 25 pathological proved early rectal cancer patients were recruited in our study. All patients underwent prospective MR examination, including both 2D and 3D T2WI. Our institutional review board approved this retrospective study and waived the requirement for informed consent.MRI Acquisition: MRI examinations were performed with a 3.0-T system (uMR780; Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd.) with phased-array surface coils. 2D fast spin-echo (FSE) T2WI was performed in four different planes (sagittal, axial, coronal and oblique axial). 3D T2WI was performed using modulated flip angle technique in refocused imaging with extended echo train (MATRIX) accelerated by compressed sensing technique, which is specially optimized in contrast and imaging speed for rectal MR imaging. The main MRI parameters are summarized in Table 1.
Image Analysis: Two gastrointestinal radiologists (F.Y. and G.Y., with 11 and 5 years of experience in rectal MRI, respectively) independently reviewed the 2D and 3D T2WI images. The two reviewers were blinded to any clinical or histopathologic information. The 2D and 3D T2WI images were separately analyzed by a 4-week interval, with 2D images assessed firstly. The reviewers independently assessed the radiologic T staging of each rectal tumor. The different results were discussed to reach a consistent diagnosis. Tumoral conspicuity and overall image quality for the 2D and 3D T2WI were scored using a three-point scale: 1, poor; 2, fair; 3, good.
Statistical Analysis: The significance of each variable was assessed with univariable analysis between pathology stage Tis–T1 (Tis, and T1) and stage T2 lesions. The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity for the differentiation of stage Tis–T1 tumors from stage T2 tumors using 2D and 3D T2WI were calculated and compared with the McNemar test. P<.05 was considered to indicate a significant difference. Statistical analyses were conducted by R software, version 3.6.1 (https://www.r-project.org/).
Results
Among the 25 patients, 7 had Tis lesions (carcinoma in situ), 5 had T1 lesions (tumor invading the submucosa), and 13 had T2 lesions (tumor invading the inner circular layer of the muscularis propria only). The 25 patients were divided into two groups: a stage Tis–T1 (Tis, T1) group and a stage T2 group. There were12 patients (median age, 65 years; 8 men) in the Tis–T1 group and 13 (median age, 68 years; 8 men) in the T2 group. Patients' clinical information and MRI findings are not significant difference between the Tis–T1 group and the T2 group. In 25 patients, T category staging accuracy of 2D and 3D T2WI was 75.0% and 92.0%, respectively. The sensitivity of 3D T2WI was higher than that of 2D T2WI (0.92 versus 0.62). The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for T stage differentiation of 2D and 3D T2WI protocols were shown in Figure 1. Tumoral conspicuity and overall image quality on the basis of artifact degree for 3D T2WI were significantly higher than 2D T2WI (Table 2).Discussion
In this study, 3D T2WI showed better local-regional T category lesion staging accuracy than 2D T2WI. 3D T2WI can distinguish anatomic structures of tumor and muscle layer more accurately, because 3D volumetric acquisition could provide higher resolution along slice direction with no gap between slices, which highly reduces the partial volume effects. In addition, isotropic 3D T2WI allows to reform images in any plane, facilitating the recognition of tumor and its adjacent structures (Figure 2). Due to the small sample size, the results were not statistically significant for the difference in diagnostic ability between 2D and 3D T2WI. We hope to collect more patients in our future research to fully explore the diagnostic ability of 3D T2WI.Conclusion
For patients with early rectal cancer, preoperative MR imaging with isotropic high-resolution 3D T2WI showed better accuracy of T category staging and image quality than 2D T2WI. Therefore, 3D T2WI presents added diagnostic value for the differentiation of Tis–T1 from T2 stage in rectal cancers.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
- Stamos MJ, Murrell Z. Management of early rectal T1 and T2 cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(22):6885s-9s.
- Wan LJ, Liu Y, Peng WJ, et al. Submucosal Enhancing Stripe as a Contrast Material-enhanced MRI-based Imaging Feature for the Differentiation of Stage T0-T1 from Early T2 Rectal Cancers. Radiology. 2021;298(1):93-101.
- Detering R, van Oostendorp SE, Meyer VM, et al. MRI cT1-2 rectal cancer staging accuracy: a population-based study. Br J Surg. 2020 ;107(10):1372-1382.
- Gérard JP, Barbet N, Gal J, Dejean C, et al.Planned organ preservation for early T2-3 rectal adenocarcinoma: A French, multicentre study. Eur J Cancer. 2019;108(1):1-16.
- Hori M, Kim T, Onishi H, et al. Uterine tumors: comparison of 3D versus 2D T2-weighted turbo spin-echo MR imaging at 3.0 T--initial experience. Radiology. 2011;258(1):154-63.
Figures
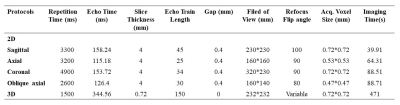
Table 1. MR imaging parameters for 2D and
3D T2WI protocols
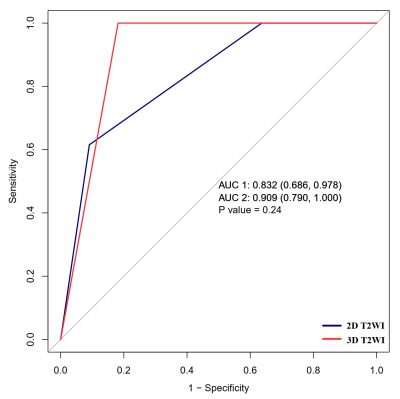
Figure 1. ROC curves for T stage
differentiation of 2D and 3D T2WI protocols.
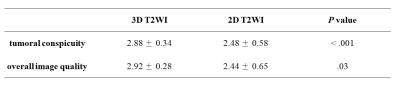
Table 2. Image quality scores for 3D and 2D
T2WI protocols
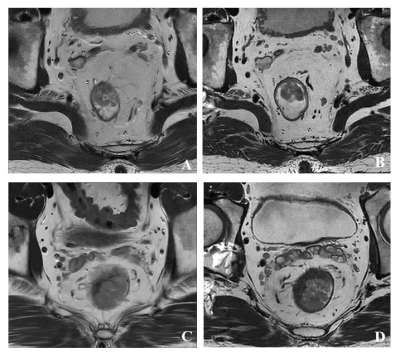
Figure 2. 2D and 3D T2WI images with rectal
cancer. A and B: Images of a 58-year-old man with surgically proved T1 rectal
cancer. A: Oblique axial 2D T2WI shows radiological stage T2; B: 3D T2WI shows
radiological stage T1. C and D: Images of a 49-year-old man with surgically
proved T2 rectal cancer. C: Oblique axial 2D T2WI shows radiological stage T3;
D: 3D T2WI shows radiological stage T2.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2022/3737