3731
The efficacy of Intravoxel incoherent motion in predicting positive margins of radical prostatectomy1Department of Radiology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
Positive surgical margins(PSMs) are associated with local recurrence and distant metastasis of prostate cancer which affect the long-term survival rate of patients1-3. IVIM can simultaneously observe microcirculatory perfusion of blood and intracellular and extracellular water molecules diffusion4. The results of our study show that f-Bi can be used to predict positive margins of radical prostatectomy.
Introduction
Prostate cancer(PCa) is the one of the most common tumor in the male urinary system and the fifth leading cause of cancer death in men5. With the improvement of screening technology, the incidence of PCa is on the rise6. The radical prostatectomy becomes the primary treatment for it. Nevertheless, the appearance of positive surgical margins(PSMs) always predicts that patients are more prone to biochemical recurrence and clinical progress7. Due to the good soft issue resolution of MRI, MRI becomes a very important method to diagnosis PSMs8. IVIM is a double exponential model that uses low b value to provide the information of vascular perfusion and distribution in tissues noninvasively4. Although pathological biopsy is still the only gold criterion to definitive diagnosis the PSMs, IVIM can be used as an evaluation to predict the postoperative situation of the patient with a non-invasive way. In this study, we explored the efficacy of the parameters of IVIM in predicting PSMs after radical prostatectomy and want to provide a useful and convenient method for diagnosis the PSMs.Methods
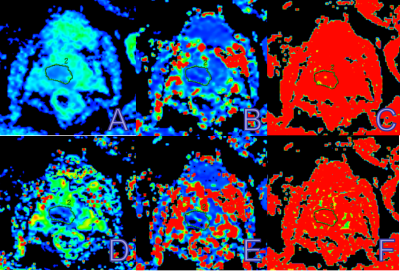
Thirty-seven PCa patients from January 2018 to December 2019 who accordant with all research conditions and recruited IVIM sequences that received 3.0T MR scans and radical prostatectomy were included in our study. Age ranged from 59 to 81 years, mean age for PSMs group was 70±7 years, and for NSMs group was 69±6 years. A 3.0T MR scanner and an 8-channel phased-array surface coil were used. IVIM applied a Echo Planar Imaging, specific parameters were as follows: TR, 2800 milliseconds; TE, 90 milliseconds; FOV, 35×31 cm2; Voxel, 1.4×1.4 mm2; Matrix, 40×32; Slice/thickness, 7.0/1.0 mm. The scan duration is 2 minutes and 31 seconds. The quantitative analysis of IVIM is to use diffusion analysis software calculate of the regions of interest (ROIs) of D-Mono, D*-Mono, f-Mono, D-Bi, D*-Bi, f-Bi. The ROI was placed on the largest slice of the tumor, and contained the whole tumor as much as possible (Figure 1). Our study analyzed the interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) to evaluate consistency between two measurements for each parameter in PSMs group and NSMs group. We used Mann-Whitney U test and independent sample T test to analyze the differences between the two groups. The ability of diagnosing PSMs was analyzed by receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves, including AUC, sensitivity, specificity, and Youden Index (Youden index = sensitivity + specificity - 1). The correlation between parameters in IVIM and postoperative Gleason score was analyzed by Spearman correlation test.Results
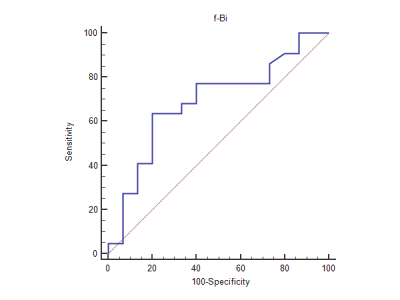
Measurement consistency between two measurements for each parameter in PSMs group and NSMs group was excellent (ICC>0.75). The f-Bi value of PSMs group was significant lower than NSMs group (P≤0.05, Table 1). The ROC curve for f-Bi of IVIM in PSMs group and NSMs group shows that f-Bi is significant in diagnosing it. The sensitivity and specificity and AUC of each parameters were shown in Table 2 and Figure 2. The Spearman correlation test shows a higher negative correlation between f-Bi and postoperative Gleason score(r=-0.490, P<0.05,Table 3).Discussion
In this study, we investigated 6 parameters in IVIM. The result of our study shows that f-Bi is valuable to diagnosis the PSMs, and the othters have no significant difference between the PSMs group and NSMs group. That might because the double exponential can more clearly reflect diffusion of water molecules and microcirculation perfusion, but at the same time, the diffusion of water molecules is not as simple as a double exponential would display9. Compared with NSMs group, the value of f-Bi in PSMs group is lower. This is similar to the research results of Liu et al10. The reason for this maybe is that f-Bi is not only associated with endocapillary microcirculation perfusion, but also includes various other factors, such as complex roles in microcirculation, exchange surface area, liquid flowing in glandular duct and secretion and so on8,11. In our study, Gleason scores of most patient are higher than or equal to 7, the microcirculation in prostate tissue is greatly affected, the atypia of the cells is obvious, and glands of tumor are abnormal and the functions of them are also affected, All of this have an influence on the value of f-Bi. So f-Bi in IVIM can be a potential non-invasive method in predicting PSMs in clinical.Conclusion
The f-Bi in IVIM is promising and valuable in predicting positive margins of radical prostatectomy.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement goundReferences
1.Chapin BF, Nguyen JN, Achim MF, et al. Positive margin length and highest Gleason grade of tumor at the margin predict for biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy in patients with organ-confifined prostate cancer [J]. Prostate Cancer Prostatic.2018, 21(2):221-227.
2.Tewari A, Sooriakumaran P, Bloch DA,et al.Positive surgical margin - and perioperative complication rates of primary surgical treatments - for prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing gretropubic,laparoscopic and robotic prostatectomy[J].Eur Urol.2012,62(1):1-15.
3.Xiaodong Xiao, Xiaolei Ye, Guobing Feng. Research progress on clinical significance of positive margin after radical prostatectomy [J. Zhejiang medical. 2015(8):710-713+716.
4.Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology. 1988 Aug;168(2):497-505.
5.Richman DM, Tirumani SH, Hornick JL, et al. Beyond gastric adenocarcinoma: M ultimodality assessment of common and un-common gastric neoplasms [J]. Abdom Radiol (N Y), 2017 (42):124-140.
6.Dingwie Ye, Yao Zhu. Epidemiological overview and enlightenment of prostate cancer in China [J]. Chinese journal of surgery.2015, 53(4):249-252.
7.Zheng Zhang, Kenan Zhang, Baoan Hong, Jiufeng Zhang, Bowen Zhou, Kan Gong. Analysis of related influencing factors of positive margin after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Oncology.2019, 46(06):299-302.
8.Guokun Liu, Jianfei Li, Yanchao Liu, Yufang Wang. Combined Application of IVIM-DWI and DCE-MRI in Diagnosis of Prostate Diseases [J]. Shandong medical journal.2020, 60(03):75-77.
9.Hui Li. Diagnostic Value of Single Index, Double Index and Stretch Index Model for Prostate Cancer [D]. Wuhan university. 2018
10.Liu x, Peng W, Zhou L, et al. Biexponential apparent diffusion values in the prostate comparison among normal Coefficients Tissue, prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatities [J]. Korean J Radiol, 2013,14(2):222-232.
11.Hui Wu, Jianjun Ren, Guangming Niu, et al. The value of IVIM in identifying prostate cancer, glandular and stromal hyperplasia [J].Journal of Inner Mongolia Medical University, 2017,39 ( 02 ) : 107-111
Figures