3705
Correlation between Ki67 expression and DKI in ovarian cancer1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Dalian Engineering Research Center for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging, Dalian, China
Synopsis
Symptoms of ovarian cancer are concealed, it is difficult to diagnose early, and the mortality rate is very high. DKI imaging can sensitively detect microstructure changes in tumor tissue and help preoperative assessment of Ki67 expression. This paper aims to study the correlation between Ki67 expression and DKI in ovarian cancer. The results show that the MK, Ka, Kr, MD, Da and Dr values in the DKI parameters have obvious correlation with Ki-67 expressions, and that the MK, Ka, and Kr values in DKI parameters were positive correlation with Ki-67 expression levels, and the difference was statistically significant.
Purpose
This paper aims to study the correlation between Ki 67 expression and DKI parameters in ovarian cancer.Introduction
In recent years, the death from ovarian cancer has occupied the first place of all kinds of gynaecological tumors, and ovarian cancer has posed a serious threat to women's lives [1]. Research shows that cell proliferation antigen Ki67 reflects cell division and proliferation activity [2], single immunomass is used to assess ovarian cancer is not easy[3],while hydromolecules[4] in DKI reaction tissue are more sensitive and specific, the characteristic parameters are more sensitive and specific. This paper focuses on the relevance of Ki67 expressions to DKI parameters in ovarian cancer. Objective To evaluate the results of tumor-related pathological indicators with DKI, to facilitate diagnosis and treatment of disease and improve the quality of patients' survival.Methods
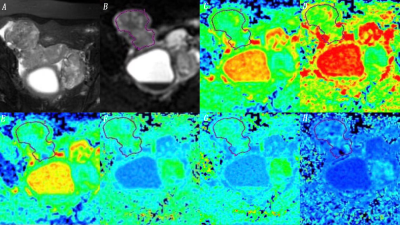
Retrospective collection of 24 cases of ovarian cancer patients with surgery and pathological confirmation in 2015 - 2021. All patients underwent abdominal MR examinations (Signa HDxt, GE Medical Systems, USA) (scanning parameters are shown in table 1). The original axial digital image of the DKI sequence is transmitted to the GE SDC-ADW 4.6 workstation (Sun Microsystems, Santa Clara, California), reprocessing using Funcool software. Based on the pathological position of the pathological pathology obtained on t2 weighted or DWI image, the diagrams of MK, Ka, Kr, MD, Da and Dr were automatically constructed and reviewed by two observers with 10 and 15 years of pelvic imaging experience, respectively. According to the fat suppression of T2WI(Figure 1), artificial areas of interest (ROIs) are drawn along the edge of tumor with the largest in the real area (we choose the entities in the tumor). Repeat measurements three times, calculate the average of three measurements. Record MK, Ka, Kr, MD, Da and Dr values. The consistency of the measurements of the two groups is tested using the intra-group correlation coefficient (Intra-group corruption, ICC). The correlation between the above value and the expression of Ki67 was compared with Pearson test. Use scattering diagram to assess the relevance.Results
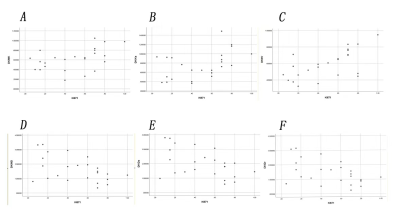
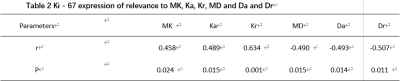
MK is positive for the expression of Ki-67 (r = 0.458, P-0.05), Ka and Ki-67 (r = 0.489, P-0.05), Kr and Ki-67 (r = 0.634, P-0.01), MD negatively correlated with Ki-67 expressions (r = 0.490, P-0.05), Da and Ki-67 expression negatively (r = 0.493, P-0.05), Dr and Ki-67 expression negatively correlated with (r = 0.507, P-0.05) (as shown in table 2, Figure 2)Discussion
The level of expression in Ki-67 is closely related to the degree of malignancy of tumor[4]. The higher the Ki-67 expression level, the more active the tumor cell proliferation, the rapid proliferation of tumor cells and neoplasms, which caused necrosis, haemorrhage, cyst changes, etc. and further increased the complexity of tumor microstructure[5] . The study on ovarian cancer showed that MK, Ka and Kr values were positive with Ki-67, while MD, Da and Dr values were negatively correlated with Ki-67 expression levels. Our research shows that DKI may be a promising imaging method to evaluate Ki 67 expressions.Conclusion
Ki67 expression and DKI characteristic parameters have correlation in ovarian cancer.Acknowledgements
None.References
[1]CHU Hui -hui, LIU Qian.Research Progress in Clinical Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. J Int Obstet Gynecol,August 2021,Vol. 48,No.4:4443-6.
[2] Su Jing, Zheng Jie. Tumor marker Ki - 67 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen and its application in pathological diagnosis.Chin J Pathol,August2009,Vol.38,No.8:568-70.
[3] JIANG Liqin, DENG Wen, GAN Jiabing, HU Kai, ZHAO Na. Clinical value of serum HE4, CA125 and ROMA index in early diagnosis of ovarian cancer. Contemporary Medicine,Oct.2021,Vol.27 No.29 Issue No.616:22-2.
[4] Fang Mengjia,Liu Weiwu,Yang Dan,Huang Sa.Research Progress on the Prediction of Ki -67 Expression in Ovarian Cancer Using Different Diffusion Models of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Int J Geriatr,September 2021,Vol.42, No. 5:301-3.
[5] ZHANG Dao-chun,HUANG Jin-biao,LIU Zi-shan,ZHOU Kai,ZHANG Min-ge,PAN Shan-jun,YU Hai-yan,CHEN Wei-cui. Relationship between the quantitative parameters of diffusion kurtosis imaging and the Ki-67 expression level in rectal adenocarcinoma. Chinese Journal of General Practice,January 2021,Vol.19,No. 1:99-102.
Figures