3687
Comparison of detection rate using compressed SENSE accelerated 3D T2-weighted FSE acquisitions and standard 2D acquisitions in bladder cancer1Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China, 2Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
Synopsis
Conventional T2-weighted images using two-dimensional (2D) fast-spin-echo (FSE) are commonly used in clinical scanning of bladder, with a drawback of high missing rate. This study compared the BCa detection rate between compressed SENSE accelerated 3D and conventional 2D FSE T2WI within the same patients. The results showed that the accelerated 3D FSE T2-weighted acquisitions had excellent performance at detecting lesions smaller than 3cm and on the uncommon site of bladder wall.
Introduction
Multiparametric magnet resonance imaging (MRI) of the bladder has become a reliable technique for the detection, localization and characterization of bladder cancer (BCa). Routine two-dimensional (2D) T2-weighted (T2WI) imaging is commonly used in clinical scanning of bladder, which adopt fast-spin-echo (FSE) sequence with a slice thickness of 3-4 mm, acquiring at least two planes of multiplanar (axial, coronal and sagittal).1 However, it is hard to identify the small lesions or lesions presented as slightly thickened bladder wall on the conventional 2D T2WI images. While three-dimensional (3D) FSE T2WI acquisitions with thinner scanning slice should enable reformation of an arbitrary plane perpendicular to the tumor base, which may help to improve the detection rate of BCa.2 However, the conventional 3D T2WI technique is also limited by the long scan time to achieve high resolution BCa detection in daily clinical practice. Recently, a combination of parallel imaging and compressed sensing (Compressed SENSE) has been developed to dramatically accelerate the acquisition while preserving high image quality.3 Therefore, the purpose of this study was to compare the BCa detection rate between compressed SENSE (CS) accelerated 3D acquisition and 2D acquisition within the same patients.Methods
The study protocol was approved by our Institutional Medical Ethics Committee and all patients recruited signed the informed consents. Twenty-five consecutive patients entered this study between May 2021 and October 2021. Patients were eligible if they were suspected of bladder cancer by ultrasound. For each patient, both standard 2D MRI examination and CS accelerated 3D optimized MRI examination were performed before any treatment on a 3T clinical system (Elition, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands ) using a 32-channel body-array coil. The scanning parameters for T2-weighted FSE acquisitions included: 3D axial imaging with a resolution of 0.8 × 0.8 × 0.8 mm3 and gap of -0.4mm, FOV=300 × 422 × 180 mm3, TR/TE=1250/149ms, NSA =2, CS acceleration factor = 10, and the total acquisition time =6:33 min. Coronal and sagittal images were then reformatted. Conventional 2D T2-weighted acquisitions were also conducted in axial,, coronal and sagittal orientations for comparison, with the following parameters: a resolution of 0.9 × 0.9 × 4 mm3 and gap of 1mm, TR/TE=3924/120ms, NSA =1, the total acquisition time in 3 orientations =10:36 min.All images were independently presented to two radiologists (both with 3 years of bladder MRI experience) in random order in two sessions. For each patient, both MR images sets were anonymized and randomized into two equally sized groups. To reduce rater bias, images of the same patient were read in two separate sessions at least 3 weeks apart. The radiologists documented details about every lesion, including lesion location, morphology, largest diameter, and locations on T2WI images. The urologic evaluation in cystoscopy included the description of lesion number, size, morphology, and location. A standardized form with a descriptive schematic map was used for cystoscopy, which served as a standard reference for radiologic assessment.
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (IBM SPSS 20, Chicago, IL). Fisher’s exact tests (two-sided) were used to test for significant difference (p<0.05) in the detection rates with respect to tumor size and each localization.
Results
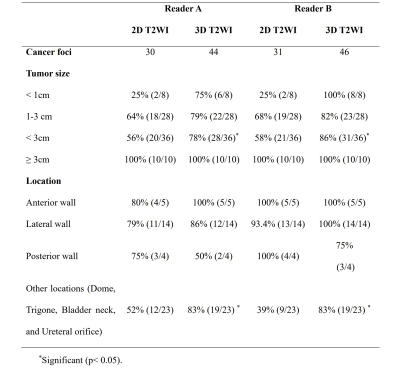
All 25 patients showed organ-confined (stage pT3) disease. A total of 46 lesions were identified by cystoscopy, of which 36 lesions were non-muscle-invasive BCa. Table 1 summarized the detection rates of BCa foci with respect to their tumor size and localization. Stratification against lesion size (diameter) showed significant differences for tumor size < 3cm (Reader A: p=0.021; Reader B: p= 0.008). Stratification against localization revealed conventional 2D T2-weighted acquisitions had a significant higher missing rate for lesions on the sites of dome, trigone, bladder neck, or ureteral orifice (Reader A: p=0.029; Reader B: p= 0.003).Discussion and Conclusion
Our preliminary results demonstrated that significant higher detection rates when performing the compressed SENSE accelerated 3D FSE T2WI imaging, especially for those small lesions on uncommon sites . The accelerated 3D FSE T2-weighted acquisitions take advantages in thinner-slice scanning and meantime allowing interactive reconstruction in any orientation in a single scan, which we believe are compatible with the properties of BCa—multiple and non-uniformity, and meantime are helpful in finding the lesions on the uncommon site, as showed in figure 1. Therefore, the accelerated 3D FSE T2-weighed technique can be a viable alternative to optimize the protocol of VI-RADS.Acknowledgements
NoneReferences
1. Panebianco V, Narumi Y, Altun E, et al. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Bladder Cancer: Development of VI-RADS (Vesical Imaging-Reporting And Data System). Eur Urol. 2018;74(3):294-306. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2018.04.0292. Lim KK, Noe G, Hornsey E, Lim RP. Clinical applications of 3D T2-weighted MRI in pelvic imaging. Abdom Imaging. 2014;39(5):1052-1062. doi:10.1007/s00261-014-0124-y
3. Yoneyama M, Kosuke M, Johannes P et al. Noise Reduction in Prostate Single-Shot DW-EPI utilizing Compressed SENSE Framework. Proc. ISMRM.2019:1634.
Figures
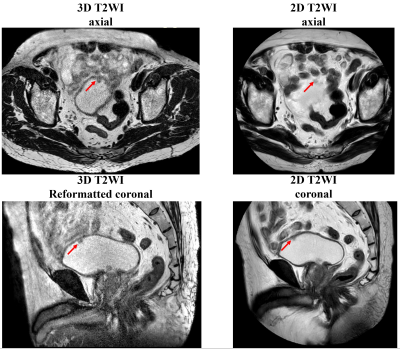
Figure 1. Representative images acquired on a patient with multiple BCa using CS accelerated 3D FSE T2-weighted acquisitions show better delineation of bladder wall and small lesions on axial orientation. The reformatted coronal images from axial 3D T2WI showed more sharpened contour of tumor, while poor delineation of bladder wall than conventional coronal T2WI.