3674
The value of APTw imaging combined with ALP to identify Prostate Cancerwith or withoutBone Metastasis
Chen Lihua1, Song Qingwei1, Gao Mingli1, Wang Jiazheng2, Lin Liangjie2, Wu Zhigang2, and Liu Ailian1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, DaLian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, DaLian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) imaging is a novel MRI imaging tool for detection of amide protons in mobile cellular proteins and peptides. This study aims to assess and differentiate prostate cancers with and without bone metastasis using APTw MRI and alkaline phosphatase (ALP).Results show that prostate cancers with bone metastasis were associated with significantly higher APTw and ALP values than those without bone metastasis. The diagnostic efficiency is the highest using APT combined with ALP. Therefore, APTw imaging together with ALP may provide an more effective tool to predict the aggressiveness of prostate cancer.
Synopsis
Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) imaging is a novel MRI imaging tool for detection of amide protons in mobile cellular proteins and peptides. This study aims to assess and differentiate prostate cancers with and without bone metastasis using APTw MRI and alkaline phosphatase (ALP).Results show that prostate cancers with bone metastasis were associated with significantly higher APTw and ALP values than those without bone metastasis. The diagnostic efficiency is the highest using APT combined with ALP. Therefore, APTw imaging together with ALP may provide an more effective tool to predict the aggressiveness of prostate cancer.Summary of main findings
Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) MRI together with alkaline phosphatase (ALP)may provide an effective tool to predict the aggressiveness of prostate cancer, which yielding higher diagnostic confidence than using APTw imaging or ALP separately.Purpose
To explore the potential of APTw MRI and ALP for differential diagnoses of prostate cancers with and without bone metastasis.Introduction
Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) imaging is a novel MRI imaging tool to detect amide protons in mobile cellular proteins and peptides 1. Previous studies have shown the potential of APTw imaging in the diagnoses of central nervous system diseases and different kind of cancers, including the prostate cancer2-3.This studyaimsto differentiate prostate cancers with and without bone metastasis using APTw MRI and ALP.Materials and Methods
This study was approved by the local IRB.A total of 38 pathology-proven prostate cancers and ECT-proven with or without bone metastasis patients (mean age 70.13±7.49 years, range 54-83 years) were included in the analysis, and recorded the alkaline phosphatase (ALP) values of all patients. The patients were categorized into two groups, Group A with bone metastasis and Group B without bone metastasis, and all patients underwent MRI at 3.0T MRI scans (IngeniaCX, Philips Healthcare, the Netherlands) with a 32-channel torso and spine coil. Sequences: 3D amide-proton-transfer weighted imaging (3D-APT), T2WI SPAIR, and diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) (parameters listed in Table 1). All data were transferred to the IntelliSpace Portal workstation (PhilipsHealthcare) and interpreted independently by two radiologists (Yunsong L and Lihua C, with 3 and 5 years of experiences respectively, blinded to the clinical information of the patients).Regions of interest (ROIs) were manually placed on the fused APTw and DWI images on the slice showing the largest lesions to cover the whole lesion in the slice (Figure 1). The average APTw (MTRasym) values were calculated to minimize measurement bias. Measurements consistency of APTw values between the two observers was tested using intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) with SPSS (IBM). APTw and ALP values were compared between Groups A and B using the Mann-Whitney Utest. Logistic regression and ROC plot were used to evaluate the diagnostic efficiency of prostate cancers with bone metastasis. Delong test was used to compare the diagnostic efficacy.Results
Measurements by the two observers were in well agreement. APTw and ALP values in Group A were significant higher than in group B (P<0.05)(Table 2).The diagnostic efficiency of APT combined with ALP was higher than those of APT or ALP separately (P>0.05)(Table3, Figure 2).Discussion and Conclusion
Prostate cancers with bone metastases were observed with significantly higher APTw and ALP values than those without bone metastasis, which might be attributed to higher proliferation rate and hence higher aggressiveness in the cancers with metastasis. In addition, the diagnostic efficiency of APT combined with ALP was higher than those of APT or ALP when used separately. In conclusion, APTw imaging together with ALP may provide an more effective tool to evaluate the metastasis potential of prostate cancers.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]. Ward KM, Aletras AH, Balaban RS. A new class of contrast agents for MRI based on proton chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST)[J].J Magn Reson, 2000, 143(1):79-87. DOI:10.1006/jmre.1999.1956. [2]. Debnath A, Gupta RK, Singh A. Evaluating the role of amide proton transfer (APT)-weighted contrast, optimized for normalization and region of interest selection, in differentiation of neoplastic and infective mass lesions on 3T MRI. Mol Imaging Biol. 2019; doi: 10.1007/s11307-019-01382-x. [3] Takayama Y, Nishie A, Sugimoto M, et al. Amide proton transfer (APT) magnetic resonance imaging of prostate cancer: comparison with Gleason scores. MAGMA 2016; 29(4):671-679.Figures
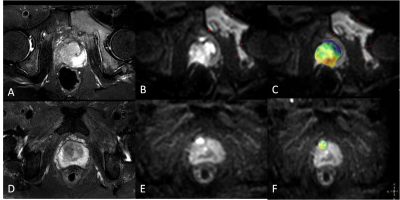
Figure 1 (A-C) images
for a59-year-old manwithprostate cancer with bone metastasis (seered arrows): T2WI
image (A), DWI image (B), APTwimage of the prostatefused with DWI image (C). The
tumor showedthe APTw value of 3.35 %, ALP value of 279 U/L.
(D-F) images for a72-year-old man with prostate
cancer without bone metastasis: T2WI image (D),DWI image (E), APTwimage of the
prostatefused with DWI image (F). The tumor showed theAPTw value of 1.3 %, ADC
value of53 U/L.
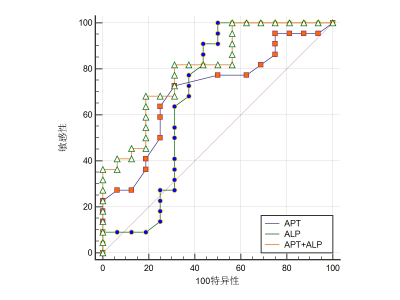
Figure 2The ROC of APT, ALP and (APT+ALP) in
differentiation of prostate cancers with and without bone metastasis.

Table
1 Scan parameters
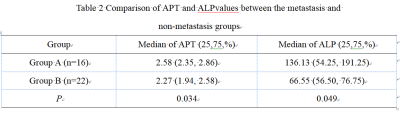
Table 2 Comparison of APT and ALPvalues
between the metastasis and non-metastasis groups
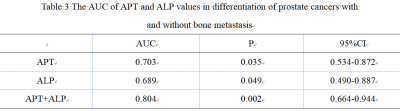
Table 3 The AUC of APT
and ALP values in differentiation of prostate cancers with and without bone metastasis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2022/3674