3672
Isotropic 3D high-resolution T2-weighted breast MRI with a deep learning constrained Compressed SENSE reconstruction: a pilot study1Department of Radiology, West China hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, 2Department of Clinical Science, Philips Healthcare, Chengdu, China, 3Department of Application, Philips Healthcare, Chongqing, China
Synopsis
2D T2-weighted (T2WI) breast MRI is prominently used for the identification of the colliquative necrosis and cysts, and it can also contribute to the characterization of lesions as benign or malignant. However, 2D imaging is routinely used in clinical practice, which has lower resolution, slice gaps, and may suffer distortion to delineate the breast lesions. In this study, we applied the Compressed-sensing Artificial Intelligence (CS-AI) framework to further increase the spatial resolution and reduce the scan time. The results of this study demonstrated that the high-resolution T2-weighted 3D CS-AI can provide further benefits to improve the depiction of diagnostic findings of breast lesions.
Synopsis
2D T2-weighted (T2WI) breast MRI is prominently used for the identification of the colliquative necrosis and cysts, and it can also contribute to the characterization of lesions as benign or malignant. However, 2D imaging is routinely used in clinical practice, which has lower resolution, slice gaps, and may suffer distortion to delineate the breast lesions. In this study, we applied the Compressed-sensing Artificial Intelligence (CS-AI) framework to further increase the spatial resolution and reduce the scan time. The results of this study demonstrated that the high-resolution T2-weighted 3D CS-AI can provide further benefits to improve the depiction of diagnostic findings of breast lesions.Purpose
T2-weighted (T2WI) breast MRI is prominently used for the identification of the colliquative necrosis and cysts, and it can also contribute to the characterization of lesions as benign or malignant [1]. However, routine T2WI breast MRI in clinics is 2D imaging, which has lower resolution, slice gaps and may suffer distortion to delineate the breast lesions. The ability to acquire T2-weighted breast images with 3D imaging should provide further benefits to improve the depiction of diagnostic findings of breast lesions in any orientation. However, the 3D acquisition is usually limited by the long scanning time, which prevent its usage in daily clinical practice. Compressed sensing (CS) could be used to achieve scan time reduction beyond that possible with conventional parallel imaging acceleration conventional parallel imaging acceleration. However, using very high acceleration factors with very high resolution can also result in degradation of image quality due to insufficient noise removal. Recently, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into MRI reconstruction has attracted much attention to further accelerate MR scans, in which a novel deep neural network was introduced and showed superior performance for reconstructing the knee image from highly undersampled k-space data [2]. This study aims to acquire isotropic 3D high-resolution T2-weighted breast images with reduced scan time and compare the image quality between images reconstructed with CS-AI and conventional CS.Methods
This IRB-approved study was performed on a 3T MR scanner with a dedicated 18-channel phased-array breast coil (Elition, Philips Healthcare). From September 2021 to October 2021, 12 patients (12 male; age range, 28-65 years) suspected breast cancer assessed by clinical evaluation were enrolled and underwent breast MRI examinations. All lesions were histopathologically confirmed by biopsy and were included for final analysis.The details of imaging parameters of 2D T2WI sequence were listed: FOV= 300×340 mm2, TR/TE=4300/70ms, slice thickness=4mm, acquired voxel size=1×1×4mm3, bandwidth= 822 Hz, acquisition time (TA)=146s, acceleration factor of GRAPPA=4. The imaging parameters of 3D T2WI CS sequence was also listed: FOV= 340×340 mm2, TR/TE=1500/129ms, slice thickness=0.8 mm, flip angle=90°, acquired voxel size=0.8×0.8×0.8mm3,bandwidth=822Hz/Px,echo-train length=240, CS acceleration factor=12, and the acquisition time TA for all the enrolled subjects =160s. In comparison, 3D CS-AI sequence used the same parameters as CS sequence, and the CS reconstruction chain is merely replaced by a convolution neural network (CNN) reconstruction.
Subjective image quality was independently assessed by two radiologists using a 5-point Likert scale (1=poor, 5 = excellent) in terms of lesion conspicuity and morphology, detail structure, the overall image quality, diagnostic information for breast lesions[3]. For quantitative objective assessment, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and lesion contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) were also measured for comparison. ROI of lesion was carefully drawn on the slice with the largest cross section of the lesion respectively. And ROI of tissue was placed on the nearby side of lesion (where the glands are homogeneous). Inter-observer agreement was assessed using Cohen’s kappa efficiency and intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) respectively for subjective and objective assessments. The Likert scales and quantitative parameters were compared using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and paired t-test. A p value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Compared to conventional 2D T2WI imaging, The 3D CS-AI and 3D CS imaging can superior higher spatial resolution (0.8×0.8×0.8mm3 vs 1×1×4.0 mm3), with the scan time slightly increased (160svs146s). Compared to 2D T2WI imaging and 3D CS imaging, the 3D CS-AI showed higher image scores in lesion conspicuity and morphology, detail structure, the overall image quality and diagnostic information (Table 1 & Figure 1). Moreover, there was significant difference in detail structure and diagnostic information (P<0.05, Table1).The 3D CS-AI can provide higher CNRs analysis when compared to 2D T2WI imaging and 3D CS imaging (mean CNR values: 1.50±2.56 vs. 1.35±2.65 vs. 0.82±2.38), however it didn’t show a significant difference. For SNRs analysis, the 3D CS-AI showed a significantly higher values when compared to 3D CS imaging (mean SNR values :5.22±1.74 vs. 4.56±1.76). There was no significant difference between 3D CS-AI and 2D T2WI (mean SNR values :5.22±1.74 vs. 6.95±1.94)
Conclusions
The results of this study demonstrated that the high-resolution T2-weighted 3D CS-AI can provide further benefits to improve the depiction of diagnostic findings of breast lesions. A large clinical study is underway to validate the diagnostic value of this technique.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]Han SH, Yi An Y, Joo Kang B, Hun Kim S, Jae Lee E. Takeaways from Pre-Contrast T1 and T2 Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Women with Recently Diagnosed Breast Cancer. Iran J Radiol. 2016 Jul 18;13(4):e36271. doi: 10.5812/iranjradiol.36271. PMID: 27895875; PMCID: PMC5116989.
[2] Knoll F, Zbontar J, Sriram A, et al. fastMRI: A Publicly Available Raw k-Space and DICOM Dataset of Knee Images for Accelerated MR ImageReconstruction Using Machine Learning. Radiol Artif Intell. 2020;2(1):e190007.
[3] Filli L, Ghafoor S, Kenkel D, et al. Simultaneous multi-slice readout-segmented echo planar imaging for accelerated diffusion-weighted imaging of the breast[J]. European journal of radiology, 2016, 85(1): 274-278.
Figures
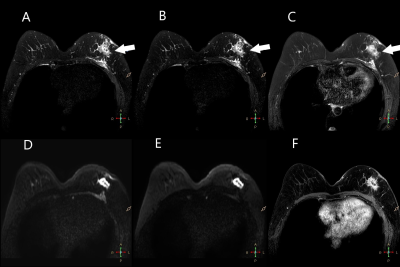
Figure 1. A 47 year-old woman with breast cancer in the left breast. A, T2WI 3D CS-AI; B, T2WI 3D CS; C, 2D T2WI; D, conventional DWI with b-value of 750 s/mm2; E, conventional DWI with b-value of 1500 s/mm2; F, T1w DCE. The irregular mass (white arrow) shows heterogeneous enhancement and equal-to-high signal intensity on the fat-saturated T2-weighted images. T2WI 3D CS-AI image shows better detail structure and less anatomic distortion.
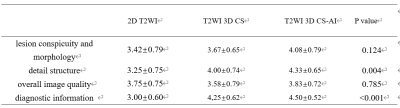
Table 1. Subjective image quality assessment of conventional T2WI 、CS 3D-T2WI and AI 3D-T2WI