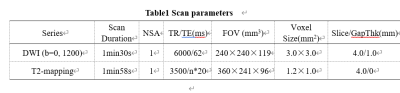
3671
Diagnosis value of T2 mapping on the of vascular invasion in rectal Cancer1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Rectal cancer is a malignant tumor with extremely high morbidity and mortality. It will change the physical microenvironments, but it is still a challenge to differentiate the rectal cancer with and without vascular invasion. T2 mapping imaging is a quantitative biomarker with good repeatability and stability. T2 mapping can non-invasively visualize and quantify tissue components (such as edema, fibrosis etc )without contrast agent. This study aims to assess the performance of T2 mapping on differentiating rectal cancer with and without vascular invasion, which may yield higher diagnostic confidence.
Summary of Main Findings
This study showed that T2 mapping imaging maybe provide a non-invasive tool to evaluate the invasion of rectal cancer which may benefit the clinical diagnosis of the invasion of rectal cancer.Introduction
The incidence of rectal cancer in our country is increasing year by year[1] . Rectal cancer is a malignant tumor with extremely high morbidity and mortality. It is particularly important to find out whether it invades surrounding tissues as early as possible. T2 mapping imaging is a quantitative biomarker, it will be different for different tissue, such as edema, fibrosis etc. For the rectal cancer, it will differ greatly in terms of pathogenesis, biological behavior, histological morphology for with and without the vasculature invasion. T2 value maybe also different, around the tumor, which it should could be changed with the vasculature vascul ature invasion. The purpose of this study was to investigate the usage of the T2mapping technique in evaluation the invasion of rectal cancer[2].Material and Methods
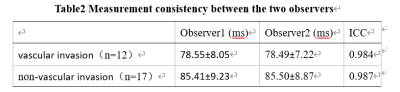
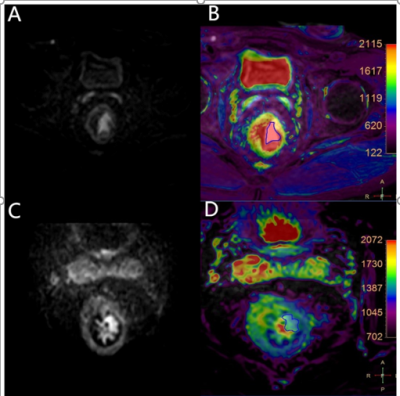
This study has been approved by the local IRB. This retrospective study included 29 patients with rectal cancer in the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University hospital from March 2019 to October 2021. All of the patients were divided into two groups based on MR imaging: vascular invasion groups (n=12, 6 males, 6 females, average age of 65±12.3 years) and non-vascular infringement group (n=17, 8 males, 9 females, average age of 61±11.3 years.) All data were transferred to the IntelliSpace Portal workstation (Philips Healthcare) and interpreted independently by two radiologists(with 3 and 5 years of experiences respectively). The MR protocols included T2- mapping and DWI sequences. Regions of interest (ROIs) were manually placed on the fused DWI and T2-mapping images on the slice showing the largest lesions to cover the whole lesion in the slice (Figure 1). Measurements consistency of T2-mapping values between the two observers was tested using intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) with SPSS (IBM).T2-mapping values were compared between Groups A and B using the independent sample tt test.The ROC curves were plotted to analyze the diagnostic efficacy of vasculature invasion of rectal cancer using T2 timevalues.Results
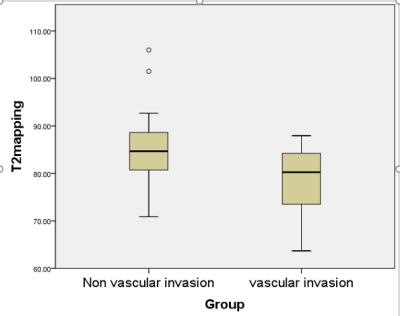
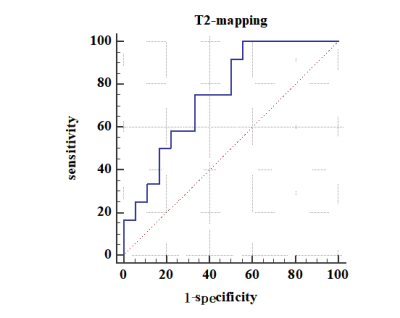
The consistency of measurements by two radiologists was in good agreement (ICC> 0.75)(Table2).Compared with the non-vascular invasion group, decreased T2 time in the vascular invasion group (85.44 ± 8.72 ms vs. 78.52 ± 7.59 ms) was found with the significant statistically difference (t = -2,234, p < 0.05) (Figure 2). In the ROC curve, the area of AUC of the sensitivity of T2 time values is 0.725 with the sensitivity of 75% and the specificity of 64.7% (Figure 3).Discussion and Conclusion
Rectal cancers with vascular invasion were observed with lower T2 time than those without vascular invasion, which might be attributed due to that the increased tumor cell density which may cause the decreased water molecules gradually . It maybe resulted in the decrease of the T2 value of the invasion group.In conclusion, T2 mapping imaging maybe provide a non-invasive tool to evaluate the invasion of rectal cancer which may benefit the clinical diagnosis of the invasion of rectal cancer..
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Wan D, Ailian L, Anliang C, et al. Comparation of amide proton transfer-weighted and T2 mapping in quantifying rectal cancer with and without chemotherapy: a preliminary study . Chin J Magn Reson Imaging, 2021, 12(7)
[2] Timo Alexander Auer, Maike Kern, Uli Fehrenbach. T2 mapping of the peritumoral infiltration zone of glioblastoma and anaplastic astrocytoma. The Neuroradiology Journal , 2021, , Vol. 34(5)
Figures