3610
Static and temporal dynamic changes of intrinsic brain activity in adolescents and adult OCD patients1The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Synopsis
This study used a novel statistical analysis-2x2 interaction effect to differentiate OCD patients from healthy controls in both adolescents and adults. We analyzed a classical index-low frequency fluctuation amplitude(ALFF) and drew a convincing conclusion that some regions had a correlation with people in different age and symptoms in OCD patients. Originally, we proposed a novel strategy of dALFF which allows estimating dynamics of intrinsic brain activity with patients. Compared to static indexes, dynamic indexes might be used as a powerful supplement differentiating patients from different age, helping us obtain a more comprehensive understanding of neural activity.
Synopsis
This study used a novel statistical analysis-2x2 interaction effect to differentiate OCD patients from healthy controls in both adolescents and adults. We analysed a classical index-low frequency fluctuation amplitude(ALFF) and drew a convincing conclusion that some regions had a correlation with people in different age and symptoms in OCD patients. Originally, we proposed a new strategy of dALFF which allows estimating dynamics of intrinsic brain activity. Compared to static indexes, dynamic indexes might be used as a powerful supplement differentiating patients from different age, helping us obtain a more comprehensive understanding of neural activity.Introduction and purpose
Obsessive compulsive disorder(OCD) affects 1% to 3% of the population and is characterized by intrusive thoughts(obsessions) and repetitive behaviors(compulsions). Alterations in habitual behaviors and thoughts manifest in affect, motor planning, and cognition in OCD1. OCD is hypothesized to be accompanied with altered spontaneous brain activity. However, the conclusion is not inconsistent. The inconformity may be partially due to the mixed effect of age. To examine the effect of age of onset on this inconformity, we evaluated the spontaneous brain activity measured by static and dynamic ALFF followed by two-way ANOVA2.Materials and Methods
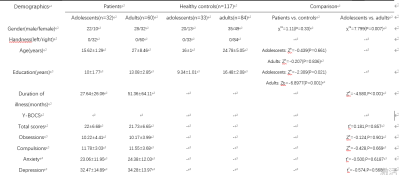
This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Review Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, with neuroimaging and clinical data from OCD patients and typically developing healthy controls subjects(i.e. free of psychopathology), including children and adults. Four groups of subjects were included: OCD patients(32 adolescents, and 60 adults); healthy controls(33 adolescents, and 84 adults). Ninety-two patients were included in the case group after meeting the following inclusion criteria:(1) OCD diagnosed by two psychiatrists according to the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders(SCID); (2) A total score on the Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale(Y-BOCS) greater than or equal to 16; (3) age ranging from 12 to 50 years; (4) dextromanuality; (5)first onset without any treatment. The course of illness and the evaluation of Y-BOCS were obtained from clinical interviews. One hundred and seventeen healthy individuals group matched for age, gender, and education were recruited through advertisements and met the same criteria as the patients.A two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was employed for whole-brain ALFF and dALFF comparisons to analyze the interaction effects between the diagnosis group (OCD vs. controls) and age status (pediatrics vs. adults). The results were set at a threshold of P < 0.05 (combined height threshold P < 0.005 and cluster extent threshold at k > 20, GRF corrected), and the Monte Carlo simulation was applied, taking into consideration both the individual voxel thresholding and cluster size.
Results
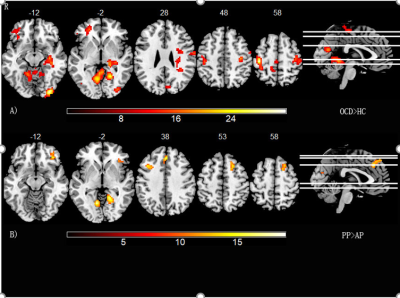
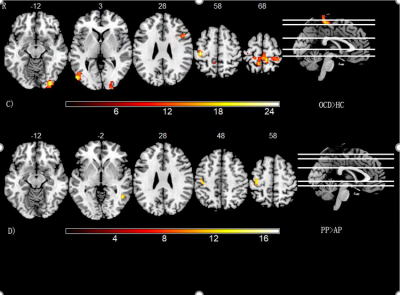
We found significantly increased ALFF in OCD patients compared with controls in the right parahippocampal gyrus , right hippocampus and temporal lobe which belong to temporal network, precuneus and posterior cingulate containing in default mode network; precentral gyrus, bilateral postcentral gyrus and paracentral lobe in the sensorimotor network and cerebellum. The dALFF in left precentral and postcentral gyrus, the left precuneus , right inferior and left middle occipital gyrus, middle temporal and medial frontal gyrus were higher in OCD patients than controls.Compared with adult OCD patients(N=60), pediatric patients(N=32) showed higher ALFF in default mode network(DMN) and visual network(VN) ,left middle frontal gyrus and right superior frontal gyrus and the inferior occipital gyrus. We did observe an increased dynamic ALFF in pediatric patients in the left precentral and postcentral gyrus, middle temporal gyrus was also included.
Discussion and conclusion
Conventional ALFF can be a proxy for static intrinsic brain activity. Previous research has reported that static brain activity is altered in OCD patients on different age of onset3,4 . So there exist some difference both in children and adult patients. ALFF generates a single, static estimate of brain activity, dALFF as a neuroimaging measure index that can accurately characterize the brain intrinsic functional tissue at rest, reflected by the dynamic variability in local neural activity at different sliding windows during the scanning period. The static intrinsic brain activity is abnormally related to the DMN and the temporal variability of intrinsic brain activity is normally related to the CN in OCD patients with age are worthy of consideration. The strength of the study is that we recruited four groups to control for age, which allowed us to investigate whether there was an interaction between disease diagnosis and age status.The default mode network, visual network and parietal cortex were implicated in both adult and pediatric OCD patients. These results support the hypothesis that the pathology of OCD cannot be explained solely by alterations of the classical cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical regions and emphasize the importance of other regions besides them. In this research, we used 2x2 interaction effect to differentiate OCD patients from healthy controls in both adolescents and adults, we analyzed a classical index-low frequency fluctuation amplitude and drew a steady conclusion that some regions had an association with people in different age and symptoms in OCD patients. Besides, we proposed dALFF estimating dynamics of intrinsic brain activity . Dynamic ALFF can use as a powerful supplement differentiating patients from different age, helping us obtain a more comprehensive understanding of neural activity. Moreover, further research will concentrate on a larger sample and the condition of medications to make a more satisfactory conclusion.
Acknowledgements
This research study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (81601467, 81871327) and Medical Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province (201701011).References
1.Z S, EK E, A V. Functional disruption of cerebello-thalamo-cortical networks in obsessive compulsive disorder. Biological psychiatry. Cognitive neuroscience and neuroimaging. 2020;5(4):438-447
2.Yang S, Meng Y, Li J, et al. Temporal dynamic changes of intrinsic brain activity in schizophrenia with cigarette smoking. Schizophr Res. Aug 2019;210:66-72
3. Boedhoe PSW, Schmaal L, Abe Y, Ameis SH. Distinct subcortical volume alterations in pediatric and adult OCD: a worldwide meta- and mega-analysis. The American journal of psychiatry. 2016.
4.Li Y, Xue YZ, Zhao WT, Li SS, Li J, Xu Y. Correlates of intelligence via resting-state functional connectivity of the amygdala in healthy adults. Brain Res. Jan 15 2021;1751:147176.
Figures