3601
The value of first-order features based on ADC map in evaluating the neuroprotective effect of LIPUS for acute traumatic brain injury with rat model1The first hospital of Qinhuangdao, Qinhuangdao, China, 2Scientific Clinical Specialist,Siemens Ltd, Beijing, China
Synopsis
In this study we studied the value of LR model established with first-order features based on ADC map in evaluating the neuroprotective effect of Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) for acute traumatic brain injury (TBI). The results demonstrated that the model based on the first-order features may have potential value in predicting the therapy effect of LITUS in clinical practice in future.
Introduction
In order to evaluate the neuroprotective effect of Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) for acute traumatic brain injury (TBI), we studied the potential of ADC values and ADC-derived first-order features about this problem.Methods
Forty-five male Sprague Dawley rats (Sham group: 15, TBI group: 15, LIPUS treated: 15, mean age: 2 months; range, 1-4 months, weight 200-280g) were enrolled and underwent MR imaging on a 3T MR scanner (MAGNETOM Verio, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). Scanning layers were aligned parallel to the anterior/posterior line and acquired using a multi-shot readout segmentation of long variable echo-trains (RESOLVE) to decrease the distortion (Table 1). LIPUS protocol: the ultrasound transducer was applied to the designated region in the injured cortical areas using a conical collimator that had a diameter of 10 mm and was filled with ultrasound coupling gel. The total stimulation duration was 10 mins. ROIs range of 0.30-0.60cm2 were manually delineated in the center of the damaged cortex on the DWI (b=800 s/mm2) images layer by layer for the TBI group and LIPUS treated group with an open-source software ITK-SNAP (Version 3.6.0). The features were extracted using an open source tool named Pyradiomics (https://pyradiomics.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html) with the following seetings: normalize: true, normalizeScale: 100, interpolator: sitkBspline, resampled pixe sapcing: [2 2 2], binWidth: 25, voxelArrayShift: 30, correctMask: True. Before analysis and modeling, the features were normalized using a z-score method, and a logistic regression (LR) model with a backwards filtering method was employed to do the modeling. Whole process was completed using R language.Results
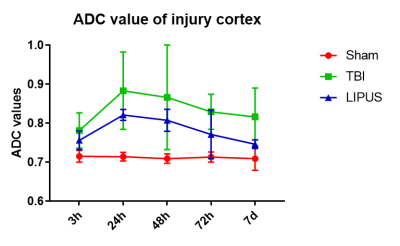
(1) Diagnostic performance of ADC values The ADC values peaked at the 24h in both TBI and LIPUS groups, with significant differences between all three groups (Sham vs. TBI Adjusted P Value <0.0001; Sham vs. LIPUS Adjusted P Value <0.0001; TBI vs. LIPUS Adjusted P Value = 0.0058), but the LIPUS group peaked lower than the TBI group (0.821 ± 0.014 vs. 0.883 ± 0.099).(2) Diagnostic performance of first-order features based on ADC maps After statistical analysis, the 10 Percentile,90 Percentile,Mean,Skewness and Uniformity, demonstrated significant difference among three groups. The 10 Percentile,90 Percentile,Mean,Skewness were higher in TBI group than in LIPUS group(P=0.024, 0.001,0.002,0.035,respectively),while The mean value of Uniformity was lower than LIPUS group(P=0.002).
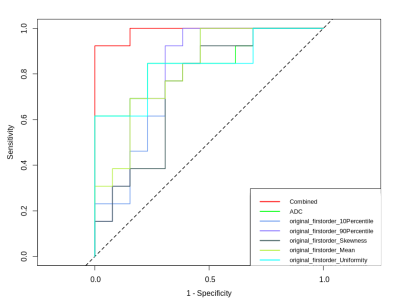
(3) Diagnostic performance of the combined LR model and concerned features The ROC analysis shows that the combined LR model exhibit a highest AUC value with the largest area under the ROC curve (AUC: 0.96). The AUCs of other features were lower than the combined model with a descending order: ADC-AUC (0.7)> Uniformity-AUC (0.68) > 90 Percentile -AUC (0.65) = Mean-AUC (0.65)>10 Percentile -AUC (0.59) >Skewness-AUC (0.53)
Conclusions
The combined LR model of first-order features based on ADC map can acquired a higher diagnostic performance than each features only in evaluating the neuroprotective effect of LIPUS for TBI. The models based on the first-order features may have potential value in predicting the therapy effect of LIPUS in clinical practice in future.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
References:
1. W.S. Su, C.H. Wu, S.F. Chen, F.Y. Yang, Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound improves behavioral and histological outcomes after experimental traumatic brain injury, Rep 7(1) (2017) 15524.Y. Yi, Y. Dong, S.
2. Hu, Z. Tao, D. Du, J. Du, L. Liu, Reduced Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Various Brain Areas following Low-Intensity Transcranial Ultrasound Stimulation, Frontiers in Neuroscience 11 (2017) 562.
3. D.J. Hou, K.A. Tong, S. Ashwal, U. Oyoyo, A. Obenaus, Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging improves outcome prediction in adult traumatic brain injury, J Neurotrauma 24(10) (2007) 1558-1569.
Figures
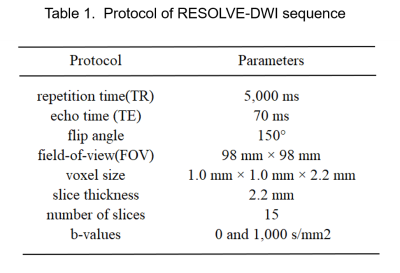
Table 1. Protocol of RESOLVE-DWI sequence