3491
Characterizing Corticobulbar and Corticospinal Tracts into the Cervical Spinal Cord with Sub-Millimeter Isotropic DTI1Brain Imaging and Analysis Center, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States
Synopsis
An ability to characterize the corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts from the motor cortex into the spinal cord with diffusion tensor imaging remains a challenge due to limiting factors such as achievable spatial resolutions, spatial coverages, and signal-to-noise ratio in the spinal cord. By extending the field-of-view through a combination of sub-millimeter isotropic axial and sagittal acquisitions, this study presents a technique to delineate the complete pyramidal tracts with data acquired at a sufficient spatial resolution to resolve intricate structural details such as the pyramidal decussation. Such a delineation can facilitate placement of spinal cord stimulation electrodes for movement disorder treatments.
Introduction
An ability to accurately characterize the pyramidal tracts (PT) that interconnect the motor cortex with the brainstem and spinal cord (SC) is essential in investigating the neuronal mechanisms associated with many neurological disorders. While diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is the dominant non-invasive technique for estimating neural pathways, such as the corticospinal (CST) and corticobulbar (CBT) tracts, an ability to delineate the complete PT at ultra-high spatial resolutions remains a challenge due to technical limitations such as the achievable spatial resolutions given the large field of view (FOV), subject movement and a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in the SC. This study aims to overcome these limitations using a combination of axial and sagittal DTI scans acquired at ultra-high (sub-millimeter) isotropic spatial resolutions to effectively resolve the PT from the lateral, medial, and superior motor cortices into the brainstem and cervical SC. With a clear delineation of the PT pathways, the results of this study can find multiple applications, such as guidance and pre-surgical planning for the placement of SC stimulation electrodes used to treat movement disorders such as Parkinson’s Disease1,2.Methods
DTI data was acquired in a GE (Waukesha, WI) Premier Performance 3 T MRI scanner equipped with a high-power 60 cm torque-balanced gradient coil (with a peak strength at 115 mT/m) specifically designed for high-resolution DTI. Written informed consent was obtained from human subjects in accordance with our institutional IRB. Each DTI scan was comprised of two b=0 volumes and 38 b=800 s/mm2 volumes. Axial DTI data was acquired using a multi-band multi-shot (MB-MUSE)3-6 pulse sequence (2 bands, 4 shots) in 150 slices (0.9 mm thickness) with a 154.8×309.6 mm FOV (172×344 matrix) and TR/TE=9800/63.2 ms (26:47 min). Two Sagittal DTI data sets were acquired using a MUSE sequence (4 shots) in 72 slices (0.9 mm thickness) with a 230.4 mm FOV (256×256 matrix) and TR/TE=8200/61.3 ms (2×22:25 min).After reconstructing all images with MB-MUSE, MRtrix37 was used to remove noise8-9, and artifacts from Gibb’s ringing10, eddy-currents11 and spatial distortions12-13. A global intensity scaling was applied to all DTI scans to achieve a uniform median white matter intensity within the b=0 volumes before registration was performed using ANTS14. Diffusion tensors15,16 and Fiber orientation distribution maps (FODs)17 were estimated for each scan and combined using the brain region of the axial data and the brainstem/SC from the sagittal data. Using second order integration over FODs (iFOD2)18, streamline fibers characterizing the pyramidal tracts were estimated from the lateral, medial and superior regions of the precentral gyri (PCG) extending through the left/right internal capsules, the cerebral peduncles in the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata.
Results and Discussion
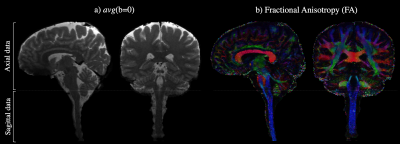
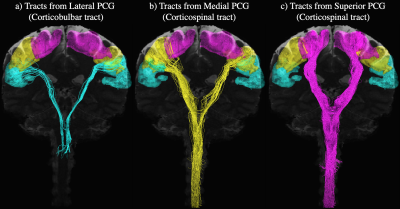
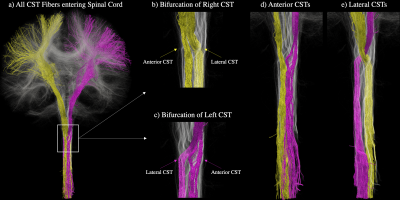
The average b=0 and fractional anisotropy (FA) maps in Fig. 1 illustrate both the continuity of the combined axial and sagittal scans as well as the high image quality achieved at a sub-millimeter spatial resolution throughout the brain and spinal cord. Fig. 2 shows the CBT (blue) and CST (yellow & pink) extending from the motor cortices into the brainstem and SC. Although the CBT in Fig. 2a is shown to follow the same initial pathway as the CST from the cortex, through the internal capsules and into the midbrain, the fibers are shown to terminate between the midbrain and medulla oblongata as expected. By contrast, the CST pathways in Figs. 2b-c extend from the medial and superior PCG the end of the SC/FOV. In addition to the combined data being able to characterize both the CBT and CST, Fig. 3a-c demonstrates that left and right fiber bundles passing through the anterior medulla oblongata bifurcate into anterior and lateral components. In Fig. 3d, the left/right anterior pathways continue along their respective sides while the lateral pathways in Fig. 3d form the well-known pyramidal tract decussation.Conclusion
When acquired at ultra-high spatial resolutions, the FOV of a typical axial DTI scan can only extend to the inferior slices of the cerebellum, limiting the ability to track the PT pathways into the SC. By contrast, the FOV in the slice dimension of an ultra-high spatial resolution sagittal DTI scan cannot readily extend to the left/right edges of the brain, thereby limiting the ability to characterize the CBT. When combining the two orientations in the manner described here, however, it has been shown that both the complete CBT and CST pathways can be tracked into the brainstem and cervical SC. Furthermore, the high spatial resolution and SNR achieved in the SC also enables the characterization of intricate structures such as the CST bifurcation and pyramidal decussation. Such a fine-grained delineation of the PT can find broad applications where a detailed knowledge of these structures is required. With a data set of this kind, it can be possible to directly track individual fiber pathways from a localized region of the motor cortex into the cervical SC, and (more importantly) vise-versa. Given the recent potential of SC stimulation treatments for neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s Disease1,2, the ability to delineate such pathways would facilitate in the accurate placement of stimulation electrodes to achieve the most efficient treatment possible.Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by NIH grants R01 NS 075017, R24-106048, and S10-OD-021480.References
1. Yadav, A. P., Nicolelis, M. A. L. Electrical stimulation of the dorsal columns of the spinal cord for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 32(6): 820-832, 2017.
2. Fuentes, R., Petersson, P., Siesser, W. B., Caron, M. G., Nicolelis, M. A. Spinal cord stimulation restores locomotion in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Science 323(5821):1578-82, 2009.
3. Chen, N. K., Guidon, A., Chang, H. C., Song, A., W. A robust multi-shot scan strategy for high-resolution diffusion weighted MRI enabled by multiplexed sensitivity-encoding (MUSE). Neuroimage 72: 41-47, 2013.
4. Bruce, I.P., Chang, H.C., Petty, C., Chen, N.K., Song, A.W. 3D-MB-MUSE: a robust 3D multi-slab, multi-band and multi-shot reconstruction approach for ultrahigh resolution diffusion MRI. Neuroimage, 159:46-56, 2017.
5. Bruce, I.P., Petty, C., Song, A.W., Imaging Cortical Columns in Gray Matter with Sub-Millimeter Isotropic DTI. Proc. Intl. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 26, 3361, 2019.
6. Bruce IP, Ma Y, Song AW. Using Sub-Millimeter Isotropic DTI to Observe the Cortical Depth Dependence of Diffusion Anisotropy and Diffusivity in-vivo. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 26, 248, 2021.
7. Tournier, J. D., Calamante, F., Connelly, A. MRtrix: Diffusion tractography in crossing fiber regions. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 22: 53-66, 2012.
8. Veraart, Jelle, et al. Denoising of diffusion MRI using random matrix theory. Neuroimage 142:394-406, 2016.
9. Veraart, J., Fieremans, E., Novikov, D.S. Diffusion MRI noise mapping using random matrix theory. Magn. Reson. Med. 76(5): 1582-1593, 2016.
10. Kellner, E., Dhital, B., Kiselev, V.G., Reisert, M. Gibbs‐ringing artifact removal based on local subvoxel‐shifts. Magn. Reson. Med. 76(5): 1574-1581, 2016.
11. Yongyue, Z., Brady, M., Smith, S. Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 20.1: 45-57, 2001.
12. Andersson JLR, Skare S, Ashburner J. How to correct susceptibility distortions in spin-echo echo-planar images: application to diffusion tensor imaging. NeuroImage, 20(2):870-888, 2003.
13. Smith SM, et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage, 23(S1):208-219, 2004.
14. Avants, BB, Tustison, N, Song, G. Advanced normalization tools (ANTS). Insight j 2.365, 1-35, 2009.
15. Basser, PJ, Mattiello, J, LeBihan, D. Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson B., 103, 247–254, 1994.
16. Veraart, J, Sijbers, J, Sunaert, S, Leemans, A, Jeurissen, B. Weighted linear least squares estimation of diffusion MRI parameters: strengths, limitations, and pitfalls. NeuroImage, 81, 335-346, 2013.
17. Tournier, JD, Calamante, F, Gadian, DG, Connelly, A. Direct estimation of the fiber orientation density function from diffusion-weighted MRI data using speherical deconvolution. NeuroImage, 23:1176-1185, 2004.
18. Tournier, JD. Calamante, F,Connelly, A. Improved probabilistic streamlines tractography by 2nd order integration over fiber orientation distributions. Proc. of the Intl. Soc. for Magn. Reson. Med., 2010, 1670.
Figures