3129
The performance of pretreatment MR-based radiomics in RHES combined chemoradiotherapy response prediction in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.1The First Affliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China, 2Guangxi Medical University Kaiyuan Langdong Hospital, Nanning, China, 3Siemens Healthineers, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
This study is to investigate a MRI radiomics model based on pre-treatment texture features to explore its application value in predicting the efficacy of recombinant human endostatin(RHES) combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The results showed that the AUC and the accuracy of radiomics-clinics combine model and radiomics model for response assessment in nasopharyngeal carcinoma(NPC) was higher than clinics model. These suggest that pretreatment MRI based radiomics could predict RHES combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy response in NPC, its accuracy was better than clinics model.
Introduction/Purpose
Antiangiogenic therapy may transiently “normalize” the tumor vasculature to increase the effect of chemoradiotherapy. The present study confirmed the combination of antiangiogenic therapy with chemoradiotherapy provides a promising strategy for the improvement of the prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma(NPC) patients. Recombinant human endostatin (RHES) is a new type of antiangiogenic agent. However, intra-tumor heterogeneity is one of the main factors affecting the sensitivity and efficacy of chemoradiotherapy. Radiomics is a new method to study tumor heterogeneity, and it can evaluate tumor heterogeneity and biological characteristics by screening these features and constructing models. The aim of this study is to investigate a MRI radiomics model based on pre-treatment texture features to explore its application value in predicting the efficacy of RHES combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Methods
Totally 65 newly diagnosed NPC patients under RHES combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy between January 2017 and February 2021 were retrospectively enrolled. Age, sex, pathologic type, TN staging and morphologic size of lesions were collected as clinical factors (Table 1). All patients had complete data of enhanced MR of nasopharynx before treatment and after RHES combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Compared with the enhanced MR images before treatment, the response after treatment was evaluated. According to the evaluation criteria of RECIST1.1, 65 cases were divided into two groups: 41 cases for the responder group and 24 cases for the non-responder group. ITK-SNAP software was used to manually sketch and segment the volume of interes (VOI) of nasopharyngeal tumor on the MR T2WI_FS and T1WI_CE by two experienced doctors and imaging features were extracted. The parameters were analyzed and extracted by using FeAture Explorer (V 0.3.6) on Python (3.7.6). We used computer-generated random numbers to assign 70% of the patients to the training cohort (n= 46) and the others to the testing cohort (n= 19). The radiomics features’ dimension was reduced by Pearson correlation coefficient after normalization. Analysis of variance and logistical regression were used for feature selection by fivefold cross-validation in the training cohort, and the machine learning model was constructed for the clinical model, radiomics model, and radiomics-clinics combine model which combined selected radiomics features and clinical parameters. The discrimination result of the model was obtained by bootstrap; The area under the ROC curve (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were performed to evaluate the model performance in both the training and testing cohorts.Result
T test demonstrated that shortest diameter was statistical significance between responder and non-responder group (P=0.036), as shown in Table 1. The AUC of radiomics-clinics combine model and radiomics model stood at 0.775 (95% CI:0.604—0.907) and 0.763[95% CI: 0.617—0.885] for training cohort. And the corresponding AUC in test cohort were 0.714(95% CI: 0.366—0.985) and 0.750 (95% CI: 0.433—1.00) for combine and radiomics model respectively. The accuracy of combine model for RHES combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy response assessment in NPC was higher than clinics model (0.804 vs. 0.699). It was also suggested improvement in combine model compared to radiomics model (0.804 vs. 0.695). More details were shown in Table 2.Discussion and Conclusion
This study to determine if there is a difference between radiomics features derived from responder and non-responder NPC patients who received RHES combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy based on pre-treatment MRI. The most important is to construct a reliable prediction model based on conventional sequence texture features to predict the efficacy of RHES combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy in NPC patients. These results suggest that pretreatment MRI based radiomics could predict RHES combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy response in NPC, its accuracy was better than clinics model.Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the participants in this study.References
1.Jain, R.K., Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med, 2001. 7(9): 987-9.
2.Peng, F., et al., Recombinant Human Endostatin Normalizes Tumor Vasculature and Enhances Radiation Response in Xenografted Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Models. PLoS ONE, 2012. 7(4): e34646.
3.Yongfeng, P., et al., The Usefulness of Pretreatment MR-Based Radiomics on Early Response of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients With Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Oncology Research Featuring Preclinical and Clinical Cancer Therapeutics, 2020. 28 (6): 605-613.
4.Zhang, L., et al., Pretreatment MRI-Derived Radiomics May Evaluate the Response of Different Induction Chemotherapy Regimens in Locally advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Academic Radiology, 2020. 27 (12): 1655-1664.
5. Song, Y., et al., FeAture Explorer (FAE): A tool for developing and comparing radiomics models. PLoS One, 2020. 15(8): e0237587.
Figures
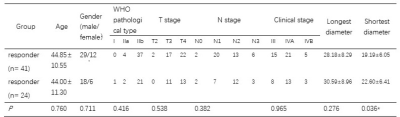
Table 1. Characteristics differences between responders and non-responders NPC were determined using the T-test (age, longest diameter, shortest diameter) or chi-square test (Classification variables), *: P < 0.05.
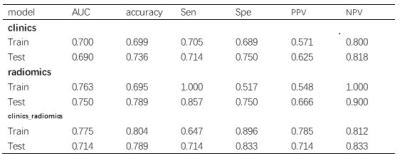
Table 2. Performance of clinics, radiomics and combine models in assessing RHES combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy response in NPC.
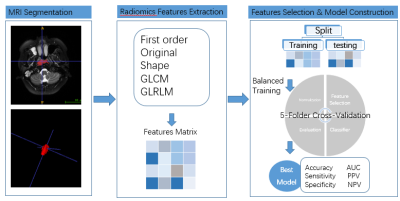
Fig.1. Flowchart showing the development of the MRI-based prediction model for the efficacy of RHES combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy for NPC.
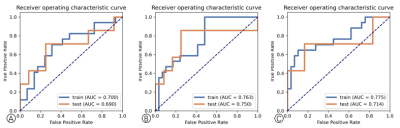
Fig.2. Performance analysis. Receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) analyses of the clinics(A), radiomics(B) and radiomics-clinics combine(C) models in training cohort and testing cohort.