3116
MRS study on the correlation between frontal GABA+/Glx ratio and abnormal cognitive function in patients with narcolepsy1China Medical University, shenyang, China, 2Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA F. M. Kirby Center for Functional Brain Imaging, Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore, MD, USA, Baltimore, MD, United States, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, BeiJing, China, 4China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Synopsis
A series of studies have suggested the cognitive deficits in patients with narcolepsy. The aim of the current study is to explore the correlation between abnormal GABA+/Glx ratio in sleep state and abnormal cognitive function in patients with narcolepsy using Hadamard Encoding and Reconstruction of Mega-Edited Spectroscopy (HERMES) method. This study demonstrate that the ratio of GABA+/Glx in prefrontal lobe of narcolepsy patients during N2 sleep stage were higher than that of normal control group, which may be related to their abnormal cognitive functions.
Introduction
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by irresistible daytime sleepiness, sudden collapse, sleep hallucinations, sleep paralysis, and nocturnal sleep disturbances. A a serie of studies have suggested the cognitive deficits in patients with narcolepsy. Previous studies have shown that the changes ratio of cerebral glutamatergic and gabaergic may be the basis of experience dependent plasticity of cortical circuits, which has defects in various neurodevelopmental disorders[1-2]. The aim of the study is to explore the correlation between abnormal GABA+/Glx ratio in sleep state and abnormal cognitive function in patients with narcolepsy using Hadamard Encoding and Reconstruction of Mega-Edited Spectroscopy (HERMES) method.Methods
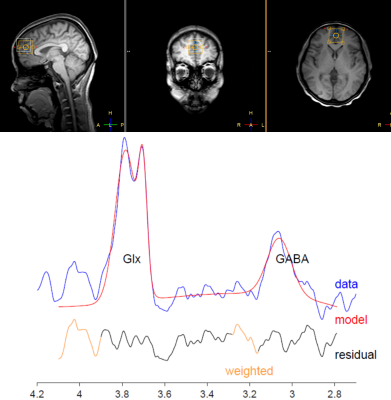
The Beijing version of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA BJ) and EEG-Mrs were performed in 20 NT1 patients (male:female ratio,11:9; age,9.0–34.0years)and 20 healthy controls(male:female ratio,10:10; age,23.0–26.0years). Synchronous EEG-MRS scans were performed on the subjects in sleep state using a 3.0 T MR scanner. Visual scoring of EEG data permitted sleep staging. A T1-weighted 3D TFE scan was performed first for localization of the HERMES MRS volume of interest (VOI) and subsequent tissue segmentation. HERMES MRS VOI (30 × 30 × 30 mm3) was placed in the frontal lobe. MRS data were postprocessed by gannet3.0 software package.GABA+ level was quantified using creatine(Cr) as concentration references. The ratios of GABA+ level and Glx level in frontal lobe was calculated and compared between patients and controls, correlation analysis was also conducted to explore the relationship between GABA+/Glx ratio between the results of cognitive assessment.Result
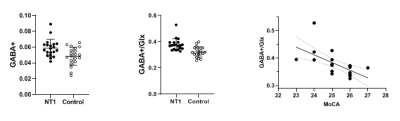
The GABA+/Glx ratios of patients with narcolepsy were higher than the normal control group (P<0.001), the GABA+ levels were higher than the control group (P=0.006) during N2 sleep stage,while there were no significant differences in Glx level(P=0.6699). The cognitive function scores of patients with narcolepsy was lower than that of the controls. The GABA+/Glx ratios were negatively related to their abnormal cognitive functions (r=-0.7453, P=0.002).Discussion
This research showed that the ratios of GABA+/Glx in prefrontal lobe of narcolepsy patients during N2 sleep were higher than that of the controls, which may be related to their abnormal cognitive function,we also found that is mainly caused by the increase of GABA+ level. The data also showed that the ratios of GABA+/Glx in prefrontal lobe were related to the the severity of cognitive impairment, given a recent study showed that the increased plasticity in the N2 sleep stage was associated with an increased Glx /GABA+ balance, we therefore spaculated that the increased GABA+ level in the N2 phase may be the major factor in cognitive dysfunction in narcolepsy patients.Conclusion
This study demonstrate that the ratiosd of GABA+/Glx in prefrontal lobe of narcolepsy patients during N2 sleep stage were higher than that of normal control group, which may be related to their abnormal cognitive functions.Acknowledgements
This study applies tools developed under NIH R01 EB016089 and P41 EB015909; RAEE also receives salary support from these grants.References
1.Maria YL, Price AN, Puts NAJ, Hughes EJ, Edden RAE, McAlonan GM, Arichi T, De Vita E. Simultaneous quantification of GABA, Glx and GSH in the neonatal human brain using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuroimage. 2021 Jun;233:117930. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.117930. Epub 2021 Mar 9. PMID: 33711485; PMCID: PMC8204265.
2.Hupfeld KE, Hyatt HW, Alvarez Jerez P, Mikkelsen M, Hass CJ, Edden RAE, Seidler RD, Porges EC. In Vivo Brain Glutathione is Higher in Older Age and Correlates with Mobility. Cereb Cortex. 2021 Aug 26;31(10):4576-4594. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhab107. PMID: 33959751; PMCID: PMC8408448.
3.Tamaki M, Wang Z, Barnes-Diana T, Guo D, Berard AV, Walsh E, Watanabe T, Sasaki Y. Complementary contributions of non-REM and REM sleep to visual learning. Nat Neurosci. 2020 Sep;23(9):1150-1156. doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-0666-y. Epub 2020 Jul 20. PMID: 32690968; PMCID: PMC7483793.