3098
Efficacy of motion-free MRI of the shoulder using Compressed SENSE MultiVane1Saitama Medical University, iruma-gun, Japan, 2Philips Japan, minato-ku, Japan
Synopsis
Combining Compressed SENSE (CS), an acceleration technique that combines with compressed sensing and SENSE, with MultiVane achieves comparable scan time to Cartesian scan and increases motion robustness while maintaining similar image quality to Cartesian scan without increasing streak artifacts. We compared this newly developed CS-MultiVane with conventional acquisition method such as routine SENSE, SENSE-MuliVane with reduction factor = 1.0 and SENSE-MuliVane with reduction factor = 1.4 in terms of the overall image quality, overall degree of artifacts and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). In conclusion, CS-MultiVane acquisition method is feasible for MRI of the shoulder.
Purpose
Combining Compressed SENSE (CS), an acceleration technique that combines with compressed sensing and SENSE, with MultiVane achieves comparable scan time to Cartesian scan and increases motion robustness while maintaining similar image quality to Cartesian scan without increasing streak artifacts. We aim to investigate the efficacy of motion-free MRI of the shoulder using CS-MultiVane.Methods
15 healthy volunteers underwent imaging of both shoulders with 4 acquisition methods [routine SENSE with reduction factor = 1.0 (routine SENSE:1.0), SENSE-MuliVane with reduction factor = 1.0 (SENSE-MultiVane:1.0), SENSE-MuliVane with reduction factor = 1.4 (SENSE-MultiVane:1.4) and CS-MuliVane with reduction factor = 2.0 (CS-MultiVane:2.0)]. Two radiologists independently rated the overall degree of artifacts and overall image quality using a four-point scale. For each acquisition method, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was measured. Results were compared among 4 acquisition methods using Steel’s multiple comparison test. Values of p < 0.05 were considered to indicate a significant difference in all statistical tests.Results
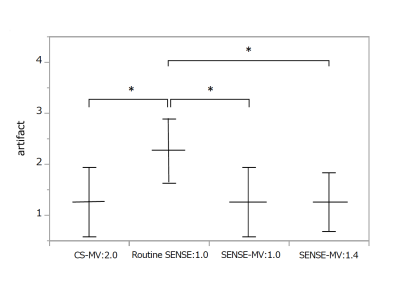
3 acquisition methods with MultiVane were significantly superior to SENSE in the overall degree of artifacts and overall image quality (p < 0.05). In terms of SNR, SENSE-MultiVane:1.0 was significantly superior to routine SENSE:1.0, SENSE-MultiVane:1.4 and CS-MultiVane:2.0. However there was no significant difference between SENSE-MultiVane:1.4 and CS-MultiVane:2.0, CS-MultiVane:2.0 was superior to SENSE-MultiVane:1.4 (p = 0.17)Conclusion
Newly developed Compressed SENSE (CS)-MultiVane acquisition method is feasible for MRI of the shoulder. CS-MultiVane could replace SENSE for the shoulder hereafter.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
Kojima T, et al. Efficacy of the radial acquisition regime (RADAR) for acquiring head and neck MR images. Br J Radiol. 2016; 89: 20160007.
Fujimoto K et al. BLADE acquisition method improves T2-weighted MR images of the female pelvis compared with a standard fast spin-echo sequence. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80:796– 801.
Dietrich TJ, et al. PROPELLER Technique to Improve Image Quality of MRI of the Shoulder. AJR. 2011;197: W1093-W1100.
JC Ye. Compressed sensing MRI: a review from signal processing perspective. BMC Biomed Eng. 2019;1:8.
Jaspan ON, et al. Compressed sensing MRI: a review of the clinical literature. Br J Radiol 2015; 88: 20150487.
Figures
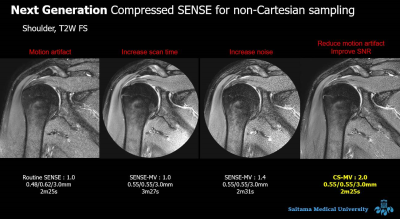
Representative images of respective acquisition methods for MRI of the shoulder.SENSE-MuliVane with reduction factor = 1.0 reduces motion artifacts, but increases scan time. SENSE-MuliVane with reduction factor = 1.4 achieves comparable scan time to routine SENSE with reduction factor = 1.0 while maintaining the reduction of motion artifacts, but decreases the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). CS-MuliVane with reduction factor = 2.0 improves the SNR while maintaining the reduction of motion artifacts and scan time comparable to routine SENSE with reduction factor = 1.0.
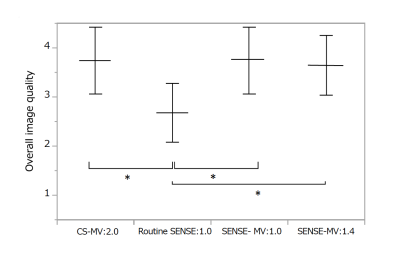
3 acquisition methods with MultiVane were significantly superior to SENSE in the overall image quality. *Statistically significant difference (p < 0.05). The overall Image quality was scored from 1 (worst) to 4 (best).
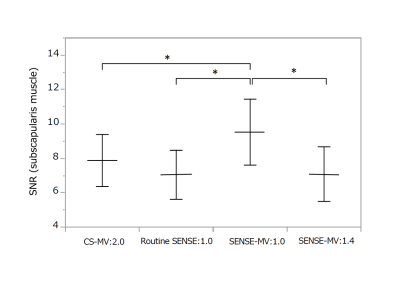
SENSE-MultiVane:1.0 was significantly superior to routine SENSE:1.0, SENSE-MultiVane:1.4 and CS-MultiVane:2.0 in the SNR.
The measurement of SNR uses the following equation: SNR=SI/standard deviation (SD), where SIm indicates the mean of signal intensity of the region of interest, and SD indicates the SD of signal intensity of the region of interest. We used SD of normal subscapularis muscle signal intensity as an estimate of local noise.