2989
Relationship between GABA+ level in occipital lobe and topological characters of cerebral EEG functional connectivity network in young adults1China Medical University, Shenyang, China, China, 2Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA, Baltimore, MD, United States, 3F. M. Kirby Center for Functional Brain Imaging, Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore, MD, USA, Baltimore, MD, United States, 4MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Beijing, China
Synopsis
We carried investigation to explore the relationship of GABA level of occipital lobe on topological and organizational properties of the entire brain using Hadamard Encoding and Reconstruction of Mega-Edited Spectroscopy (HERMES) method. Synchronous EEG-MRS data were obtained from forty healthy volunteers. GABA+ level and the global topological topological characters of the EEG functional connectivity network were calculated. The results demonstrate that the GABA+ level of the occipital lobe showed a significant negative correlation with the small world index of EEG functional connectivity network in the EEG α band.
Introduction
Previous studies have shown that abnormal GABA level of occipital lobe have been associated with a variety of neurological , psychiatric disorders and visual perceptual alterations[1-2]. Many patients with neuropsychiatric disorders show abnormal brain network topology properties[3-4]. However the effects of GABA level on the topological efficiency of EEG connectivity network remained unknown. Hence we carried investigation to explore the relationship of GABA level of occipital lobe on topological and organizational properties of the entire brain using Hadamard Encoding and Reconstruction of Mega-Edited Spectroscopy (HERMES) method.Methods
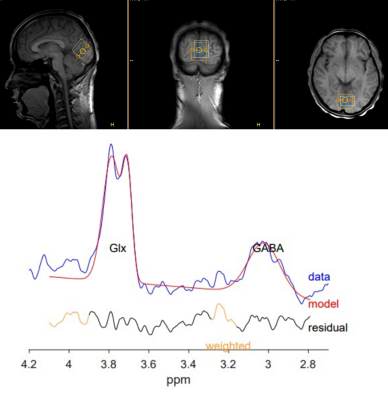
Synchronous EEG-MRS scans were performed on forty healthy volunteers (male:female ratio,16:24; age:20–30 years,with a median age of 24 years) in resting state on a 3T MRI scanner using a 64-channel head coil. A T1-weighted 3D TFE scan was performed first for localization of the HERMES MRS volume of interest (VOI) and subsequent tissue segmentation. HERMES MRS VOI (30 × 30 × 30 mm3) was placed in the occipital lobe. The occipital lobe GABA+ level was calculated using the Gannet 3.0 software package for each participant. 3D-TFE T1WI data were also segmented to estimate the relative gray matter contribution to the voxel volume (GMratio). GABA+ level was quantified using creatine(Cr) as concentration references.The EEG functional connectivity network was constructed by calculating the cross-correlation between different brain regions using EEGlab software package for each participant in different EEG band respectively. Graph-theoretical network analysis was then performed to assess the global topological characters of the EEG functional connectivity network (global efficiency, local efficiency, and small-world index) by GRETNA software package.
Spearman’s correlation analysis was performed to explore the relationship between GABA+ level of occipital lobe and the topological characters.
Results
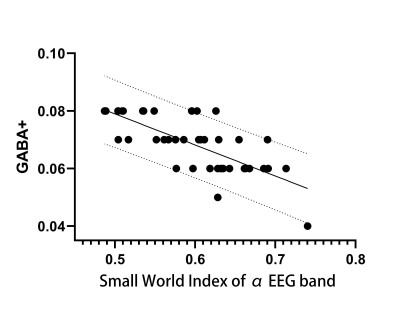
The GABA+ level of the occipital lobe showed a significant negative correlation with the small world index of EEG functional connectivity network in the EEG α band in resting state. (sperman r=-0.736, P=0.003).Discussion
Our findings reveal that the occipital lobe GABA+ level was negatively correlated with small-world network parameters in α band. Studies have shown that abnormal GABA+ levels of occipital lobe have been associated with a variety of neurological , psychiatric disorders and visual perceptual alterations.So we think the occipital lobe is an important node in the EEG connection network. GABA played an important role in modulating regional microcircuits and the hemodynamic response of a region[6]. The increased GABA+ level of occipital lobe may inhibit neuronal activity in this region and, therefore, correlate with FC. We hypothesize that, GABA+ level in the occipital lobe can predict FC changes in the functional brain networks of EEG. Applying the combined EEG/MRS methodology to occipital lobe and networks, future studies may be able to associate drug-induced changes in regional neurochemistry with changes in network function and clinical outcomes and aid in the development of new treatments.Conclusion
Our results indicate the occipital lobe GABA+ level was negatively correlated with small-world network parameters of EEG network. This associations may help us further understand the normal brain function and the pathogenesis of neurological disorders.Acknowledgements
This study applies tools developed under NIH R01 EB016089 and P41 EB015909; RAEE also receives salary support from these grants.References
1. Greicius MD, Supekar K, Menon V, Dougherty RF. Resting-state functional connectivity reflects structural connectivity in the default mode network. Cereb Cortex. 2009 Jan;19(1):72-8. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhn059. Epub 2008 Apr 9. PMID: 18403396; PMCID: PMC2605172.
2. Simmonite M, Carp J, Foerster BR, Ossher L, Petrou M, Weissman DH, Polk TA. Age-Related Declines in Occipital GABA are Associated with Reduced Fluid Processing Ability. Acad Radiol. 2019 Aug;26(8):1053-1061. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2018.07.024. Epub 2018 Oct 14. PMID: 30327163; PMCID: PMC6462248.
3. Li K, Sweeney JA, Hu XP. Context-dependent dynamic functional connectivity alteration of lateral occipital cortex in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2020 Jun;220:201-209. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2020.03.020. Epub 2020 Mar 20. PMID: 32201032.
4. Yang X, Liu J, Meng Y, Xia M, Cui Z, Wu X, Hu X, Zhang W, Gong G, Gong Q, Sweeney JA, He Y. Network analysis reveals disrupted functional brain circuitry in drug-naive social anxiety disorder. Neuroimage. 2019 Apr 15;190:213-223. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.12.011. Epub 2017 Dec 7. PMID: 29223742.
5. Bullmore E, Sporns O. Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009 Mar;10(3):186-98. doi: 10.1038/nrn2575. Epub 2009 Feb 4. Erratum in: Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009 Apr;10(4):312. PMID: 19190637.
6. Logothetis NK. What we can do and what we cannot do with fMRI. Nature. 2008 Jun 12;453(7197):869-78. doi: 10.1038/nature06976. PMID: 18548064.
Figures