2817
Assessing intrinsic parallel diffusivity changes in pediatric subjects acquired with NODDI.1Bambino Gesù Children's Hospital, Rome, Italy
Synopsis
Investigating optimal NODDI intrinsic diffusivity d|| values in the first years of life would provide accurate diffusion properties estimation. We aimed to investigate d|| for 1-36 months range. Diffusion data from 265 baby Human Connectome Project subjects were processed and used for NODDI model fitting with MDT tool. Among different d|| tested, optimal value was chosen according to maximum LogLikelihood maps and investigated as a function of age. Infants exhibit optimal d|| values of 1.95 µm2 ms-1, where d|| decreases for increasing age. Based on our results, 1.7 µm2 ms-1 represent a suboptimal assumption in the case of infant population.
INTRODUCTION.
NODDI model is nowadays extensively used in the field of diffusion MRI as it represents powerful tool for the assessment of brain microstructure. Although intrinsic diffusivity d|| was normally set to 1.7 µm2 ms-1, this assumption might not be the best choice when considering pediatric population, especially in the first years of life. Previous studies investigated how d|| changes with age, trying to find optimal NODDI d|| values for different age range [1-3]. In this context, the aim of this study is to assess optimal d|| for infant population, focusing analysis on different age ranges between 1 and 36 months.METHODS.
Diffusion data from baby Human Connectome Project (HCP) were used for this work. Preliminary d|| assessment was performed on 265 pediatric subjects, acquired at 3T Siemens Prisma scanner with different imaging protocols (in terms of b-values and diffusion encoding directions). Diffusion data were firstly processed for denoising, eddy current and motion artifacts correction using MRTrix3 dwidenoise and dwipreproc functions and then segmented with SPM12 toolbox in order to produce brain mask. Whenever available (205/265 subjects), a susceptibility-induced off-resonance field was estimated from the pairs of images acquired with reversed phase-encode directions using topup of FSL. NODDI-Watson model was applied to processed data, performing model fitting with Microstructure Diffusion Toolbox (MDT) software [4]. In particular, for each subject NODDI fitting was performed for different values of d||, ranging from 0.5 to 2.9 µm2 ms-1 with increment of 0.1 µm2 ms-1. Optimal d|| for each participant was obtained by looking at that value responsible for maximum MDT Log Likelihood map within the entire brain area. Finally, optimal d|| values were investigated as related to subject age, expressed in months.RESULTS.
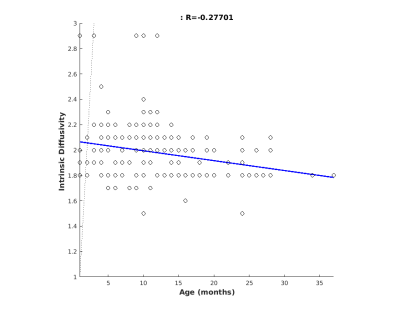
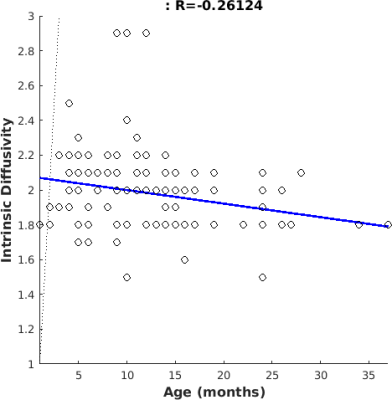
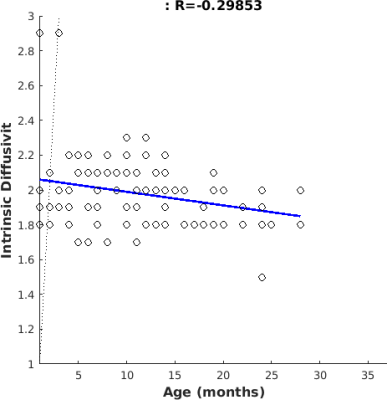
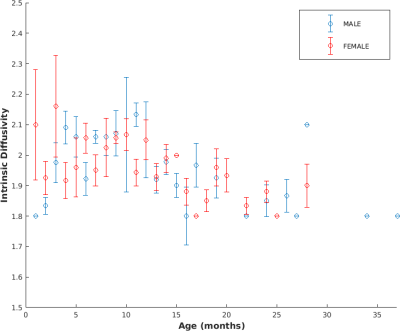
Intrinsic diffusivity optimization within the entire brain area was performed on 265 pediatric subjects (49% female, mean age = 12.2 ± 7.3 months, range = 1-37 months). Evaluating relationship between subject age and optimal intrinsic diffusivity, we found that these variables are slightly negative correlated (R=-0.28) (Figure 1). Moreover, when looking at gender distribution we found similar negative correlation for both male (R=-0.26) and female (R=-0.30) cohorts, thus optimal d|| decreases for increasing age of subjects (see Figure 2, Figure 3). Moreover, mean and standard deviation values of intrinsic diffusivity was investigated as a function of age (Figure 4), with overall mean value of 1.96 ± 0.09 µm2 ms-1 for females and 1.94 ± 0.11 µm2 ms-1 for males.DISCUSSION.
Pediatric subjects of less than 3 years exhibit optimal intrinsic diffusivity values close to 1.95 µm2 ms-1, where d|| decreases for increasing age. These results seem to be in contrast with Guerrero at al., findings, where d|| was investigated for both white matter (WM) and grey matter (GM), exhibiting respectively optimal values of 1.2 and 1.4 µm2 ms-1 in infants with less than 1 year. We can hypothesize that this result mismatch refers to the different age range considered, since we considered a broader range of infant age, ranging from 1 to 36 months. Further analyses need to be performed in order to establish optimal d|| in WM and GM for different narrow age ranges.CONCLUSION.
The present study aimed to investigate optimality of NODDI intrinsic diffusivity parameter for pediatric population. Based on our preliminary results, setting the intrinsic parallel diffusivity to 1.7 µm2 ms-1 represent a suboptimal assumption in the case of infant population (within the first three years of life). Based on these preliminary results, intrinsic diffusivity optimization within specific brain tissue, such as WM and GM will be further addressed. Once optimal d|| values for different infant age range will be established for both WM and GM, NODDI model fitting will provide diffusion properties estimation as precise as possible, both in healthy and pathologic subjects.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]. Jelescu, I.O., Veraart, J., Adisetiyo, V.,Milla, S.S., Novikov, D.S., Fieremans, E. (2015). One diffusion acquisition and different white matter models: How does microstructure change in human early development based on WMTI and NODDI?. NeuroImage 107 (2015) 242–256.
[2]. Guerrero, J.M., Adluru, N., Bendlin, B.B., Goldsmith, H.H., Schaefer, S.M., Davidson, R.J, Kecskemeti, S.R., Zhang, H., Alexander A.L. (2019). Optimizing the intrinsic parallel diffusivity in NODDI: An extensive empirical evaluation. PLoS ONE 14(9): e0217118.
[3]. Kunz, N., Zhang, H., Vasung, L., O'Brien K.R., Assaf, Y., Lazeyras, F., Alexander, D.C., Hüppi, P.S. (2014). Assessing white matter microstructure of the newborn with multi-shell diffusion MRI and biophysical compartment models. NeuroImage 96 (2014) 288–299.
[4]. Harms, R.L., Fritz, F.J., Tobisch, A., Goebel, R., Roebroeck, A. (2017). Robust and fast nonlinear optimization of diffusion MRI microstructure models. Neuroimage 155, 82–96.